Pthreads多线程实战之“桶排序”
1. 前言
桶排序的主要思想是分而治之,是将待排序数组里的所有元素分放至不同的桶形容器里,然后在每个桶容器里分别进行排序(可以用其他排序算法,如插入排序,冒泡排序等),也可以通过递归实现桶排序来实现。最后再把每个桶容器里面有序的元素整合在一起完成最终的排序。
1.1 基本流程
(1)构建一堆空的桶容器;
(2)遍历原始待排序数组,并将每个元素放入到各自对应的桶容器中;
(3)对非空的桶容器进行排序;
(4)按照顺序遍历这些桶容器,并放回到原始数组中即可构成排序后的数组。
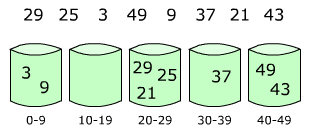
下面两副图模拟了桶排序的大概流程:

1.2 伪代码
下面是桶排序的伪代码:
function bucketSort(array, n) is
buckets ← new array of n empty lists
for i = 0 to (length(array)-1) do
insert array[i] into buckets[array[i]/bucket_range]
for i = 0 to n - 1 do
nextSort(buckets[i]);
return the concatenation of buckets[0], ...., buckets[n-1]其中array是要排序的原始数组,n是桶容器的个数,bucket_range是桶容器的步进大小,用来决定元素属于哪一个桶容器。
2. 桶排序
这个代码相对比较简单,直接给出“桶排序”的代码,其中每个桶容器中选用的排序算法是“插入排序”。
void bucket_sort(int array[], int arraySize)
{
int i,j;
node ** all_buckets;
//分配内存
all_buckets = (node **)malloc(sizeof(node *)*MAX_BUCKET);
//初始化
for(i = 0; i//将待排序的数据按照一定的规律分配到每个桶形容器里
for(i = 0; i//计算当前数据映射到哪一个桶
int bucket_index = returnBucketIndex(array[i]);
cur = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
cur->data = array[i];
cur->next = all_buckets[bucket_index];
all_buckets[bucket_index] = cur;
}
//打印出结果查看每个桶容器里的数据
for(i = 0; iif(temp != NULL)
{
printf("当前是第%d个桶容器,包含的数据有:\n",i);
while(temp!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//用其他排序方法对每个桶容器里面的数据进行排序,这里选择的是插入排序
for(i = 0; iprintf("\n");
printf("**********华丽的分割线**********\n",i);
printf("\n");
printf("排序之后每个桶容器里面的数据如下:\n");
//打印出结果查看每个桶容器里的数据
for(i = 0; iif(temp != NULL)
{
printf("当前是第%d个桶容器,包含的数据有:\n",i);
while(temp!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n最终排序好的数组如下:\n");
//将每个桶容器里面的数据取出来重新放回数组里
for(j =0, i = 0; i < MAX_BUCKET; i++) {
node *temp_node = all_buckets[i];
while(temp_node != NULL)
{
array[j++] = temp_node->data;
printf("%d ", temp_node->data);
temp_node = temp_node->next;
}
}
printf("\n");
//释放内存
for(i = 0; iwhile(head != NULL)
{
node *temp;
temp = head;
head = head->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(all_buckets);
} 完整的代码请去资源页0积分下载:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/wblgers1234/9859922
3. Pthread多线程实现桶排序
利用Pthread针对每一个桶容器创建一个线程,在每个线程中进行插入排序,最后在线程退出之前更新桶容器,得到有序的数组。
加入多线程实现的桶排序函数:
//桶排序函数定义
void bucket_sort(int array[], int arraySize)
{
int i,j;
//分配内存
all_buckets = (node **)malloc(sizeof(node *)*MAX_BUCKET);
all_buckets_t =(node **)malloc(sizeof(node *)*MAX_BUCKET);
//初始化
for(i = 0; i//将待排序的数据按照一定的规律分配到每个桶形容器里
for(i = 0; i//计算当前数据映射到哪一个桶
int bucket_index = returnBucketIndex(array[i]);
cur = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
cur->data = array[i];
cur->next = all_buckets[bucket_index];
all_buckets[bucket_index] = cur;
}
//打印出结果查看每个桶容器里的数据
for(i = 0; iif(temp != NULL)
{
printf("当前是第%d个桶容器,包含的数据有:\n",i);
while(temp!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n");
printf("**********华丽的分割线**********\n",i);
printf("\n");
printf("排序之后每个桶容器里面的数据如下:\n");
//用其他排序方法对每个桶容器里面的数据进行排序,这里选择的是插入排序
for(i = 0; iint rc = pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, thread_bucket_sort, (void *) &thread_data_array[i]);
if (rc)
{
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d\n", rc);
return;
}
}
for(i=0; iint rc = pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
if (rc)
{
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_join() is %d\n", rc);
return;
}
}
//打印出结果查看每个桶容器里的数据
printf("\n最终排序好的数组如下:\n");
//将每个桶容器里面的数据取出来重新放回数组里
for(j =0, i = 0; i < MAX_BUCKET; i++) {
node *temp_node = all_buckets_t[i];
while(temp_node != NULL)
{
array[j++] = temp_node->data;
printf("%d ", temp_node->data);
temp_node = temp_node->next;
}
}
printf("\n数组总长度为%d\n",j);
//释放内存
for(i = 0; iwhile(head != NULL)
{
node *temp;
temp = head;
head = head->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(all_buckets_t);
free(all_buckets);
} 在函数中对每一个桶容器创建一个对应的线程pthread_create,并将包含有线程ID和当前桶容器的所有元素(链表的头元素即可)。
//定义数据结构,传递至线程执行函数里面
struct thread_data{
int thread_id;//当前线程的ID
node *in;//当前线程需要处理的单链表
};线程执行函数:
//每个线程执行的函数
void *thread_bucket_sort(void *in)
{
struct thread_data *strcut_data = (struct thread_data *)in;
node *list = (strcut_data->in);
node *out = insert_sort(list);
node *temp = out;
//分配内存
all_buckets_t[strcut_data->thread_id] = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
all_buckets_t[strcut_data->thread_id] = out;
if(list != NULL)
{
printf("当前是第%d个桶容器,包含的数据有:\n",strcut_data->thread_id);
while(temp!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//退出线程
pthread_exit(NULL);
}在线程执行函数中,从结构提形参中取出线程ID和待排序的元素,调用插入排序insert_sort完成排序,并且将排序后的元素保存在另外一组buckets里面all_buckets_t。
完整的代码请去资源页0积分下载:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/wblgers1234/9859925
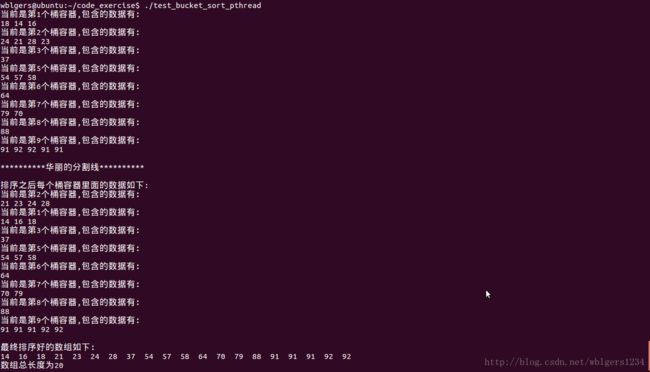
请注意,整个代码在linux下调试通过,用gcc编译的命令如下:
gcc test_bucket_sort_pthread.c -o test_bucket_sort_pthread -lpthread其中加入Pthread库的支持由“-lpthread”来示意。代码的运行结果如下图所示:
4. 参考
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bucket_sort
http://blog.csdn.net/lg1259156776/article/details/48803043