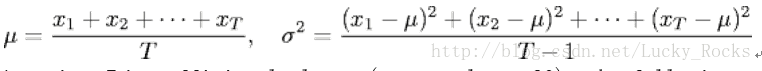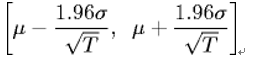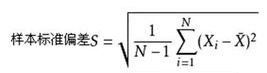渗漏(Percolation)问题(java语言实现)
使用合并-查找数据结构,实现估计渗漏(Percolation)问题阈值的程序。
编写一个程序,通过蒙特卡罗模拟来估计渗滤阈值。
引言:
给定一个由随机分布的绝缘材料和金属材料组成的复合系统:多少材料需要是金属的,以便复合系统是电导体?考虑到地表(或下面的油)有水的多孔景观,在什么条件下水能够通过底部排出(或油喷到表面)?科学家已经定义了一个被称为渗流的抽象过程来模拟这种情况。该模型。我们用一个N×N的网格模型来建立一个渗流系统。每个网站都是开放或封锁。一个完整的网站是一个开放的网站,可以通过一系列相邻的(左,右,上,下)开放网站连接到最上面的一个开放网站。我们说如果底部有一个完整的网站,系统会渗透。换句话说,如果我们填充连接到最上一行的所有打开的站点,并且该过程填满最下一行的一些打开站点,那么系统会渗透。 (对于绝缘/金属材料的例子,开放部位对应于金属材料,使得渗透的体系具有从上到下的金属路径,并且完整的部位导电。对于多孔物质实例,开放部位对应于空的空间水可以通过它流动,使渗透的系统让水充满开放的地点,从上到下流动。)
问题:(如果已经知道题目,可以直接越过此处)
在一个著名的科学问题中,研究人员对以下问题感兴趣:如果网站独立设置为以概率p打开(因此以概率1-p被阻塞),系统渗透的概率是多少?当p等于0时,系统不会渗透;当p等于1时,系统渗透。下面的图显示了20×20随机网格(左)和100×100随机网格(右)的网站空置概率p对渗滤概率


当N足够大时,存在阈值p’,使得当p < p’时,随机N×N网格几乎不渗滤,并且当p> p’时,随机N×N网格几乎总是渗滤。尚未推导出用于确定渗透阈值p’的数学解决方案。你的任务是编写一个计算机程序来估计p’。
程序Percolation实现的API接口如下:
public class Percolation {
public Percolation(int N) // create N-by-N grid, with all sites blocked
public void open(int i, int j) // open site (row i, column j) if it is not already
public boolean isOpen(int i, int j) // is site (row i, column j) open?
public boolean isFull(int i, int j) // is site (row i, column j) full?
public boolean percolates() // does the system percolate?
public static void main(String[] args) // test client, optional
}
按照惯例,行和列索引i和j是1和N之间的整数,其中(1,1)是左上角站点:如果open(),isOpen()或isFull()的任何参数抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException超出了规定的范围。如果N≤0,构造函数应该抛出IllegalArgumentException。构造函数应该花费与N2成正比的时间;所有方法都应该花费不变的时间加上对union(),find(),connected()和count()的联合查找方法的不断调用。
蒙特卡洛模拟。为了估计逾渗阈值,考虑下面的计算实验:
•初始化所有要阻止的站点。
•重复以下操作,直到系统渗漏:
o在所有被封锁的网站中随机选择一个网站(第i行,第j列)。
o打开网站(第i行,第j列)。
•系统渗透时打开的部分网站提供了渗透阈值的估计值。
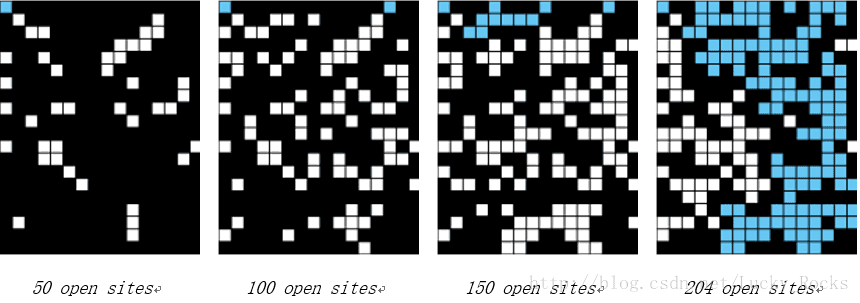
例如,如果按照下面的快照打开网格,那么我们估计的渗滤阈值是204/400 = 0.51,因为当第204个站点打开时,系统渗透。
通过重复该计算实验T次并平均结果,我们获得更准确的逾渗阈值估计。 设x_t为计算实验t中开放点的分数。 样本平均值μ提供了渗透阈值的估计; 样本标准偏差σ测量阈值的清晰度。
假设T足够大(例如至少30),下面提供渗透阈值的95%置信区间
程序PercolationStats 的API接口:
public class PercolationStats {
public PercolationStats(int N, int T) // perform T independent computational experiments on an N-by-N grid
public double mean() // sample mean of percolation threshold
public double stddev() // sample standard deviation of percolation threshold
public double confidenceLo() // returns lower bound of the 95% confidence interval
public double confidenceHi() // returns upper bound of the 95% confidence interval
public static void main(String[] args) // test client, described below
}
此外,还包括一个main()方法,该方法使用两个命令行参数N和T(其中N代表网格大小,T代表实验尝试的次数),在N×N网格上执行T个独立的计算实验(上面讨论),打印出平均值,标准偏差,95% 置信阈值的置信区间。 使用标准库中的标准随机数生成随机数; 使用标准统计来计算样本均值和标准差。
% java PercolationStats 200 100
mean = 0.5929934999999997
stddev = 0.00876990421552567
95% confidence interval = 0.5912745987737567, 0.5947124012262428
% java PercolationStats 200 100
mean = 0.592877
stddev = 0.009990523717073799
95% confidence interval = 0.5909188573514536, 0.5948351426485464
% java PercolationStats 2 10000
mean = 0.666925
stddev = 0.11776536521033558
95% confidence interval = 0.6646167988418774, 0.6692332011581226
% java PercolationStats 2 100000
mean = 0.6669475
stddev = 0.11775205263262094
95% confidence interval = 0.666217665216461, 0.6676773347835391
Percolation
public class Percolation {
private int matrixLength;
private boolean[] matrix;
// private WeightedQuickUnion wqu;
private PathCompressWQU pwqu;
private int virtualTop;
private int virtualbottom;
public Percolation(int N){
if (N <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length must be positive");
}
matrixLength = N;
virtualTop = matrixLength * matrixLength;
virtualbottom = matrixLength * matrixLength + 1;
matrix = new boolean[N * N];
// wqu = new WeightedQuickUnion(N * N + 2);
pwqu = new PathCompressWQU(N * N + 2);
}
private void checkValidIndex(int row,int col){
if(row <= 0 || row >matrixLength){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("row index out of bounds");
}
if(col <= 0 || col >matrixLength){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("col index out of bounds");
}
}
private int rowCol_to_real(int row,int col){
return (row - 1) * matrixLength + col - 1;
}
public void open(int row,int col){
checkValidIndex(row, col); //检查边界
int real = rowCol_to_real(row, col); //转换成以为坐标
if (matrix[real]) {
return; //如果已经是打开的,就直接返回
}
matrix[real] = true;
if (row == 1) { //如果是第一行的情况,那么让他连接top的虚拟点
// wqu.union(real, virtualTop);
pwqu.union(real, virtualTop);
//System.out.println("Connected Top");
}
if (row == matrixLength) { //如果是最后一行的情况,那么让他连接bottom的虚拟点
// wqu.union(real, virtualbottom);
pwqu.union(real, virtualbottom);
//System.out.println("Connected Bottom");
}
int neighbor;
//判断周围的四个点是否是打开的,如果是的话就连接
if (row > 1) { // up
neighbor = rowCol_to_real(row - 1, col);
if (matrix[neighbor]) {
// wqu.union(real, neighbor);
pwqu.union(real, neighbor);
}
}
if (row < matrixLength) { // down
neighbor = rowCol_to_real(row + 1, col);
if (matrix[neighbor]) {
// wqu.union(real, neighbor);
pwqu.union(real, neighbor);
}
}
if (col > 1) { // left
neighbor = rowCol_to_real(row, col - 1);
if (matrix[neighbor]) {
// wqu.union(real, neighbor);
pwqu.union(real, neighbor);
}
}
if (col < matrixLength) { // right
neighbor = rowCol_to_real(row, col + 1);
if (matrix[neighbor]) {
// wqu.union(real, neighbor);
pwqu.union(real, neighbor);
}
}
}
public boolean isOpen(int row,int col){ //判断这个点是不是打开的
checkValidIndex(row, col);
return matrix[rowCol_to_real(row, col)];
}
public boolean isFull(int row,int col){ //判断这个点是不是和virtualtop连接,也就是是不是开放的,能不能连接到顶端的点
checkValidIndex(row, col);
// return wqu.isConnect(virtualTop, rowCol_to_real(row, col));
return pwqu.isConnect(virtualTop, rowCol_to_real(row, col));
}
public boolean isPercolated(){ //判断是否渗透
// return wqu.isConnect(virtualTop, virtualbottom);
return pwqu.isConnect(virtualTop, virtualbottom);
}
}
在这里我们需要考虑一个问题就是当你输入的N=1的时候,更具下面的公式我们就会发现在计算偏差的时候就会出现除0的情况,所以在代码中应该考虑到。
matrixLength = N;
if (matrixLength == 1) {
mean = 1;
stddev = Double.NaN;
confidenceLow = Double.NaN;
confidenceHigh = Double.NaN;
}PercolationStats
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PercolationStats {
private int matrixLength;
private double[] threshold;
private double mean; //平均值
private double stddev; //标准偏差
private double confidenceLow; // 最低置信度
private double confidenceHigh; // 高置信度
public PercolationStats(int N, int T) {
if (N <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length must be positive");
}
if (T <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("trials must be positive");
}
matrixLength = N;
if (matrixLength == 1) {
mean = 1;
stddev = Double.NaN;
confidenceLow = Double.NaN;
confidenceHigh = Double.NaN;
}
else {
threshold = new double[T];
for(int i = 0;i < T;++i){
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(N);
int count = 0;
do {
int row = (int)(Math.random()*(matrixLength)) + 1;
int col = (int)(Math.random()*(matrixLength)) + 1;
//System.out.println("row= " + row+" , " + " col= " + col);
//System.out.println("count= " + count);
if(percolation.isOpen(row, col)){
continue;
}
else{
percolation.open(row, col);
++count;
}
} while (!percolation.isPercolated());
threshold[i] = (double)count / (matrixLength * matrixLength);
}
mean = Computemean(threshold,T);
stddev = Computestddev(threshold,T);
double diff = (1.96 * stddev) / Math.sqrt(T);
confidenceLow = mean - diff;
confidenceHigh = mean + diff;
}
}
private double Computemean(double[] threshold,int T) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i =0 ;i < threshold.length;++i){
sum += threshold[i];
}
return sum / T;
}
private double Computestddev(double[] threshold,int T) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i =0 ;i < threshold.length;++i){
sum += Math.pow(threshold[i]-mean, 2);
}
return Math.sqrt(sum/ (T - 1));
}
public double Getmean() {
return mean;
}
//
public double Getstddev() {
return stddev;
}
//
public double GetconfidenceLow() {
return confidenceLow;
}
//
public double GetconfidenceHigh() {
return confidenceHigh;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Please enter N and T : "); //Length and Times
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = in.nextInt();
int T = in.nextInt();
PercolationStats percolationStats = new PercolationStats(N,T);
System.out.println("The mean of percolationStats is " + percolationStats.Getmean());
System.out.println("The stddev of percolationStats is " + percolationStats.Getstddev());
System.out.println("The condidence intervals of percolationStats is " + "[" + percolationStats.GetconfidenceLow() +
" , " + percolationStats.GetconfidenceHigh() + "]");
in.close();
}
}
路径压缩算法
//import java.util.Scanner;
public class PathCompressWQU {
private int[] id;
private int[] sz;
private int count;
public PathCompressWQU(int N){
count=N;
id=new int[N];
sz=new int[N];
for(int i=0;i1;
}
}
public int getcount(){
return count;
}
public boolean isConnect(int p,int q){
return find(p)==find(q);
}
public int find(int p) {//复杂度为两倍的树的高度h 即2h
int temp = p;
while(p!=id[p]){
p=id[p];
}
while(temp != id[p]){
int tempId = id[temp];
id[temp] = id[p];
temp = tempId;
}
return id[p];
}
public void union(int p,int q){//不计算find的情况下 union的算法复杂度为1
int pRoot=find(p);
int qRoot=find(q);
if(pRoot==qRoot){
return;
}
if(sz[pRoot]else{
id[qRoot]=pRoot;
sz[pRoot]+=sz[qRoot];
}
count--;
}
/*
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int N=in.nextInt();
PathCompressWQU pcwqu=new PathCompressWQU(N);
while(in.hasNext()){
int p=in.nextInt();
int q=in.nextInt();
if(pcwqu.isConnect(p, q)){
System.out.println("p and q had benn in a componment!");
continue;
}
pcwqu.union(p, q);
System.out.println(pcwqu.getcount()+" componments" );
}
in.close();
}
*/
}