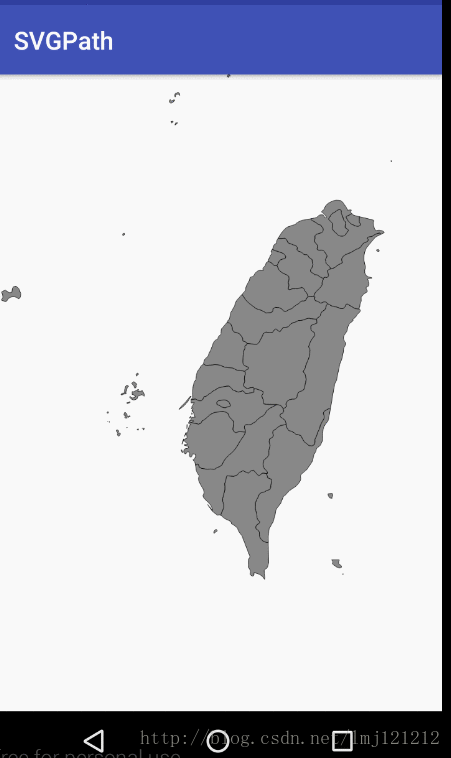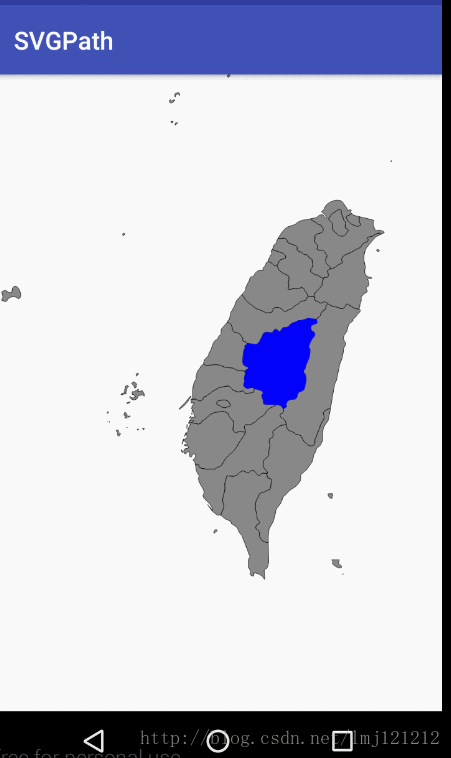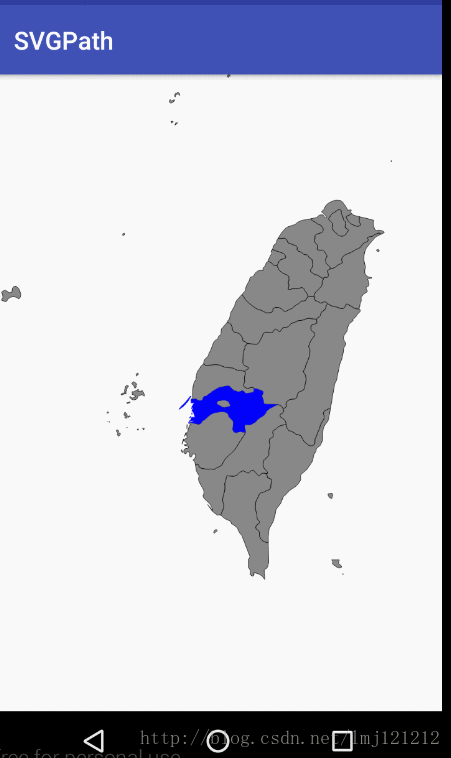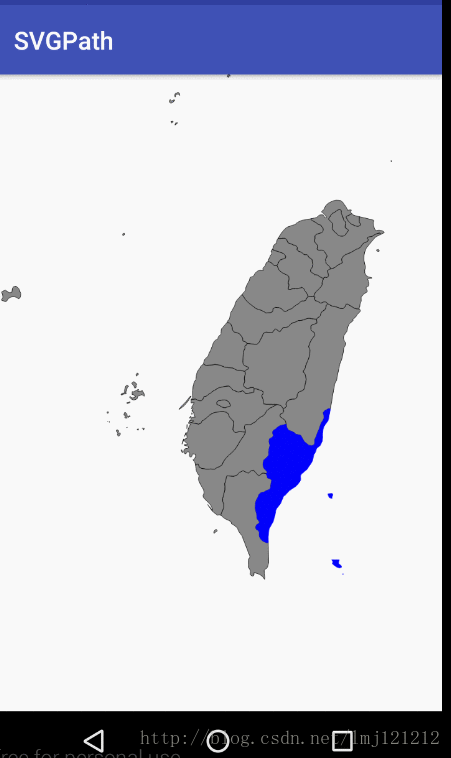
Region实战SVG地图点击
Region实战SVG地图点击
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj121212/article/details/72832087技术分析:
1、首先通过svg,画出图像,更加美工提供的svg文件,来到http://inloop.github.io/svg2android/
转出
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="-1dp"
android:height="-1dp"
android:viewportWidth="-1"
android:viewportHeight="-1">
<path
android:fillColor="#CCCCCC"
android:strokeColor="#ffffff"
android:strokeWidth="0.5"
android:pathData="M368.13,96.5L367.26,96.77L367.14,97.52L365.19,97.09L363.28,101.53L365.09,100.55L366.44,99.9L368,98.3L368.13,96.5zM358.84,95.81L360.35,94.95L358.2,93.84L355.43,94.81L357.25,97.52L358.84,95.81zM356.34,52.71L354.61,52.09L354.37,51.47L354.41,50.4L353.58,50.52L352.76,52.12L352.37,54.28L352.98,56.17L354.96,57.5L356.27,57.29L360.57,55.04L362.81,52.54L362.76,51.07L360.61,51.09L357.15,53.1L356.34,52.71zM373.11,38.78L372.64,38.12L371.96,37.71L370.92,36.15L368.96,35.86L367.23,36.92L366.67,37.62L364.62,38.29L363.73,38.84L363.33,40.1L362.98,43.46L363.35,44.68L364.2,45.22L365.16,41.25L366.32,39.96L367.33,39.69L368.1,40L369.95,39L370.82,39.59L371.96,41.25L372.97,42.13L373.04,41.44L372.64,40.53L372.94,39.74L373.11,38.78zM471.57,0L469.82,1.43L469.1,1.86L469.5,2.95L468.65,4.3L469.57,4.81L470.07,5.1L471.02,5.27L471.27,5.67L472.12,4.03L472.66,3.31L473.22,2.98L473.67,3.17L474.11,3.29L475,2.95L474.11,2.19L473.62,1.17L471.57,0z" />
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
拿到转出的文件,进行xml解析,得到path标签的pathData属性,(其实就是多条path)
Path指令解析如下所示:
M = moveto(M X,Y) :将画笔移动到指定的坐标位置,相当于 android Path 里的moveTo()
L = lineto(L X,Y) :画直线到指定的坐标位置,相当于 android Path 里的lineTo()
H = horizontal lineto(H X):画水平线到指定的X坐标位置
V = vertical lineto(V Y):画垂直线到指定的Y坐标位置
C = curveto(C X1,Y1,X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY):三次贝赛曲线
S = smooth curveto(S X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY) 同样三次贝塞尔曲线,更平滑
Q = quadratic Belzier curve(Q X,Y,ENDX,ENDY):二次贝赛曲线
T = smooth quadratic Belzier curveto(T ENDX,ENDY):映射 同样二次贝塞尔曲线,更平滑
A = elliptical Arc(A RX,RY,XROTATION,FLAG1,FLAG2,X,Y):弧线 ,相当于arcTo()
Z = closepath():关闭路径(会自动绘制链接起点和终点)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
利用工具类将pathData转成一个path对象,拿到path就可以直接绘制了。
public class TaiWanSVG extends View {
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
}
};
private List areaPathItemList = new ArrayList<>();
private AreaPathItem selectAreaPath;
private Paint paint;
private float Scale = 0.8f;
public TaiWanSVG(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public TaiWanSVG(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public void init() {
paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
//开启线程,读取svg中的pathdata数据
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream ips = getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.taiwan);
//解析器工厂
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//解析器对象
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
//解析xml文件
Document document = builder.parse(ips);
//得到所有path节点
NodeList nl = document.getElementsByTagName("path");
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
String pathData = ((Element) nl.item(i)).getAttribute("android:pathData");
areaPathItemList.add(new AreaPathItem(PathParser.createPathFromPathData(pathData)));
}
handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
super.draw(canvas);
if(null!=areaPathItemList&&areaPathItemList.size()>0){
canvas.scale(Scale,Scale);
for(AreaPathItem areaPathItem:areaPathItemList){
if(areaPathItem!=selectAreaPath){
areaPathItem.draw(canvas,paint,false);
}else{
}
}
if(selectAreaPath!=null){
selectAreaPath.draw(canvas,paint,true);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if(null!=areaPathItemList&&areaPathItemList.size()>0){
for(AreaPathItem areaPathItem:areaPathItemList){
if(areaPathItem.isContain(event.getX()/Scale,event.getY()/Scale)){
selectAreaPath = areaPathItem;
postInvalidate();
break;
}
}
}
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
2.通过Region判断点击的点,是否在path的区域中
要判断一个点是否在矩形范围很好判断,但是要判断一个点是否在一个不规则的范围中,则很难判断
Region这个类,可以将一个不规则的path,在一个矩形区域内,分割成很多个小的矩形区域,类似微积分,从而实现判断点是否包含在path,矩形区域是否包含或者相交于path等功能
/**
* Set the region to the area described by the path and clip.
* Return true if the resulting region is non-empty. This produces a region
* that is identical to the pixels that would be drawn by the path
* (with no antialiasing).
*/
public boolean setPath(Path path, Region clip) {
return nativeSetPath(mNativeRegion, path.readOnlyNI(), clip.mNativeRegion);
}
public class AreaPathItem {
private Path path;
public AreaPathItem(Path path) {
this.path = path;
}
public void draw(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, boolean isSelect) {
if (!isSelect) {
//绘制区域
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(Color.GRAY);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
//绘制区域边界
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
} else {
//绘制选中背景
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setShadowLayer(8,0,0,Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
paint.clearShadowLayer();
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
}
/**
* @param x
* @param y
* @return path区域是否包含 x,y坐标点
*/
public boolean isContain(float x, float y) {
RectF rectF = new RectF();
path.computeBounds(rectF,false);
Region region = new Region();
region.setPath(path,new Region((int)rectF.left,(int)rectF.top,(int)rectF.right,(int)rectF.bottom));
return region.contains((int)x,(int)y);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
源码下载