Linq中SelectMany图文详解-Chinar
Chinar blog :www.chinar.xin
|
助力快速理解 SelectMany 的高级用法 为初学者节省宝贵的时间,避免采坑! |
|
我们的初衷是将一种简单的生活方式带给世人 使有限时间 具备无限可能 |
文章目录
- 1 Intro —— 简介
- 1 Overload 1 —— 重载 1
- 2 Overload 2 —— 重载 2
- 3 Overload 2 —— 重载 3
- 4 Overload 2 —— 重载 4
- 5 Project —— 全脚本文件
- 支持
- May Be —— 开发者,总有一天要做的事!
1 Intro —— 简介
Linq函数关键字大全!( Chinar Blog )
SelectMany对于初学者来讲,是一个比较难理解的函数。其内部逻辑,有点绕。
在使用上,对初学者来讲,尤其是容易懵逼…
但它的用途极其广泛,且极大的节省代码、提高代码可读性。
避免大量的循环代码
这里我以 4个例子,说明SelectMany的多种用法。
请大家仔细、耐心的看完。
![]()
/// 初始化,填入数据
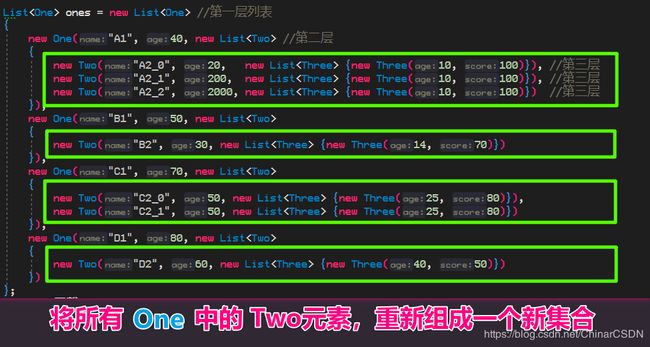
为了便于大家理解,我用了
one、two、three 做为3层嵌套的子父类;
one 对应的数据值为: 爹、年龄
Two 对应:儿子 、 年龄
List<One> ones = new List<One> //第一层列表
{
new One("爹1", 1, new List<Two> //第儿子层
{
new Two("儿子_0", 20, new List<Three> {new Three(30, 100)}), //第三层
new Two("儿子_1", 21, new List<Three> {new Three(31, 100)}), //第三层
new Two("儿子_2", 22, new List<Three> {new Three(32, 100)}) //第三层
}),
new One("爹2", 10, new List<Two>
{
new Two("儿子_0", 23, new List<Three> {new Three(33, 70)})
}),
new One("爹3", 100, new List<Two>
{
new Two("儿子_0", 24, new List<Three> {new Three(34, 80)}),
new Two("儿子_1", 25, new List<Three> {new Three(35, 80)})
}),
new One("爹4", 1000, new List<Two>
{
new Two("儿子_0", 26, new List<Three> {new Three(36, 50)})
})
};
1 Overload 1 —— 重载 1
我们来看下官方的代码注释:
//
// 摘要:
// 一个序列的每个元素投影 System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable`1 并将合并为一个序列将结果序列。
//
// 参数:
// source:
// 一个要投影的值序列。
//
// selector:
// 应用于每个元素的转换函数。
//
// 类型参数:
// TSource:
// 中的元素的类型 source。
//
// TResult:
// 返回的序列的元素的类型 selector。
//
// 返回结果:
// System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable`1 其元素是一种一对多转换函数对输入序列中的每个元素调用的结果。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// source 或 selector 为 null。
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source,
Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);
懵逼不?这才是重载第一个
不要怕,有我,跟我来看个栗子
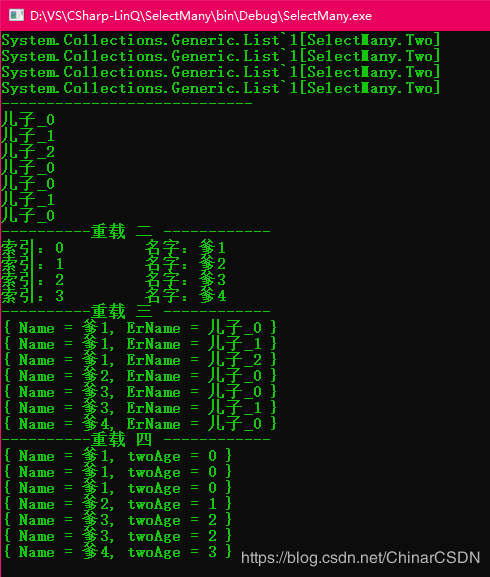
IEnumerable<List<Two>> onesSelect = ones.Select(one => one.TwoList); //Select 返回 List输出结果
System.Collections.Generic.List`1[SelectMany.Two]
System.Collections.Generic.List`1[SelectMany.Two]
System.Collections.Generic.List`1[SelectMany.Two]
System.Collections.Generic.List`1[SelectMany.Two]
----------------------------
儿子_0
儿子_1
儿子_2
儿子_0
儿子_0
儿子_1
儿子_0
![]()
为了便于理解,我用
A B C - 1 2 3对应了列表和对象的级别。
SelectMany 作用:
Ones列表中的 每个One 实例下都包含了一个TwoList列表
列表Ones每个One 对象: A1 B1 C1 D1都包含了一个List
A2_0
A2_1
A2_2
B2_0
C2_0
C2_1
D2_0
将所有的
List重新组合成了一个新集合
就是语句的真谛
IEnumerable
返回类型为:IEnumerable的新集合
2 Overload 2 —— 重载 2
我们来看下第二个重载
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource,
int, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);
这个函数其实别第一个重载就多了一个 Int,这个是循环的下标
//这里的 index 指的是 List ones 对象的循环索引
IEnumerable<string> stringEnumerable = ones.SelectMany((one, index) => new List<string> { "索引:" + index + " 名字:" + one.Name });
foreach (var v in stringEnumerable)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=String
}
输出结果
索引:0 名字:爹1
索引:1 名字:爹2
索引:2 名字:爹3
索引:3 名字:爹4
可以看出SelectMany 内部循环时,Index作为循环的下标 0-3
SelectMany 作用:
Ones列表中的 每个元素 One 的实例,
"索引:" + index + " 名字:" + one.Name"=循环的 [
索引 0-3+爹名字] 字符串拼接
将每个 字符串 ,重新组合成一个集合,并返回 所以类型是IEnumerable;
![]()
其内部函数运行原理基本与下方代码一致,只是返回类型为 IEnumerable
List<string> stringList=new List<string>();
for (int index = 0; index < ones.Count; index++)
{
stringList.Add("索引:" + index + " 名字:" + ones[index].Name);
}
return stringList
3 Overload 2 —— 重载 3
我们来看下第3个重载
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TCollection, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source,
Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TCollection>> collectionSelector,
Func<TSource, TCollection, TResult> resultSelector);
更加有难度了啊
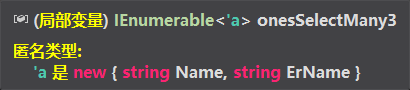
//返回匿名类型: <爹的名字,儿子的名字> 组成一个集合返回
var onesSelectMany3 = ones.SelectMany(one => one.TwoList, (one, two) => new {one.Name, two.ErName});
//可自定义返回类型
//var onesSelectMany3 = ones.SelectMany(one => one.TwoList, (one, two) => new Dictionary {{ one.Name, two.Age } });
foreach (var v in onesSelectMany3)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=匿名类型
}
输出结果
{ Name = 爹1, ErName = 儿子_0 }
{ Name = 爹1, ErName = 儿子_1 }
{ Name = 爹1, ErName = 儿子_2 }
{ Name = 爹2, ErName = 儿子_0 }
{ Name = 爹3, ErName = 儿子_0 }
{ Name = 爹3, ErName = 儿子_1 }
{ Name = 爹4, ErName = 儿子_0 }
SelectMany 重载3的作用:
第一个参数:one => one.TwoList
这个不难理解,就是我们重载1中提到过的。其返回的是IEnumerable 所有 儿子的大集合。
第二个参数:(one, two) => new {one.Name, two.ErName}
one和two分别指 映射后的 one和two实例
循环中,会执行每一项 父和子其顺序为:
1. { Name = 爹1, ErName = 儿子_0 }
2. { Name = 爹1, ErName = 儿子_1 }
3. { Name = 爹1, ErName = 儿子_2 }
4. { Name = 爹2, ErName = 儿子_0 }
5. { Name = 爹3, ErName = 儿子_0 }
6. { Name = 爹3, ErName = 儿子_1 }
7. { Name = 爹4, ErName = 儿子_0 }
返回值为自定义匿名类型new {one.Name, two.ErName}
也就是 {父的名字,儿子的名字}组成的自定义类型,遍历每一项,并返回一个由匿名类型组成的大集合。
![]()
自定义类型根据需求自行变更,扩展性非常强健!
var onesSelectMany3 = ones.SelectMany(one => one.TwoList, (one, two) => new Dictionary<string, int> {{ one.Name, two.Age } });
4 Overload 2 —— 重载 4
我们来看下第4个重载
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TCollection, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source,
Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TCollection>> collectionSelector,
Func<TSource, TCollection, TResult> resultSelector);
只比第三个多了个Index下标,没什么难的。思维不要乱!
为了便于初学者理解,我们先写个简单的式子,看下每个儿子的年龄现在是多少?
var onesSelectMany5 = ones.SelectMany((one) => one.TwoList.Select(two => two.Age));
foreach (var v in onesSelectMany5)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=int 年龄
}
输出结果
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
- 我们把
儿子们的年龄,改为第四个重载函数的Index值
并返回自定义类型
//将每个儿子的年龄值改为当前 Index 索引值
//并返回匿名类型{爹,儿子年龄改为索引后的值}
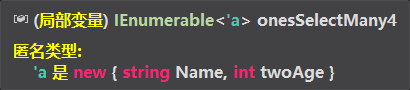
var onesSelectMany4 = ones.SelectMany((one, index) => one.TwoList.Select(two => two.Age = index), (one, twoAge) => new {one.Name, twoAge}); //返回匿名类型: 1级的名字,2级的年龄
foreach (var v in onesSelectMany4)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=匿名类型
}
输出结果
{ Name = 爹1, twoAge = 0 }
{ Name = 爹1, twoAge = 0 }
{ Name = 爹1, twoAge = 0 }
{ Name = 爹2, twoAge = 1 }
{ Name = 爹3, twoAge = 2 }
{ Name = 爹3, twoAge = 2 }
{ Name = 爹4, twoAge = 3 }
![]()
SelectMany 重载4的作用:
第一个参数:(one, index) => one.TwoList.Select(two => two.Age = index)
就是将每个Two中 儿子的年龄,改为Index的值,返回类型为 IEnumerable 儿子们年龄的大集合
第二个参数:(one, twoAge) => new {one.Name, twoAge}
one和 twoAge 分别指 映射后的 one和twoAge实例
返回值为自定义匿名类型new {one.Name, twoAge}
也就是 {父的名字,儿子的年龄(索引)}组成的自定义类型,遍历每一项,并返回一个由匿名类型组成的大集合。
学习更多Linq知识,请看我其他表达式的讲解;
Linq函数关键字大全!( Chinar Blog )
5 Project —— 全脚本文件
项目文件为 C# 控制台脚本文件
![]()
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SelectMany
{
/// ones 中对象的索引
IEnumerable<string> stringEnumerable = ones.SelectMany((one, index) => new List<string> {"索引:" + index + " 名字:" + one.Name});
foreach (var v in stringEnumerable)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=String
}
#endregion
#region 重载 3
Console.WriteLine("----------重载 三 ------------");
//返回匿名类型: <爹的名字,儿子的名字> 组成一个集合返回
var onesSelectMany3 = ones.SelectMany(one => one.TwoList, (one, two) => new {one.Name, two.ErName});
//可自定义返回类型
//var onesSelectMany3 = ones.SelectMany(one => one.TwoList, (one, two) => new Dictionary {{ one.Name, two.Age } });
foreach (var v in onesSelectMany3)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=匿名类型
}
#endregion
#region 重载 4
Console.WriteLine("----------重载 四 ------------");
////先看下儿子的年龄现在是多少?
////var onesSelectMany5 = ones.SelectMany((one) => one.TwoList.Select(two => two.Age));
////foreach (var v in onesSelectMany5)
////{
//// Console.WriteLine(v); //v=int 年龄
////}
//将每个儿子的年龄值改为当前 Index 索引值
//并返回匿名类型{爹,儿子年龄改为索引后的值}
var onesSelectMany4 = ones.SelectMany((one, index) => one.TwoList.Select(two => two.Age = index), (one, twoAge) => new {one.Name, twoAge}); //返回匿名类型: 1级的名字,2级的年龄
foreach (var v in onesSelectMany4)
{
Console.WriteLine(v); //v=匿名类型
}
#endregion
Console.ReadLine();
}
/// 内存地址
public static string GetMemoryAddress(object obj)
{
return GCHandle.Alloc(obj, GCHandleType.Pinned).AddrOfPinnedObject().ToString("X");
}
}
}
支持
May Be —— 开发者,总有一天要做的事!
|
Chinar 提供一站式《零》基础教程 使有限时间 具备无限可能! |
先点击领取 —— 阿里全产品优惠券 (享受最低优惠)
Chinar 免费服务器、建站教程全攻略!( Chinar Blog )
本博客为非营利性个人原创,除部分有明确署名的作品外,所刊登的所有作品的著作权均为本人所拥有,本人保留所有法定权利。违者必究
对于需要复制、转载、链接和传播博客文章或内容的,请及时和本博主进行联系,留言,Email: [email protected]
对于经本博主明确授权和许可使用文章及内容的,使用时请注明文章或内容出处并注明网址