java实现串口通信
1.搭建串口通信开发环境
1.1. 下载串口通信支持库
下载javacomm20-win32.zip
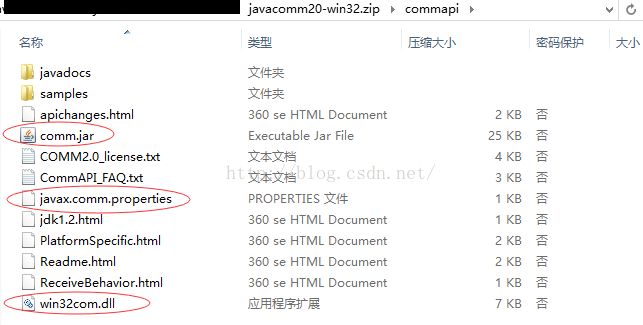
图1 javacomm20-win32目录结构图
打开图1中的Readme.html,进入Installation Instructions and Platform Specific notes 就可以看到环境的搭建方法,翻译过来如下:
a).复制win32com.dll 到
C:\>copyc:\commapi\win32com.dll to c:\jdk1.1.6\bin
b).复制comm.jar 到
C:\>copyc:\commapi\comm.jar c:\jdk1.1.6\lib
c).复制javax.comm.properties 到
C:\>copyc:\commapi\javax.comm.properties c:\jdk1.1.6\lib
d).其中b)的comm.jar可以选择直接复制到项目中,如果放入
C:\>setCLASSPATH=c:\jdk1.1.6\lib\comm.jar;%classpath%
(The javax.comm.properties file must be installed. If it is not, no portswill be found by the system.)
2.串口通信类编写
<下面的串口通信类可以直接copy到项目中使用>
【SerialIO.java】
public class SerialIO
{
private SerialPort serialPort = null; //串口对象
private InputStream is = null; //输入流
private OutputStream os = null; //输出流
private int datebits = DATABITS_8; //默认8位数据位
private int stopbits = STOPBITS_1; //默认1位停止位
private int parity = PARITY_NONE; //默认无校验位
public final static int DATABITS_5 = SerialPort.DATABITS_5;
public final static int DATABITS_6 = SerialPort.DATABITS_6;
public final static int DATABITS_7 = SerialPort.DATABITS_7;
public final static int DATABITS_8 = SerialPort.DATABITS_8;
public final static int STOPBITS_1 = SerialPort.STOPBITS_1;
public final static int STOPBITS_1_5 = SerialPort.STOPBITS_1_5;
public final static int STOPBITS_2 = SerialPort.STOPBITS_2;
public final static int PARITY_EVEN = SerialPort.PARITY_EVEN;
public final static int PARITY_MARK = SerialPort.PARITY_MARK;
public final static int PARITY_NONE = SerialPort.PARITY_NONE;
public final static int PARITY_ODD = SerialPort.PARITY_ODD;
public final static int PARITY_SPACE = SerialPort.PARITY_SPACE;
/**
* 设置数据位
* @param databits
* DATABITS_5
* DATABITS_6
* DATABITS_7
* DATABITS_8
*/
public void setDatabits(int databits)
{
this.datebits = databits;
}
/**
* 设置停止位
* @param stopbits
* STOPBITS_1
* STOPBITS_1_5
* STOPBITS_2
*/
public void setStopbits(int stopbits)
{
this.stopbits = stopbits;
}
/**
* 设置校验位
* @param parity
* PARITY_EVEN
* PARITY_MARK
* PARITY_NONE
* PARITY_ODD
* PARITY_SPACE
*/
public void setParity(int parity)
{
this.parity = parity;
}
/**
* 打开串口
* @param com 串口号
* @param baud 波特率
* @return
* true - 成功
* false - 失败
*/
public boolean open(int com, int baud)
{
if ( !isPortBaudSupported(baud) )
{
System.out.println("暂不支持的波特率");
return false;
}
try
{
CommPortIdentifier portId = CommPortIdentifier.getPortIdentifier("COM" + com);
serialPort = (SerialPort)portId.open("DeviceTestSystem", 0); //立即返回
serialPort.setSerialPortParams(baud, datebits, stopbits, parity);//设置串口波特率,数据位,停止位,校验位
is = serialPort.getInputStream();
os = serialPort.getOutputStream();
}
catch(NoSuchPortException nspe)
{
nspe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
catch(PortInUseException piue)
{
piue.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
catch(UnsupportedCommOperationException ucoe)
{
ucoe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 设置串口超时时间
* @param timeout 超时时间(秒),若为-1则永不超时
* @return
* true - 成功
* false - 失败
*/
public boolean setReceiveTimeout(int timeout)
{
if ( serialPort == null )
{
System.out.println("尚未初始化SerialPort");
return false;
}
try
{
if ( timeout < -1 )
{
return false;
}
else if ( timeout == -1 )
{
serialPort.disableReceiveTimeout();
}
else
{
serialPort.enableReceiveTimeout(1000*timeout);
}
}
catch(UnsupportedCommOperationException ucoe)
{
ucoe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 读数据
* @return 当前的字节,如果为-1,代表已读到末尾或者超时,如果为-2,代表读取异常
*/
public int read()
{
if ( is == null )
{
System.out.println("尚未初始化InputStream");
return -2;
}
try
{
return is.read();
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
return -2;
}
}
/**
* 读数据
* @param readByte 存放读取数据的字节数组
* @return 总共读取的字节数,如果为0,代表超时,如果为-1,代表已读到末尾,如果为-2,代表读取异常
*/
public int read(byte[] readByte)
{
if ( is == null )
{
System.out.println("尚未初始化InputStream");
return -2;
}
try
{
return is.read(readByte);
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
return -2;
}
}
/**
* 写数据
* @param writeByte 存放写入数据的字节数组
* @return
* true - 成功
* false - 失败
*/
public boolean write(byte[] writeByte)
{
if ( os == null )
{
System.out.println("尚未初始化OutputStream");
return false;
}
try
{
os.write(writeByte);
os.flush();
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 关闭串口
* @return
* true - 成功
* false - 失败
*/
public boolean close()
{
if ( serialPort != null )
{
if ( is != null )
{
try
{
is.close();
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
if ( os != null )
{
try
{
os.close();
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
serialPort.close();
serialPort = null;
return true;
}
return true;
}
/*
* 检查波特率是否支持
* @param portBaud 波特率
*/
private boolean isPortBaudSupported(int baud)
{
int[] supportedPortBaudList = {300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200}; //支持的波特率
for ( int i = 0; i < supportedPortBaudList.length; i++ )
{
if ( baud == supportedPortBaudList[i] )
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}3.串口通信类使用方法
SerialIO serialIO = new SerialIO();
【打开串口】
serialIo.open(com,baud); //根据需要传入相应的串口号和波特率
【像串口写数据】
serialIO.write(byteArray); //写入数据byte[]
【从串口读取数据】
serialIO.read(byteArrayPointer); //读取数据 byte[]
serialIO.read(); //读取数据 byte
【关闭串口】
serialIO.close(); //关闭串口