Android内存泄露抓取工具leakcanary
引言
“A small leak will sink a great ship.” - Benjamin Franklin
概述
某些对象的生命周期有限,当它们的工作完成以后,将会被GC回收。如果一个对象在其生命周期结束以后仍在内存中存在引用,将会导致内存泄露。当泄露积累过多,该应用将耗尽内存引起OOM,挂掉。
比如,在Activity.OnDestroy()方法被调用以后,这个activity的各种层级视图和它们关联的位图都应该被回收掉,如果一个后台运行的线程有该activity的引用,activity相对应的内存将不能被回收,这最终会导致OutOfMemoryError崩溃。
我们知道JAVA的内存回收由GC来回收,通常我们不用太关心内存的问题,但是对于资源比较紧张的手机系统来说,本来系统就不大,你还泄露了,这不是扯呢么,内存泄露的最终结果就是达到应用的内存阀值,应用崩溃。
为什么使用leakcanary
通常我们为了解决内存泄露的问题,一般有几个步骤
- 找到内存泄露的地方
- 记录堆栈内容
- 使用MAT 查看堆栈内容,并从中找出应该被回收的对象。
- 找到引用该对象的GC最短路径
- 分析代码,解决之
- 测试是否已修复
对于找内存泄露,之前的做法是连接AndroidStudio的Memory Monitor工具,查看内存使用曲线

当进入一个界面内存自然升高,退出时内存没有下降,当再次进入时内存继续升高,如果出现这种情况就有可能内存泄露的可能。这种方式效率上比较低,并且有时会不准确。具体的可参考这篇文章
http://hukai.me/android-performance-memory/
因此我们选择检测内存泄露高效并可以看到堆栈信息的leakcanary
leakcanary使用
leakcanary是square团队开源的一款检测并抓取android应用内存泄露的工具,优点
- 集成简单
- 检测准确并且高效
- 可以打出堆栈信息
- 平时debug下开启不占用开发时间,有log记录
使用
Android Studio 下gradle依赖
dependencies {
debugCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.3.1'
releaseCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.3.1'
}repositories {
mavenCentral()
}在Application中
public class ExampleApplication extends Application {
@Override public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
LeakCanary.install(this);
}
}如果gradle依赖不能区分deubg和release的话可以这样
compile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.3.1'public class ExampleApplication extends Application {
@Override public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
//内存分析工具
LeakCanary.install(this);
}
}
}LeakCanary.install() 会返回一个预定义的 RefWatcher,同时也会启用一个 ActivityRefWatcher,用于自动监控调用 Activity.onDestroy() 之后泄露的 activity。
配置很简单,当应用中发生内存泄露的时候会弹窗提示,并且在跟你应用程序同一个图标名字叫做Leaks的应用中就相应地记录
在Fragment中使用
public class ExampleApplication extends Application {
public static RefWatcher getRefWatcher(Context context) {
ExampleApplication application = (ExampleApplication) context.getApplicationContext();
return application.refWatcher;
}
private RefWatcher refWatcher;
@Override public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
refWatcher = LeakCanary.install(this);
}
}使用 RefWatcher 监控 Fragment:
public abstract class BaseFragment extends Fragment {
@Override public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
RefWatcher refWatcher = ExampleApplication.getRefWatcher(getActivity());
refWatcher.watch(this);
}
}工作机制
- RefWatcher.watch() 创建一个 KeyedWeakReference 到要被监控的对象。
- RefWatcher.watch() 创建一个 KeyedWeakReference 到要被监控的对象。
- 如果引用还是未被清除,把 heap 内存 dump 到 APP 对应的文件系统中的一个 .hprof 文件中。
- 在另外一个进程中的 HeapAnalyzerService 有一个 HeapAnalyzer 使用HAHA 解析这个文件。
- 得益于唯一的 reference key, HeapAnalyzer 找到 KeyedWeakReference,定位内存泄露。
- HeapAnalyzer 计算 到 GC roots 的最短强引用路径,并确定是否是泄露。如果是的话,建立导致泄露的引用链。
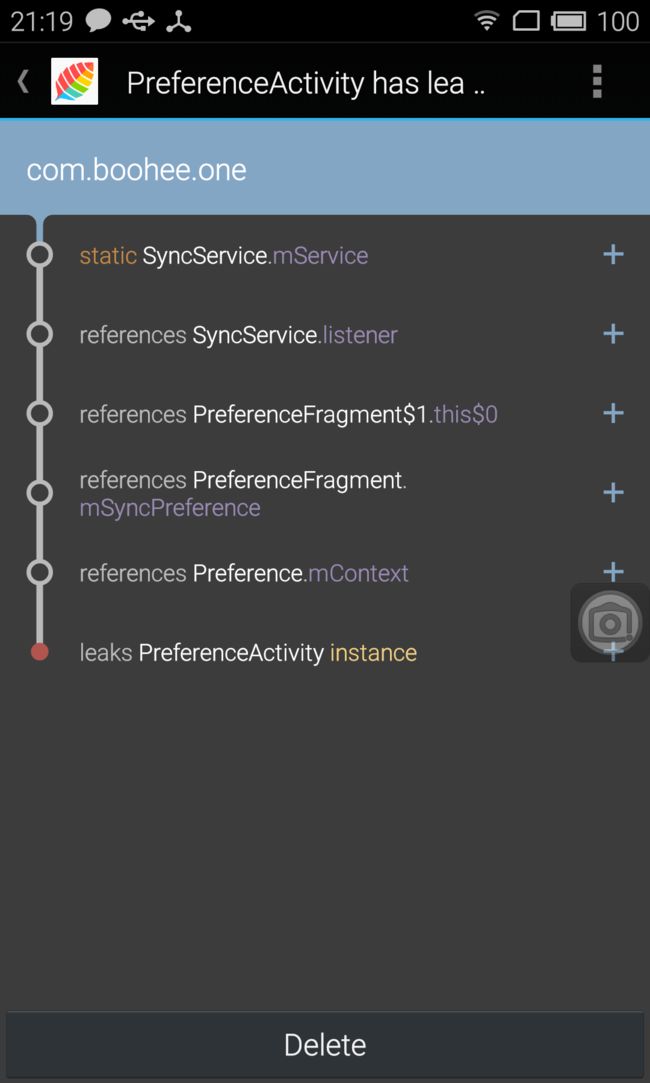
- 引用链传递到 APP 进程中的 DisplayLeakService, 并以通知的形式展示出来。
In com.example.leakcanary:1.0:1 com.example.leakcanary.MainActivity has leaked:
* GC ROOT thread java.lang.Thread. (named 'AsyncTask #1')
* references com.example.leakcanary.MainActivity$3.this$0 (anonymous class extends android.os.AsyncTask)
* leaks com.example.leakcanary.MainActivity instance
* Reference Key: e71f3bf5-d786-4145-8539-584afaecad1d
* Device: Genymotion generic Google Nexus 6 - 5.1.0 - API 22 - 1440x2560 vbox86p
* Android Version: 5.1 API: 22
* Durations: watch=5086ms, gc=110ms, heap dump=435ms, analysis=2086ms 但是有时这些log是不够的,找到内存泄露后,我们可以用MAT来分析内存泄露的原因,参考这篇文章
自定义
DisplayLeakActivity 有一个默认的图标和标签,你只要在你自己的 APP 资源中,替换以下资源就可。
res/
drawable-hdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-mdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-xhdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-xxhdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-xxxhdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
<resources>
<string name="__leak_canary_display_activity_label">MyLeaksstring>
resources>保存leak trace
在 APP 的目录中,DisplayLeakActivity 保存了 7 个 dump 文件和 leak trace。你可以在你的 APP 中,定义 R.integer.__leak_canary_max_stored_leaks 来覆盖类库的默认值。
<resources>
<integer name="__leak_canary_max_stored_leaks">20integer>
resources>总结
在项目中使用leakcanary可以极大的简化内存泄露分析的过程,并且最重要的可以提高程序的性能,避免OOM提高操作体验。
关于 Square
在开源世界里我们应该感谢那些为开源项目做出杰出贡献的个人和公司,而Square就是其中之一,Square已经将超过60多个项目提交到开源社区,贡献了25万行左右的代码。正是因为这样的公司个人,coder的世界正变的更美好。
android开源项目代表作:
- picasso 图片加载缓存库
A powerful image downloading and caching library for Android - okhttp 网络加载库
- An HTTP+SPDY client for Android and Java applications.
- retrofit 网络请求库
Type-safe REST client for Android and Java by Square, Inc. - otto android 事件总线 - EventBus模式的一个框架
An enhanced Guava-based event bus with emphasis on Android support. - dragger 依赖注入框架
A fast dependency injector for Android and Java. - android-times-square
Standalone Android widget for picking a single date from a calendar view. - spoon兼容性测试工具
Distributing instrumentation tests to all your Androids. - assertj-android 辅助测试库
A set of AssertJ helpers geared toward testing Android.
等等
参考
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/l-JavaMemoryLeak/
https://github.com/square/leakcanary
https://corner.squareup.com/2015/05/leak-canary.html
http://www.liaohuqiu.net/cn/posts/leak-canary-read-me/
http://www.liaohuqiu.net/cn/posts/leak-canary/
https://github.com/square
http://hukai.me/android-performance-memory/