学习 axios 源码整体架构,打造属于自己的请求库
前言
这是
学习源码整体架构系列第六篇。整体架构这词语好像有点大,姑且就算是源码整体结构吧,主要就是学习是代码整体结构,不深究其他不是主线的具体函数的实现。本篇文章学习的是实际仓库的代码。
学习源码整体架构系列文章如下:
1.学习 jQuery 源码整体架构,打造属于自己的 js 类库
2.学习underscore源码整体架构,打造属于自己的函数式编程类库
3.学习 lodash 源码整体架构,打造属于自己的函数式编程类库
4.学习 sentry 源码整体架构,打造属于自己的前端异常监控SDK
5.学习 vuex 源码整体架构,打造属于自己的状态管理库
感兴趣的读者可以点击阅读。下一篇可能是vue-router源码。
本文比较长,手机上阅读,可以滑到有图的地方直接看文中的几张图即可。建议点赞或收藏后在电脑上阅读,按照文中调试方式自己调试或许更容易吸收消化。
导读
文章详细介绍了 axios 调试方法。详细介绍了 axios 构造函数,拦截器,取消等功能的实现。最后还对比了其他请求库。
本文学习的版本是v0.19.0。克隆的官方仓库的master分支。截至目前(2019 年 12 月 14 日),最新一次commit是2019-12-09 15:52 ZhaoXC dc4bc49673943e352,fix: fix ignore set withCredentials false (#2582)。
本文仓库在这里若川的 axios-analysis github 仓库。求个star呀。
如果你是求职者,项目写了运用了axios,面试官可能会问你:
1.为什么
axios既可以当函数调用,也可以当对象使用,比如axios({})、axios.get。
2.简述axios调用流程。
3.有用过拦截器吗?原理是怎样的?
4.有使用axios的取消功能吗?是怎么实现的?
5.为什么支持浏览器中发送请求也支持node发送请求?
诸如这类问题。
chrome 和 vscode 调试 axios 源码方法
前不久,笔者在知乎回答了一个问题一年内的前端看不懂前端框架源码怎么办?推荐了一些资料,阅读量还不错,大家有兴趣可以看看。主要有四点:
1.借助调试
2.搜索查阅相关高赞文章
3.把不懂的地方记录下来,查阅相关文档
4.总结
看源码,调试很重要,所以笔者详细写下 axios 源码调试方法,帮助一些可能不知道如何调试的读者。
chrome 调试浏览器环境的 axios
调试方法
axios打包后有sourcemap文件。
# 可以克隆笔者的这个仓库代码
git clone https://github.com/lxchuan12/axios-analysis.git
cd axios-analaysis/axios
npm install
npm start
# open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000)
# chrome F12 source 控制面板 webpack// . lib 目录下,根据情况自行断点调试
本文就是通过上述的例子axios/sandbox/client.html来调试的。
顺便简单提下调试example的例子,虽然文章最开始时写了这部分,后来又删了,最后想想还是写下。
找到文件axios/examples/server.js,修改代码如下:
server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
var url = req.url;
// 调试 examples
console.log(url);
// Process axios itself
if (/axios\.min\.js$/.test(url)) {
// 原来的代码 是 axios.min.js
// pipeFileToResponse(res, '../dist/axios.min.js', 'text/javascript');
pipeFileToResponse(res, '../dist/axios.js', 'text/javascript');
return;
}
// 原来的代码 是 axios.min.map
// if (/axios\.min.map$/.test(url)) {
if (/axios\.map$/.test(url)) {
// 原来的代码 是 axios.min.map
// pipeFileToResponse(res, '../dist/axios.min.map', 'text/javascript');
pipeFileToResponse(res, '../dist/axios.map', 'text/javascript');
return;
}
}
# 上述安装好依赖后
# npm run examples 不能同时开启,默认都是3000端口
# 可以指定端口 5000
# npm run examples === node ./examples/server.js
node ./examples/server.js -p 5000
打开http://localhost:5000,然后就可以开心的在Chrome浏览器中调试examples里的例子了。
axios 是支持 node 环境发送请求的。接下来看如何用 vscode 调试 node 环境下的axios。
vscode 调试 node 环境的 axios
在根目录下 axios-analysis/创建.vscode/launch.json文件如下:
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Launch Program",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/axios/sandbox/client.js",
"skipFiles": [
"/**"
]
},
]
}
按F5开始调试即可,按照自己的情况,单步跳过(F10)、单步调试(F11)断点调试。
其实开源项目一般都有贡献指南axios/CONTRIBUTING.md,笔者只是把这个指南的基础上修改为引用sourcemap的文件可调试。
先看 axios 结构是怎样的
git clone https://github.com/lxchuan12/axios-analysis.git
cd axios-analaysis/axios
npm install
npm start
按照上文说的调试方法, npm start 后,直接在 chrome 浏览器中调试。打开 http://localhost:3000,在控制台打印出axios,估计很多人都没打印出来看过。
console.log({axios: axios});
层层点开来看,axios 的结构是怎样的,先有一个大概印象。
笔者画了一张比较详细的图表示。
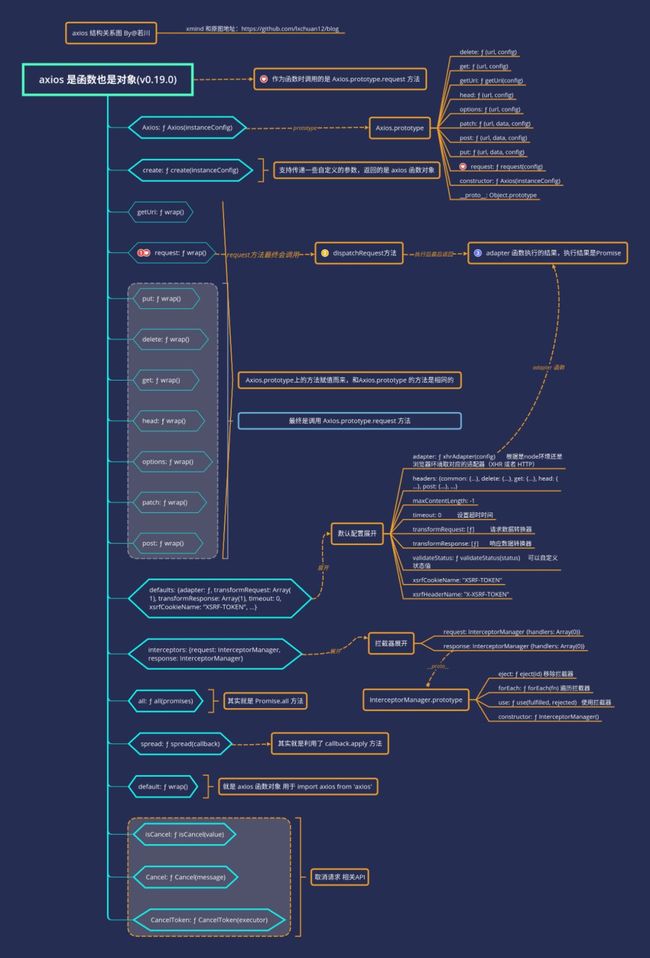
看完结构图,如果看过jQuery、underscore和lodash源码,会发现其实跟axios源码设计类似。
jQuery 别名 $,underscore loadsh 别名 _ 也既是函数,也是对象。比如jQuery使用方式。$('#id'), $.ajax。
接下来看具体源码的实现。可以跟着断点调试一下。
断点调试要领:
赋值语句可以一步跳过,看返回值即可,后续详细再看。
函数执行需要断点跟着看,也可以结合注释和上下文倒推这个函数做了什么。
axios 源码 初始化
看源码第一步,先看package.json。一般都会申明 main 主入口文件。
// package.json
{
"name": "axios",
"version": "0.19.0",
"description": "Promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js",
"main": "index.js",
// ...
}
主入口文件
// index.js
module.exports = require('./lib/axios');
lib/axios.js主文件
axios.js文件 代码相对比较多。分为三部分展开叙述。
第一部分:引入一些工具函数
utils、Axios构造函数、默认配置defaults等。第二部分:是生成实例对象
axios、axios.Axios、axios.create等。第三部分取消相关 API 实现,还有
all、spread、导出等实现。
第一部分
引入一些工具函数utils、Axios构造函数、默认配置defaults等。
// 第一部分:
// lib/axios
// 严格模式
'use strict';
// 引入 utils 对象,有很多工具方法。
var utils = require('./utils');
// 引入 bind 方法
var bind = require('./helpers/bind');
// 核心构造函数 Axios
var Axios = require('./core/Axios');
// 合并配置方法
var mergeConfig = require('./core/mergeConfig');
// 引入默认配置
var defaults = require('./defaults');
第二部分
是生成实例对象 axios、axios.Axios、axios.create等。
/**
* Create an instance of Axios
*
* @param {Object} defaultConfig The default config for the instance
* @return {Axios} A new instance of Axios
*/
function createInstance(defaultConfig) {
// new 一个 Axios 生成实例对象
var context = new Axios(defaultConfig);
// bind 返回一个新的 wrap 函数,
// 也就是为什么调用 axios 是调用 Axios.prototype.request 函数的原因
var instance = bind(Axios.prototype.request, context);
// Copy axios.prototype to instance
// 复制 Axios.prototype 到实例上。
// 也就是为什么 有 axios.get 等别名方法,
// 且调用的是 Axios.prototype.get 等别名方法。
utils.extend(instance, Axios.prototype, context);
// Copy context to instance
// 复制 context 到 intance 实例
// 也就是为什么默认配置 axios.defaults 和拦截器 axios.interceptors 可以使用的原因
// 其实是new Axios().defaults 和 new Axios().interceptors
utils.extend(instance, context);
// 最后返回实例对象,以上代码,在上文的图中都有体现。这时可以仔细看下上图。
return instance;
}
// Create the default instance to be exported
// 导出 创建默认实例
var axios = createInstance(defaults);
// Expose Axios class to allow class inheritance
// 暴露 Axios class 允许 class 继承 也就是可以 new axios.Axios()
// 但 axios 文档中 并没有提到这个,我们平时也用得少。
axios.Axios = Axios;
// Factory for creating new instances
// 工厂模式 创建新的实例 用户可以自定义一些参数
axios.create = function create(instanceConfig) {
return createInstance(mergeConfig(axios.defaults, instanceConfig));
};
这里简述下工厂模式。axios.create,也就是用户不需要知道内部是怎么实现的。
举个生活的例子,我们买手机,不需要知道手机是怎么做的,就是工厂模式。
看完第二部分,里面涉及几个工具函数,如bind、extend。接下来讲述这几个工具方法。
工具方法之 bind
axios/lib/helpers/bind.js
'use strict';
// 返回一个新的函数 wrap
module.exports = function bind(fn, thisArg) {
return function wrap() {
var args = new Array(arguments.length);
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
args[i] = arguments[i];
}
// 把 argument 对象放在数组 args 里
return fn.apply(thisArg, args);
};
};
传递两个参数函数和thisArg指向。
把参数arguments生成数组,最后调用返回参数结构。
其实现在 apply 支持 arguments这样的类数组对象了,不需要手动转数组。
那么为啥作者要转数组,为了性能?当时不支持?抑或是作者不知道?这就不得而知了。有读者知道欢迎评论区告诉笔者呀。
关于apply、call和bind等不是很熟悉的读者,可以看笔者的另一个面试官问系列。
面试官问:能否模拟实现 JS 的 bind 方法
举个例子
function fn(){
console.log.apply(console, arguments);
}
fn(1,2,3,4,5,6, '若川');
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 '若川'
工具方法之 utils.extend
axios/lib/utils.js
function extend(a, b, thisArg) {
forEach(b, function assignValue(val, key) {
if (thisArg && typeof val === 'function') {
a[key] = bind(val, thisArg);
} else {
a[key] = val;
}
});
return a;
}
其实就是遍历参数 b 对象,复制到 a 对象上,如果是函数就是则用 bind 调用。
工具方法之 utils.forEach
axios/lib/utils.js
遍历数组和对象。设计模式称之为迭代器模式。很多源码都有类似这样的遍历函数。比如大家熟知的jQuery $.each。
/**
* @param {Object|Array} obj The object to iterate
* @param {Function} fn The callback to invoke for each item
*/
function forEach(obj, fn) {
// Don't bother if no value provided
// 判断 null 和 undefined 直接返回
if (obj === null || typeof obj === 'undefined') {
return;
}
// Force an array if not already something iterable
// 如果不是对象,放在数组里。
if (typeof obj !== 'object') {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
obj = [obj];
}
// 是数组 则用for 循环,调用 fn 函数。参数类似 Array.prototype.forEach 的前三个参数。
if (isArray(obj)) {
// Iterate over array values
for (var i = 0, l = obj.length; i < l; i++) {
fn.call(null, obj[i], i, obj);
}
} else {
// Iterate over object keys
// 用 for in 遍历对象,但 for in 会遍历原型链上可遍历的属性。
// 所以用 hasOwnProperty 来过滤自身属性了。
// 其实也可以用Object.keys来遍历,它不遍历原型链上可遍历的属性。
for (var key in obj) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
fn.call(null, obj[key], key, obj);
}
}
}
}
如果对Object相关的API不熟悉,可以查看笔者之前写过的一篇文章。JavaScript 对象所有 API 解析
第三部分
取消相关 API 实现,还有all、spread、导出等实现。
// Expose Cancel & CancelToken
// 导出 Cancel 和 CancelToken
axios.Cancel = require('./cancel/Cancel');
axios.CancelToken = require('./cancel/CancelToken');
axios.isCancel = require('./cancel/isCancel');
// Expose all/spread
// 导出 all 和 spread API
axios.all = function all(promises) {
return Promise.all(promises);
};
axios.spread = require('./helpers/spread');
module.exports = axios;
// Allow use of default import syntax in TypeScript
// 也就是可以以下方式引入
// import axios from 'axios';
module.exports.default = axios;
这里介绍下 spread,取消的API暂时不做分析,后文再详细分析。
假设你有这样的需求。
function f(x, y, z) {}
var args = [1, 2, 3];
f.apply(null, args);
那么可以用spread方法。用法:
axios.spread(function(x, y, z) {})([1, 2, 3]);
实现也比较简单。源码实现:
/**
* @param {Function} callback
* @returns {Function}
*/
module.exports = function spread(callback) {
return function wrap(arr) {
return callback.apply(null, arr);
};
};
上文var context = new Axios(defaultConfig);,接下来介绍核心构造函数Axios。
核心构造函数 Axios
axios/lib/core/Axios.js
构造函数Axios。
function Axios(instanceConfig) {
// 默认参数
this.defaults = instanceConfig;
// 拦截器 请求和响应拦截器
this.interceptors = {
request: new InterceptorManager(),
response: new InterceptorManager()
};
}
Axios.prototype.request = function(config){
// 省略,这个是核心方法,后文结合例子详细描述
// code ...
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
// code ...
return promise;
}
// 这是获取 Uri 的函数,这里省略
Axios.prototype.getUri = function(){}
// 提供一些请求方法的别名
// Provide aliases for supported request methods
// 遍历执行
// 也就是为啥我们可以 axios.get 等别名的方式调用,而且调用的是 Axios.prototype.request 方法
// 这个也在上面的 axios 结构图上有所体现。
utils.forEach(['delete', 'get', 'head', 'options'], function forEachMethodNoData(method) {
/*eslint func-names:0*/
Axios.prototype[method] = function(url, config) {
return this.request(utils.merge(config || {}, {
method: method,
url: url
}));
};
});
utils.forEach(['post', 'put', 'patch'], function forEachMethodWithData(method) {
/*eslint func-names:0*/
Axios.prototype[method] = function(url, data, config) {
return this.request(utils.merge(config || {}, {
method: method,
url: url,
data: data
}));
};
});
module.exports = Axios;
接下来看拦截器部分。
拦截器管理构造函数 InterceptorManager
请求前拦截,和请求后拦截。
在Axios.prototype.request函数里使用,具体怎么实现的拦截的,后文配合例子详细讲述。
axios github 仓库 拦截器文档
如何使用:
// Add a request interceptor
// 添加请求前拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
// Do something before request is sent
return config;
}, function (error) {
// Do something with request error
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// Add a response interceptor
// 添加请求后拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
// Any status code that lie within the range of 2xx cause this function to trigger
// Do something with response data
return response;
}, function (error) {
// Any status codes that falls outside the range of 2xx cause this function to trigger
// Do something with response error
return Promise.reject(error);
});
如果想把拦截器,可以用eject方法。
const myInterceptor = axios.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
axios.interceptors.request.eject(myInterceptor);
拦截器也可以添加自定义的实例上。
const instance = axios.create();
instance.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
源码实现:
构造函数,handles 用于存储拦截器函数。
function InterceptorManager() {
this.handlers = [];
}
接下来声明了三个方法:使用、移除、遍历。
InterceptorManager.prototype.use 使用
传递两个函数作为参数,数组中的一项存储的是{fulfilled: function(){}, rejected: function(){}}。返回数字 ID,用于移除拦截器。
/**
* @param {Function} fulfilled The function to handle `then` for a `Promise`
* @param {Function} rejected The function to handle `reject` for a `Promise`
*
* @return {Number} 返回ID 是为了用 eject 移除
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function use(fulfilled, rejected) {
this.handlers.push({
fulfilled: fulfilled,
rejected: rejected
});
return this.handlers.length - 1;
};
InterceptorManager.prototype.eject 移除
根据 use 返回的 ID 移除 拦截器。
/**
* @param {Number} id The ID that was returned by `use`
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.eject = function eject(id) {
if (this.handlers[id]) {
this.handlers[id] = null;
}
};
有点类似定时器setTimeout 和 setInterval,返回值是id。用clearTimeout 和clearInterval来清除定时器。
// 提一下 定时器回调函数是可以传参的,返回值 timer 是数字
var timer = setInterval((name) => {
console.log(name);
}, 1000, '若川');
console.log(timer); // 数字 ID
// 在控制台等会再输入执行这句,定时器就被清除了
clearInterval(timer);
InterceptorManager.prototype.forEach 遍历
遍历执行所有拦截器,传递一个回调函数(每一个拦截器函数作为参数)调用,被移除的一项是null,所以不会执行,也就达到了移除的效果。
/**
* @param {Function} fn The function to call for each interceptor
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.forEach = function forEach(fn) {
utils.forEach(this.handlers, function forEachHandler(h) {
if (h !== null) {
fn(h);
}
});
};
实例结合
上文叙述的调试时运行npm start 是用axios/sandbox/client.html路径的文件作为示例的,读者可以自行调试。
以下是一段这个文件中的代码。
axios(options)
.then(function (res) {
response.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(res.data, null, 2);
})
.catch(function (res) {
response.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(res.data, null, 2);
});
先看调用栈流程
如果不想一步步调试,有个偷巧的方法。
知道 axios 使用了XMLHttpRequest。
可以在项目中搜索:new XMLHttpRequest。
定位到文件 axios/lib/adapters/xhr.js
在这条语句 var request = new XMLHttpRequest();chrome 浏览器中 打个断点调试下,再根据调用栈来细看具体函数等实现。
Call Stack
dispatchXhrRequest (xhr.js:19)
xhrAdapter (xhr.js:12)
dispatchRequest (dispatchRequest.js:60)
Promise.then (async)
request (Axios.js:54)
wrap (bind.js:10)
submit.onclick ((index):138)
简述下流程:
Send Request按钮点击submit.onclick调用
axios函数实际上是调用Axios.prototype.request函数,而这个函数使用bind返回的一个名为wrap的函数。调用
Axios.prototype.request(有请求拦截器的情况下执行请求拦截器),中间会执行
dispatchRequest方法dispatchRequest之后调用adapter (xhrAdapter)最后调用
Promise中的函数dispatchXhrRequest,(有响应拦截器的情况下最后会再调用响应拦截器)
如果仔细看了文章开始的axios 结构关系图,其实对这个流程也有大概的了解。
接下来看 Axios.prototype.request 具体实现。
Axios.prototype.request 请求核心方法
这个函数是核心函数。主要做了这几件事:
1.判断第一个参数是字符串,则设置 url,也就是支持
axios('example/url', [, config]),也支持axios({})。
2.合并默认参数和用户传递的参数
3.设置请求的方法,默认是是get方法
4.将用户设置的请求和响应拦截器、发送请求的dispatchRequest组成Promise链,最后返回还是Promise实例。
也就是保证了请求前拦截器先执行,然后发送请求,再响应拦截器执行这样的顺序。
也就是为啥最后还是可以`then`,`catch`方法的缘故。
Axios.prototype.request = function request(config) {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
// Allow for axios('example/url'[, config]) a la fetch API
// 这一段代码 其实就是 使 axios('example/url', [, config])
// config 参数可以省略
if (typeof config === 'string') {
config = arguments[1] || {};
config.url = arguments[0];
} else {
config = config || {};
}
// 合并默认参数和用户传递的参数
config = mergeConfig(this.defaults, config);
// Set config.method
// 设置 请求方法,默认 get 。
if (config.method) {
config.method = config.method.toLowerCase();
} else if (this.defaults.method) {
config.method = this.defaults.method.toLowerCase();
} else {
config.method = 'get';
}
// Hook up interceptors middleware
// 组成`Promise`链 这段拆开到后文再讲述
};
组成Promise链,返回Promise实例
这部分:用户设置的请求和响应拦截器、发送请求的
dispatchRequest组成Promise链。也就是保证了请求前拦截器先执行,然后发送请求,再响应拦截器执行这样的顺序
也就是保证了请求前拦截器先执行,然后发送请求,再响应拦截器执行这样的顺序
也就是为啥最后还是可以`then`,`catch`方法的缘故。
如果读者对Promise不熟悉,建议读阮老师的书籍《ES6 标准入门》。阮一峰老师 的 ES6 Promise-resolve 和 JavaScript Promise 迷你书(中文版)
// 组成`Promise`链
// Hook up interceptors middleware
// 把 xhr 请求 的 dispatchRequest 和 undefined 放在一个数组里
var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined];
// 创建 Promise 实例
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
// 遍历用户设置的请求拦截器 放到数组的 chain 前面
this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(interceptor) {
chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
// 遍历用户设置的响应拦截器 放到数组的 chain 后面
this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(interceptor) {
chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
// 遍历 chain 数组,直到遍历 chain.length 为 0
while (chain.length) {
// 两两对应移出来 放到 then 的两个参数里。
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}
return promise;
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
解释下这句。作用是生成Promise实例。
var promise = Promise.resolve({name: '若川'})
// 等价于
// new Promise(resolve => resolve({name: '若川'}))
promise.then(function (config){
console.log(config)
});
// {name: "若川"}
同样解释下后文会出现的Promise.reject(error);:
Promise.reject(error);
var promise = Promise.reject({name: '若川'})
// 等价于
// new Promise(reject => reject({name: '若川'}))
// promise.then(null, function (config){
// console.log(config)
// });
// 等价于
promise.catch(function (config){
console.log(config)
});
// {name: "若川"}
接下来结合例子,来理解这段代码。
很遗憾,在example文件夹没有拦截器的例子。笔者在example中在example/get的基础上添加了一个拦截器的示例。axios/examples/interceptors,便于读者调试。
node ./examples/server.js -p 5000
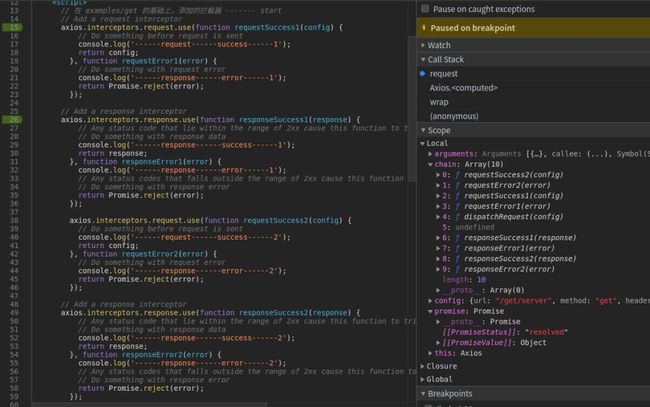
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());这段代码打个断点。
特别关注下,右侧,local中的chain数组。也就是这样的结构。
var chain = [
'请求成功拦截2', '请求失败拦截2',
'请求成功拦截1', '请求失败拦截1',
dispatch, undefined,
'响应成功拦截1', '响应失败拦截1',
'响应成功拦截2', '响应失败拦截2',
]
这段代码相对比较绕。也就是会生成如下类似的代码,中间会调用dispatchRequest方法。
// config 是 用户配置和默认配置合并的
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
promise.then('请求成功拦截2', '请求失败拦截2')
.then('请求成功拦截1', '请求失败拦截1')
.then(dispatchRequest, undefined)
.then('响应成功拦截1', '响应失败拦截1')
.then('响应成功拦截2', '响应失败拦截2')
.then('用户写的业务处理函数')
.catch('用户写的报错业务处理函数');
这里提下promise then和catch知识:Promise.prototype.then方法的第一个参数是resolved状态的回调函数,第二个参数(可选)是rejected状态的回调函数。所以是成对出现的。Promise.prototype.catch方法是.then(null, rejection)或.then(undefined, rejection)的别名,用于指定发生错误时的回调函数。then方法返回的是一个新的Promise实例(注意,不是原来那个Promise实例)。因此可以采用链式写法,即then方法后面再调用另一个then方法。
结合上述的例子更详细一点,代码则是这样的。
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
// promise.then('请求成功拦截2', '请求失败拦截2')
promise.then(function requestSuccess2(config) {
console.log('------request------success------2');
return config;
}, function requestError2(error) {
console.log('------response------error------2');
return Promise.reject(error);
})
// .then('请求成功拦截1', '请求失败拦截1')
.then(function requestSuccess1(config) {
console.log('------request------success------1');
return config;
}, function requestError1(error) {
console.log('------response------error------1');
return Promise.reject(error);
})
// .then(dispatchRequest, undefined)
.then( function dispatchRequest(config) {
/**
* 适配器返回的也是Promise 实例
adapter = function xhrAdapter(config) {
return new Promise(function dispatchXhrRequest(resolve, reject) {})
}
**/
return adapter(config).then(function onAdapterResolution(response) {
// 省略代码 ...
return response;
}, function onAdapterRejection(reason) {
// 省略代码 ...
return Promise.reject(reason);
});
}, undefined)
// .then('响应成功拦截1', '响应失败拦截1')
.then(function responseSuccess1(response) {
console.log('------response------success------1');
return response;
}, function responseError1(error) {
console.log('------response------error------1');
return Promise.reject(error);
})
// .then('响应成功拦截2', '响应失败拦截2')
.then(function responseSuccess2(response) {
console.log('------response------success------2');
return response;
}, function responseError2(error) {
console.log('------response------error------2');
return Promise.reject(error);
})
// .then('用户写的业务处理函数')
// .catch('用户写的报错业务处理函数');
.then(function (response) {
console.log('哈哈哈,终于获取到数据了', response);
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.log('哎呀,怎么报错了', err);
});
仔细看这段Promise链式调用,代码都类似。then方法最后返回的参数,就是下一个then方法第一个参数。catch错误捕获,都返回Promise.reject(error),这是为了便于用户catch时能捕获到错误。
举个例子:
var p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(new Error({name: '若川'}));
});
p1.catch(err => {
console.log(res, 'err');
return Promise.reject(err)
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err, 'err1');
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err, 'err2');
});
err2不会捕获到,也就是不会执行,但如果都返回了return Promise.reject(err),则可以捕获到。
最后画个图总结下 Promise 链式调用。
 axios promise 链式调用
axios promise 链式调用
小结:1. 请求和响应的拦截器可以写
Promise。
如果设置了多个请求响应器,后设置的先执行。
如果设置了多个响应拦截器,先设置的先执行。
dispatchRequest(config) 这里的config是请求成功拦截器返回的。接下来看dispatchRequest函数。
dispatchRequest 最终派发请求
这个函数主要做了如下几件事情:
1.如果已经取消,则
throw原因报错,使Promise走向rejected。
2.确保config.header存在。
3.利用用户设置的和默认的请求转换器转换数据。
4.拍平config.header。
5.删除一些config.header。
6.返回适配器adapter(Promise实例)执行后then执行后的Promise实例。返回结果传递给响应拦截器处理。
'use strict';
// utils 工具函数
var utils = require('./../utils');
// 转换数据
var transformData = require('./transformData');
// 取消状态
var isCancel = require('../cancel/isCancel');
// 默认参数
var defaults = require('../defaults');
/**
* 抛出 错误原因,使`Promise`走向`rejected`
*/
function throwIfCancellationRequested(config) {
if (config.cancelToken) {
config.cancelToken.throwIfRequested();
}
}
/**
* Dispatch a request to the server using the configured adapter.
*
* @param {object} config The config that is to be used for the request
* @returns {Promise} The Promise to be fulfilled
*/
module.exports = function dispatchRequest(config) {
// 取消相关
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);
// Ensure headers exist
// 确保 headers 存在
config.headers = config.headers || {};
// Transform request data
// 转换请求的数据
config.data = transformData(
config.data,
config.headers,
config.transformRequest
);
// Flatten headers
// 拍平 headers
config.headers = utils.merge(
config.headers.common || {},
config.headers[config.method] || {},
config.headers || {}
);
// 以下这些方法 删除 headers
utils.forEach(
['delete', 'get', 'head', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'common'],
function cleanHeaderConfig(method) {
delete config.headers[method];
}
);
// adapter 适配器部分 拆开 放在下文讲
};
dispatchRequest 之 transformData 转换数据
上文的代码里有个函数 transformData ,这里解释下。其实就是遍历传递的函数数组 对数据操作,最后返回数据。
axios.defaults.transformResponse 数组中默认就有一个函数,所以使用concat链接自定义的函数。
使用:
文件路径axios/examples/transform-response/index.html
这段代码其实就是对时间格式的字符串转换成时间对象,可以直接调用getMonth等方法。
var ISO_8601 = /(\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2})T(\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2})Z/;
function formatDate(d) {
return (d.getMonth() + 1) + '/' + d.getDate() + '/' + d.getFullYear();
}
axios.get('https://api.github.com/users/mzabriskie', {
transformResponse: axios.defaults.transformResponse.concat(function (data, headers) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(function (k) {
if (ISO_8601.test(data[k])) {
data[k] = new Date(Date.parse(data[k]));
}
});
return data;
})
})
.then(function (res) {
document.getElementById('created').innerHTML = formatDate(res.data.created_at);
});
源码:
就是遍历数组,调用数组里的传递 data 和 headers 参数调用函数。
module.exports = function transformData(data, headers, fns) {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
utils.forEach(fns, function transform(fn) {
data = fn(data, headers);
});
return data;
};
dispatchRequest 之 adapter 适配器执行部分
适配器,在设计模式中称之为适配器模式。讲个生活中简单的例子,大家就容易理解。
我们常用以前手机耳机孔都是圆孔,而现在基本是耳机孔和充电接口合二为一。统一为typec。
这时我们需要需要一个typec转圆孔的转接口,这就是适配器。
// adapter 适配器部分
var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter;
return adapter(config).then(function onAdapterResolution(response) {
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);
// Transform response data
// 转换响应的数据
response.data = transformData(
response.data,
response.headers,
config.transformResponse
);
return response;
}, function onAdapterRejection(reason) {
if (!isCancel(reason)) {
// 取消相关
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);
// Transform response data
// 转换响应的数据
if (reason && reason.response) {
reason.response.data = transformData(
reason.response.data,
reason.response.headers,
config.transformResponse
);
}
}
return Promise.reject(reason);
});
接下来看具体的 adapter。
adapter 适配器 真正发送请求
var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter;
看了上文的 adapter,可以知道支持用户自定义。比如可以通过微信小程序 wx.request 按照要求也写一个 adapter。
接着来看下 defaults.ddapter。
文件路径:axios/lib/defaults.js
根据当前环境引入,如果是浏览器环境引入xhr,是node环境则引入http。
类似判断node环境,也在sentry-javascript源码中有看到。
function getDefaultAdapter() {
var adapter;
// 根据 XMLHttpRequest 判断
if (typeof XMLHttpRequest !== 'undefined') {
// For browsers use XHR adapter
adapter = require('./adapters/xhr');
// 根据 process 判断
} else if (typeof process !== 'undefined' && Object.prototype.toString.call(process) === '[object process]') {
// For node use HTTP adapter
adapter = require('./adapters/http');
}
return adapter;
}
var defaults = {
adapter: getDefaultAdapter(),
// ...
};
xhr
接下来就是我们熟悉的 XMLHttpRequest 对象。
可能读者不了解可以参考XMLHttpRequest MDN 文档。
主要提醒下:onabort是请求取消事件,withCredentials是一个布尔值,用来指定跨域 Access-Control 请求是否应带有授权信息,如 cookie 或授权 header 头。
这块代码有删减,具体可以看若川的axios-analysis仓库,也可以克隆笔者的axios-analysis仓库调试时再具体分析。
module.exports = function xhrAdapter(config) {
return new Promise(function dispatchXhrRequest(resolve, reject) {
// 这块代码有删减
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open()
request.timeout = config.timeout;
// 监听 state 改变
request.onreadystatechange = function handleLoad() {
if (!request || request.readyState !== 4) {
return;
}
// ...
}
// 取消
request.onabort = function(){};
// 错误
request.onerror = function(){};
// 超时
request.ontimeout = function(){};
// cookies 跨域携带 cookies 面试官常喜欢考这个
// 一个布尔值,用来指定跨域 Access-Control 请求是否应带有授权信息,如 cookie 或授权 header 头。
// Add withCredentials to request if needed
if (!utils.isUndefined(config.withCredentials)) {
request.withCredentials = !!config.withCredentials;
}
// 上传下载进度相关
// Handle progress if needed
if (typeof config.onDownloadProgress === 'function') {
request.addEventListener('progress', config.onDownloadProgress);
}
// Not all browsers support upload events
if (typeof config.onUploadProgress === 'function' && request.upload) {
request.upload.addEventListener('progress', config.onUploadProgress);
}
// Send the request
// 发送请求
request.send(requestData);
});
}
而实际上现在 fetch 支持的很好了,阿里开源的 umi-request 请求库,就是用fetch封装的,而不是用XMLHttpRequest。文章末尾,大概讲述下 umi-request 和 axios 的区别。
http
http这里就不详细叙述了,感兴趣的读者可以自行查看,若川的axios-analysis仓库。
module.exports = function httpAdapter(config) {
return new Promise(function dispatchHttpRequest(resolvePromise, rejectPromise) {
});
};
上文 dispatchRequest 有取消模块,我觉得是重点,所以放在最后来细讲:
dispatchRequest 之 取消模块
可以使用cancel token取消请求。
axios cancel token API 是基于撤销的 promise 取消提议。
The axios cancel token API is based on the withdrawn cancelable promises proposal.
axios 文档 cancellation
文档上详细描述了两种使用方式。
很遗憾,在example文件夹也没有取消的例子。笔者在example中在example/get的基础上添加了一个取消的示例。axios/examples/cancel,便于读者调试。
node ./examples/server.js -p 5000
request中的拦截器和dispatch中的取消这两个模块相对复杂,可以多调试调试,吸收消化。
const CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
const source = CancelToken.source();
axios.get('/get/server', {
cancelToken: source.token
}).catch(function (err) {
if (axios.isCancel(err)) {
console.log('Request canceled', err.message);
} else {
// handle error
}
});
// cancel the request (the message parameter is optional)
// 取消函数。
source.cancel('哎呀,我被若川取消了');
取消请求模块代码示例
结合源码取消流程大概是这样的。这段放在代码在axios/examples/cancel-token/index.html。
参数的 config.cancelToken 是触发了source.cancel('哎呀,我被若川取消了');才生成的。
// source.cancel('哎呀,我被若川取消了');
// 点击取消时才会 生成 cancelToken 实例对象。
// 点击取消后,会生成原因,看懂了这段在看之后的源码,可能就好理解了。
var config = {
name: '若川',
// 这里简化了
cancelToken: {
promise: new Promise(function(resolve){
resolve({ message: '哎呀,我被若川取消了'})
}),
reason: { message: '哎呀,我被若川取消了' }
},
};
// 取消 抛出异常方法
function throwIfCancellationRequested(config){
// 取消的情况下执行这句
if(config.cancelToken){
// 这里源代码 便于执行,我改成具体代码
// config.cancelToken.throwIfRequested();
// if (this.reason) {
// throw this.reason;
// }
if(config.cancelToken.reason){
throw config.cancelToken.reason;
}
}
}
function dispatchRequest(config){
// 有可能是执行到这里就取消了,所以抛出错误会被err2 捕获到
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);
// adapter xhr适配器
return new Promise((resovle, reject) => {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
console.log('request', request);
if (config.cancelToken) {
// Handle cancellation
config.cancelToken.promise.then(function onCanceled(cancel) {
if (!request) {
return;
}
request.abort();
reject(cancel);
// Clean up request
request = null;
});
}
})
.then(function(res){
// 有可能是执行到这里就才取消 取消的情况下执行这句
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);
console.log('res', res);
return res;
})
.catch(function(reason){
// 有可能是执行到这里就才取消 取消的情况下执行这句
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);
console.log('reason', reason);
return Promise.reject(reason);
});
}
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
// 没设置拦截器的情况下是这样的
promise
.then(dispatchRequest, undefined)
// 用户定义的then 和 catch
.then(function(res){
console.log('res1', res);
return res;
})
.catch(function(err){
console.log('err2', err);
return Promise.reject(err);
});
// err2 {message: "哎呀,我被若川取消了"}
接下来看取消模块的源码
看如何通过生成config.cancelToken。
文件路径:
axios/lib/cancel/CancelToken.js
const CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
const source = CancelToken.source();
source.cancel('哎呀,我被若川取消了');
由示例看 CancelToken.source的实现,
CancelToken.source = function source() {
var cancel;
var token = new CancelToken(function executor(c) {
cancel = c;
});
// token
return {
token: token,
cancel: cancel
};
};
执行后source的大概结构是这样的。
{
token: {
promise: new Promise(function(resolve){
resolve({ message: '哎呀,我被若川取消了'})
}),
reason: { message: '哎呀,我被若川取消了' }
},
cancel: function cancel(message) {
if (token.reason) {
// Cancellation has already been requested
// 已经取消
return;
}
token.reason = {message: '哎呀,我被若川取消了'};
}
}
接着看 new CancelToken
// CancelToken
// 通过 CancelToken 来取消请求操作
function CancelToken(executor) {
if (typeof executor !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('executor must be a function.');
}
var resolvePromise;
this.promise = new Promise(function promiseExecutor(resolve) {
resolvePromise = resolve;
});
var token = this;
executor(function cancel(message) {
if (token.reason) {
// Cancellation has already been requested
// 已经取消
return;
}
token.reason = new Cancel(message);
resolvePromise(token.reason);
});
}
module.exports = CancelToken;
发送请求的适配器里是这样使用的。
// xhr
if (config.cancelToken) {
// Handle cancellation
config.cancelToken.promise.then(function onCanceled(cancel) {
if (!request) {
return;
}
request.abort();
reject(cancel);
// Clean up request
request = null;
});
}
dispatchRequest 中的throwIfCancellationRequested具体实现:throw 抛出异常。
// 抛出异常函数
function throwIfCancellationRequested(config) {
if (config.cancelToken) {
config.cancelToken.throwIfRequested();
}
}
// 抛出异常 用户 { message: '哎呀,我被若川取消了' }
CancelToken.prototype.throwIfRequested = function throwIfRequested() {
if (this.reason) {
throw this.reason;
}
};
取消流程调用栈
1.source.cancel()
2.resolvePromise(token.reason);
3.config.cancelToken.promise.then(function onCanceled(cancel) {})
最后进入request.abort();``reject(cancel);
到这里取消的流程就介绍完毕了。主要就是通过传递配置参数cancelToken,取消时才会生成cancelToken,判断有,则抛出错误,使Promise 走向rejected,让用户捕获到消息{message: '用户设置的取消信息'}。
文章写到这里就基本到接近尾声了。
能读到最后,说明你已经超过很多人啦^_^
axios是非常优秀的请求库,但肯定也不能满足所有开发者的需求,接下来对比下其他库,看看其他开发者有什么具体需求。
对比其他请求库
KoAjax
FCC 成都社区负责人水歌开源的KoAJAX。
如何用开源软件办一场技术大会?以下这篇文章中摘抄的一段。
前端请求库 —— KoAJAX 国内前端同学最常用的 HTTP 请求库应该是 axios 了吧?虽然它的 Interceptor(拦截器)API 是 .use(),但和 Node.js 的 Express、Koa 等框架的中间件模式完全不同,相比 jQuery .ajaxPrefilter()、dataFilter() 并没什么实质改进;上传、下载进度比 jQuery.Deferred() 还简陋,只是两个专门的回调选项。所以,它还是要对特定的需求记忆特定的 API,不够简洁。
幸运的是,水歌在研究如何用 ES 2018 异步迭代器实现一个类 Koa 中间件引擎的过程中,做出了一个更有实际价值的上层应用 —— KoAJAX。它的整个执行过程基于 Koa 式的中间件,而且它自己就是一个中间件调用栈。除了 RESTful API 常用的 .get()、.post()、.put()、.delete() 等快捷方法外,开发者就只需记住 .use() 和 next(),其它都是 ES 标准语法和 TS 类型推导。
umi-request 阿里开源的请求库
umi-request github 仓库
umi-request 与 fetch, axios 异同。

umi-request
与
fetch,
axios
异同
不得不说,umi-request 确实强大,有兴趣的读者可以阅读下其源码。
看懂axios的基础上,看懂umi-request源码应该不难。
比如 umi-request 取消模块代码几乎与axios一模一样。
总结
文章详细介绍了 axios 调试方法。详细介绍了 axios 构造函数,拦截器,取消等功能的实现。最后还对比了其他请求库。
最后画个图总结一下 axios 的总体大致流程。
 axios的总体大致流程
axios的总体大致流程
解答下文章开头提的问题:
如果你是求职者,项目写了运用了axios,面试官可能会问你:
1.为什么
axios既可以当函数调用,也可以当对象使用,比如axios({})、axios.get。
答:axios本质是函数,赋值了一些别名方法,比如get、post方法,可被调用,最终调用的还是Axios.prototype.request函数。
2.简述axios调用流程。
答:实际是调用的Axios.prototype.request方法,最终返回的是promise链式调用,实际请求是在dispatchRequest中派发的。
3.有用过拦截器吗?原理是怎样的?
答:用过,用axios.interceptors.request.use添加请求成功和失败拦截器函数,用axios.interceptors.response.use添加响应成功和失败拦截器函数。在Axios.prototype.request函数组成promise链式调用时,Interceptors.protype.forEach遍历请求和响应拦截器添加到真正发送请求dispatchRequest的两端,从而做到请求前拦截和响应后拦截。拦截器也支持用Interceptors.protype.eject方法移除。
4.有使用axios的取消功能吗?是怎么实现的?
答:用过,通过传递config配置cancelToken的形式,来取消的。判断有传cancelToken,在promise链式调用的dispatchRequest抛出错误,在adapter中request.abort()取消请求,使promise走向rejected,被用户捕获取消信息。
5.为什么支持浏览器中发送请求也支持node发送请求?
答:axios.defaults.adapter默认配置中根据环境判断是浏览器还是node环境,使用对应的适配器。适配器支持自定义。
回答面试官的问题,读者也可以根据自己的理解,组织语言,笔者的回答只是做一个参考。
axios 源码相对不多,打包后一千多行,比较容易看完,非常值得学习。
建议 clone 若川的 axios-analysis github 仓库,按照文中方法自己调试,印象更深刻。
基于Promise,构成Promise链,巧妙的设置请求拦截,发送请求,再试试响应拦截器。
request中的拦截器和dispatch中的取消这两个模块相对复杂,可以多调试调试,吸收消化。
axios 既是函数,是函数时调用的是Axios.prototype.request函数,又是对象,其上面有get、post等请求方法,最终也是调用Axios.prototype.request函数。
axios 源码中使用了挺多设计模式。比如工厂模式、迭代器模式、适配器模式等。如果想系统学习设计模式,一般比较推荐豆瓣评分 9.1 的JavaScript 设计模式与开发实践
如果读者发现有不妥或可改善之处,再或者哪里没写明白的地方,欢迎加我微信 lxchuan12 交流。另外觉得写得不错,对您有些许帮助,可以点赞、评论、转发分享,也是对笔者的一种支持,非常感谢呀。