Java Bean Copy框架性能对比
一、问题分析
背景
相同server机器上的相同方法在方法调用链任何参数都一致的情况消耗时间差别非常大,举例说明,类A有方法demo(), 通过分析发现同一台机器(也是一个jvm进程)对该方法的两次调用消耗时间竟然有200ms的差距。
同时,方法实现上没有使用任何的并发以及缓存,唯一特殊的是方法内使用了Apache BeanUtils.copyProperties,怀疑是这个方法有猫腻,于是开始重点分析该方法实现。
分析过程
现象分析
猜想如果是BeanUtils.copyProperties有问题,那么现象上应该是调用BeanUtils.copyProperties完成bean copy的过程可能会偶然出现性能问题,于是写了一个demo 循环调用BeanUtils.copyProperties完成bean copy,demo可以参考下文
验证结果:
* 单线程模型下,第一次访问BeanUtils.copyProperties耗时有200-300ms左右,后续访问几乎都是0ms,也就是微秒级别
* 并发模型下,每个线程访问BeanUtils.copyProperties会有一次200-300ms耗时, 也就是高性能耗时次数与并发线程数一致
根据以上验证结果猜测:
* BeanUtils.copyProperties有一种线程级别的“缓存”,第一次刷新缓存耗时较长,后续直接读”缓存”耗时较短
* 这种“缓存”是线程粒度
源码剖析
首先,要获取一个BeanUtilsBean实例,猜测这应该是一个单例模型的实现 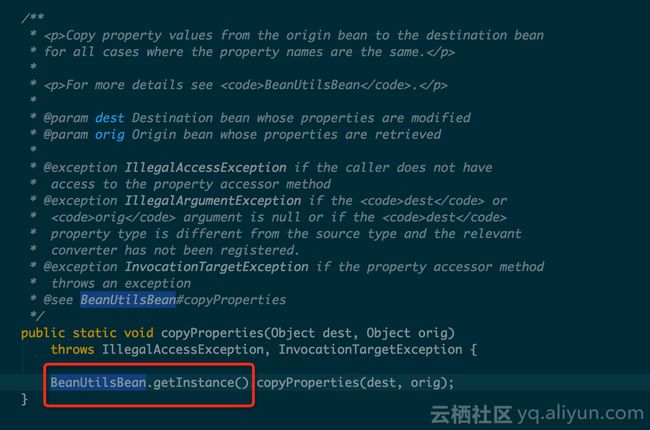
接下来我们看其实现,原来是一个“假单例”,并且是一个线程对应一个BeanUtils实例,接着看下去
实现上为了保证线程安全使用了synchronized ,随后debug了一下性能耗时主要在initalvalue(),可以看到线程内只有第一次调用get会初始化执行该方法,那么理论上是说得通了。
通过分析源码很容易解释为啥同一个方法调用会偶然耗时较长了,主要两个原因:
- 两个方法在不同线程执行,如果其中一个线程是第一次调用,框架需要先初始化BeanUtils实例,需要消耗200ms左右的性能
- 并发访问同一个BeanUtils实例时会出现线程阻塞
二 、Apache, Cglib, Spring bean copy 性能对比
目前主流的bean copy框架有apache, cglib, springframework 等,写法上大同小异,作为开发者我们更关注的偏向于性能,下文demo将综合对比apache,cglib,springframework以及传统的java bean 属性set等四种方案的性能指标。
2.1 代码结构介绍
首先,定义一个通用接口,包含一个方法copyBean
package com.free.life.base.beancopy;
/**
* bean copy common facade.
*
* @author yzq
* @date 2018/01/16
*/
public interface BeanCopyFacade {
/**
* bean copy.
*
* @param sourceBean source bean
* @param targetBean target bean
* @throws Exception root exception
*/
void copyBean(S sourceBean, T targetBean) throws Exception;
}
使用apache BeanUtils实现方式
package com.free.life.base.beancopy;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
/**
* apache copyProperties.
*
* @author yzq
* @date 2018/01/16
*/
public class ApacheBeanCopy implements BeanCopyFacade {
@Override
public void copyBean(SourceBean sourceBean, TargetBean targetBean) throws Exception {
long start = System.nanoTime();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(targetBean, sourceBean);
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(String.format("%s consume %d microsecond", "apache copy property", (end - start) / 1000));
}
}
使用cglib BeanCopier实现
package com.free.life.base.beancopy;
import net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanCopier;
/**
* cglib BeanCopier copy.
*
* @author yzq
* @date 2018/01/16
*/
public class CglibBeanCopy implements BeanCopyFacade {
private BeanCopier beanCopier = BeanCopier.create(SourceBean.class, TargetBean.class, false);
@Override
public void copyBean(SourceBean sourceBean, TargetBean targetBean) throws Exception {
long start = System.nanoTime();
beanCopier.copy(sourceBean, targetBean, null);
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(String.format("%s consume %d microsecond", "cglib BeanCopier", (end - start) / 1000));
}
}
使用spring BeanUtils
package com.free.life.base.beancopy;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
/**
* spring framework copy bean.
*
* @author yzq
* @date 2018/01/16
*/
public class SpringBeanCopy implements BeanCopyFacade {
@Override
public void copyBean(SourceBean sourceBean, TargetBean targetBean) throws Exception {
long start = System.nanoTime();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourceBean, targetBean);
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(String.format("%s consume %d microsecond", "spring copyProperties", (end - start) / 1000));
}
}
使用 java setter
package com.free.life.base.beancopy;
/**
* use setter/getter
*
* @author yzq
* @date 2018/01/16
*/
public class JavaBeanCopy implements BeanCopyFacade {
@Override
public void copyBean(SourceBean sourceBean, TargetBean targetBean) throws Exception {
long start = System.nanoTime();
targetBean.setId(sourceBean.getId());
targetBean.setName(sourceBean.getName());
targetBean.setResult(sourceBean.getResult());
targetBean.setContent(sourceBean.getContent());
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(String.format("%s consume %d microsecond", "use setter", (end - start) / 1000));
}
}
Main方法入口测试多种方案性能
package com.free.life.base.beancopy;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* bean copy demo.
*
* @author yzq
* @date 2018/01/16
*/
public class BeanCopyDemo {
private static BeanCopyFacade apacheBeanCopy;
private static BeanCopyFacade cglibBeanCopy;
private static BeanCopyFacade springBeanCopy;
private static BeanCopyFacade javaBeanCopy;
static {
apacheBeanCopy = new ApacheBeanCopy();
cglibBeanCopy = new CglibBeanCopy();
springBeanCopy = new SpringBeanCopy();
javaBeanCopy = new JavaBeanCopy();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final Integer loopCount = 10;
SourceBean sourceBean = new SourceBean();
sourceBean.setId(1);
sourceBean.setName("yzq");
sourceBean.setResult(Boolean.TRUE);
sourceBean.setContent("bean copy test.");
TargetBean targetBean = new TargetBean();
multiThread(loopCount, sourceBean, targetBean);
singleThreadTest(loopCount, sourceBean, targetBean);
}
private static void multiThread(Integer loopCount, SourceBean sourceBean, TargetBean targetBean) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount; i++) {
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
apacheBeanCopy.copyBean(sourceBean, targetBean);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
private static void singleThreadTest(Integer loopCount, SourceBean sourceBean, TargetBean targetBean)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("---------------- apache ----------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount; i++) {
apacheBeanCopy.copyBean(sourceBean, targetBean);
}
System.out.println("---------------- cglib ----------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount; i++) {
cglibBeanCopy.copyBean(sourceBean, targetBean);
}
System.out.println("----------------- spring ---------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount; i++) {
springBeanCopy.copyBean(sourceBean, targetBean);
}
System.out.println("----------------- setter ---------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount; i++) {
javaBeanCopy.copyBean(sourceBean, targetBean);
}
}
}2.2 测试结果
运行环境:
* macbook pro i7,4core,16g
* jdk:1.8.0_144
测试方式:
* 循环1w次调用
测试结果均值(单位为微秒):
* apache: 200
* cglib: 1
* spring: 20
* setter: 0
综上: 性能 setter > cglib > spring > apache
三 、最佳实践
bean copy对比传统的做法优缺点
优点
* 写法优雅简洁
* 一些相对高阶的使用方式比较简洁,比如反射方式获取类属性值等
缺点
* 性能较差,因为beancopy框架背后的实现都是通过[java反射](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/reflect/index.html)机制去做的,通常情况性能不会比normal方式更优。
* 引用查找难,bean copy的实现会隐藏对象属性的设置的调用,比如copy(source,taget) 我想查看target属性A有哪些地方被设值了,那么通过IDE查找引用会漏掉bean copy的引用。
实践建议
- bean copy场景较少或者对性能要求较高的部分避免使用任何bean copy框架
- 如果要使用bean copy框架,优先使用cglib,且要做性能测试。同时需要注意:cglib使用BeanCopier.create()也是非常耗时,避免多次调用,尽可能做成全局初始化一次
- 可以使用lombok builder或者自己封装builder模式相对优雅的代替setter/bean copy
- 关注IDE的任何一个警告信息,尽可能消除任何警告信息
一点感想
- 代码没有秘密,代码是可信的,同时它也是不可信的!
- 充分利用工具解决问题