FF首次适应算法与BF最佳适应算法(C++实现)
【实验目的】
本实验主要练习主存的各种分配和回收。所谓分配,就是解决多道作业或多进程如何共享主存空间的问题。所谓回收,就是当作业运行完成时,将作业或进程所占用的主存空间归还给系统。主存的分配和回收的实现就是与主存储器的管理方式有关的。通过本实验理解在不同的存储管理方式下,如何实现主存空间的分配与回收。
【实验原理】
- 首次适应算法(First Fit)
该算法从空闲分区链首开始查找,直至找到一个能满足其大小要求的空闲分区为止。然后再按照作业的大小,从该分区中划出一块内存分配给请求者,余下的空闲分区仍留在空闲分区链中。
特点:该算法倾向于使用内存中低地址部分的空闲区,在高地址部分的空闲区很少被利用,从而保留了高地址部分的大空闲区。显然为以后到达的大作业分配大的内存空间创造了条件。
缺点:低地址部分不断被划分,留下许多难以利用、很小的空闲区,而每次查找又都从低地址部分开始,会增加查找的开销。 - 最佳适应算法(Best Fit)
该算法总是把既能满足要求,又是最小的空闲分区分配给作业。为了加速查找,该算法要求将所有的空闲区按其大小排序后,以递增顺序形成一个空白链。这样每次找到的第一个满足要求的空闲区,必然是最优的。孤立地看,该算法似乎是最优的,但事实上并不一定。因为每次分配后剩余的空间一定是最小的,在存储器中将留下许多难以利用的小空闲区。同时每次分配后必须重新排序,这也带来了一定的开销。
特点:每次分配给文件的都是最合适该文件大小的分区。
缺点:内存中留下许多难以利用的小的空闲区。
【实验内容】
采用可变式分区管理,使用首次或最佳适应算法实现主存的分配与回收。
1.数据结构与符号说明
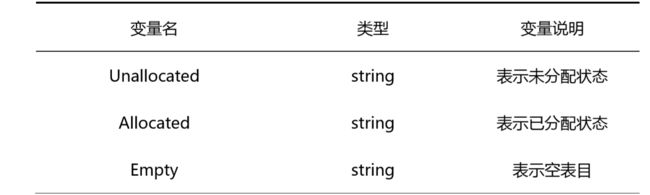
1.1全局变量
1.2 PST 类

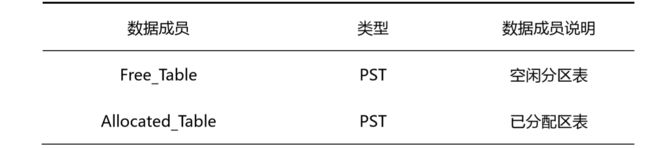
1.3 Memory 类
2. 程序流程图与源程序
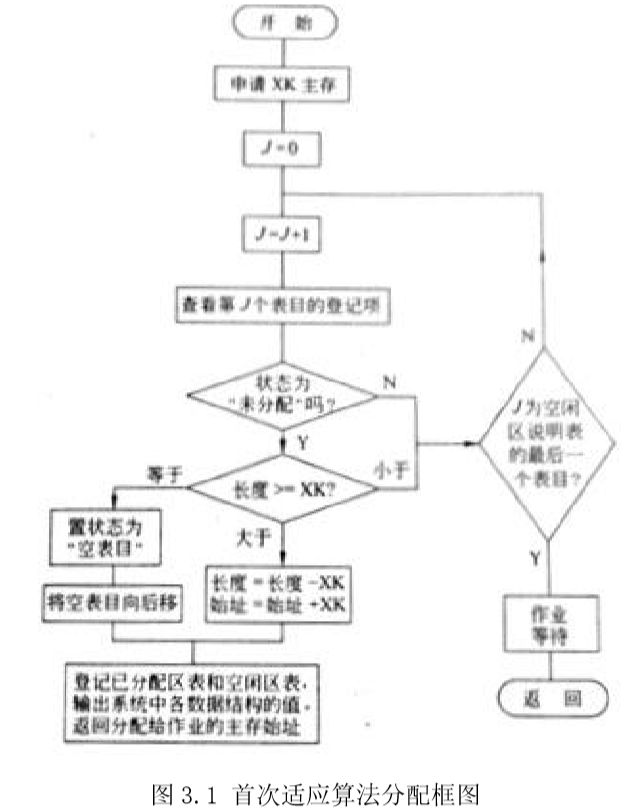
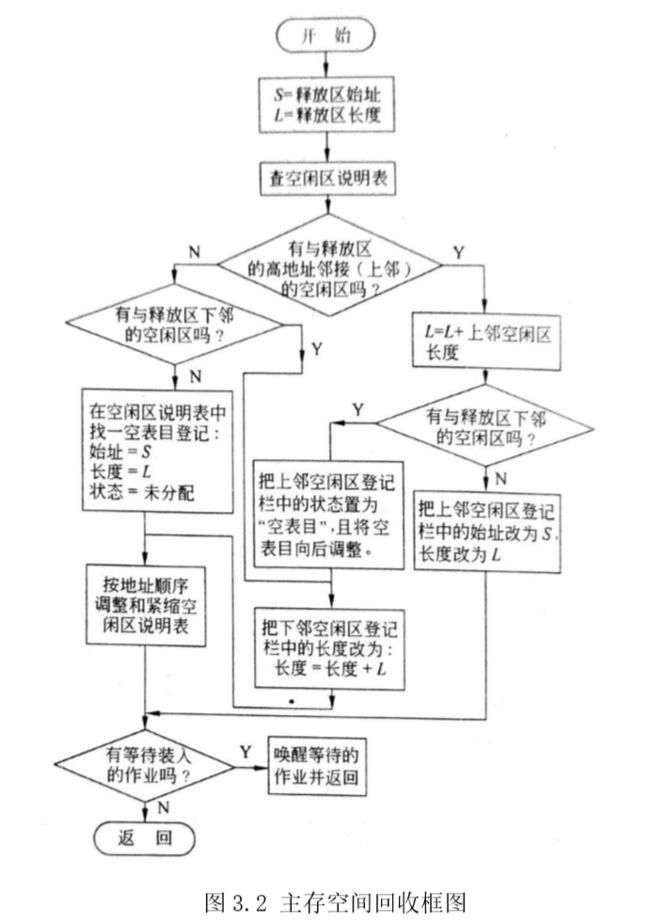
2.1 程序流程图
首次适应算法分配框图和首次适应算法回收框图分别如图3.1和图3.2所示,最佳适应算法则在首次适应算法基础上加上对内存按大小排序,流程图几乎一致,这里不再给出。
2.2 源程序
#include3. 运行结果
3.1 手动初始化主存
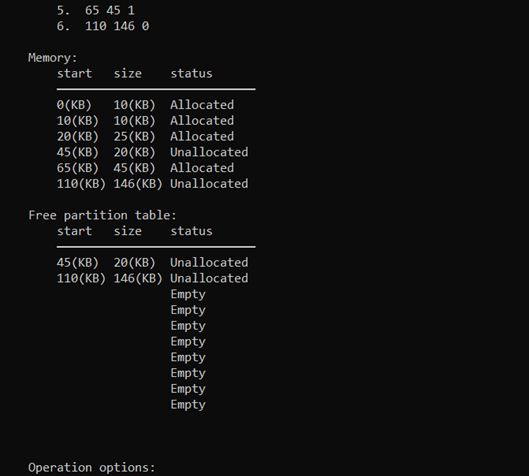
手动输入主存主存初始状态的分区数,这里输入的是6个;再手动输入每个分区的起始地址,长度,状态。

输入完毕,打印主存和空闲分区表:
3.2 首次适应算法
操作选择,输入1,为作业分配空间;这里输入作业大小为30(KB);算法选择,输入1,首次适应算法。

分配成功后的主存和空闲分区表:(从起始地址为110KB的分区分配了30KB给作业)

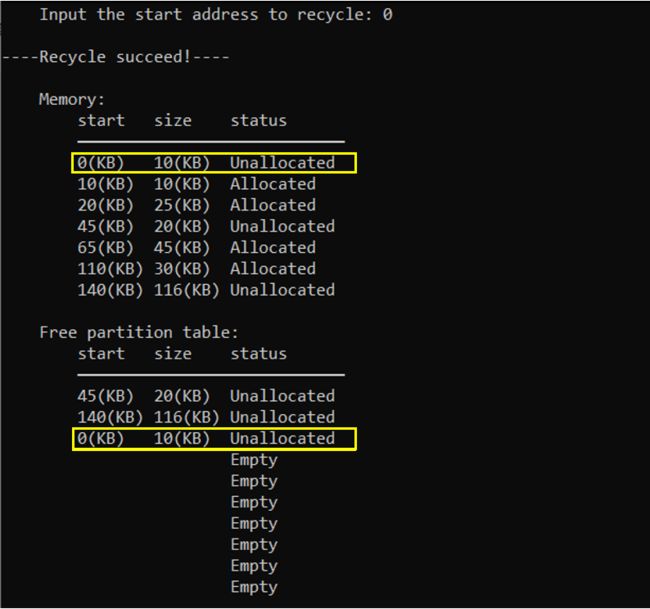
操作选择,输入2,回收作业空间;这里回收的空间起始地址为0KB;

成功回收地址为0KB的分区(低地址,高地址都不邻接,新的空闲分区加入表中):
3.3 最佳适应算法
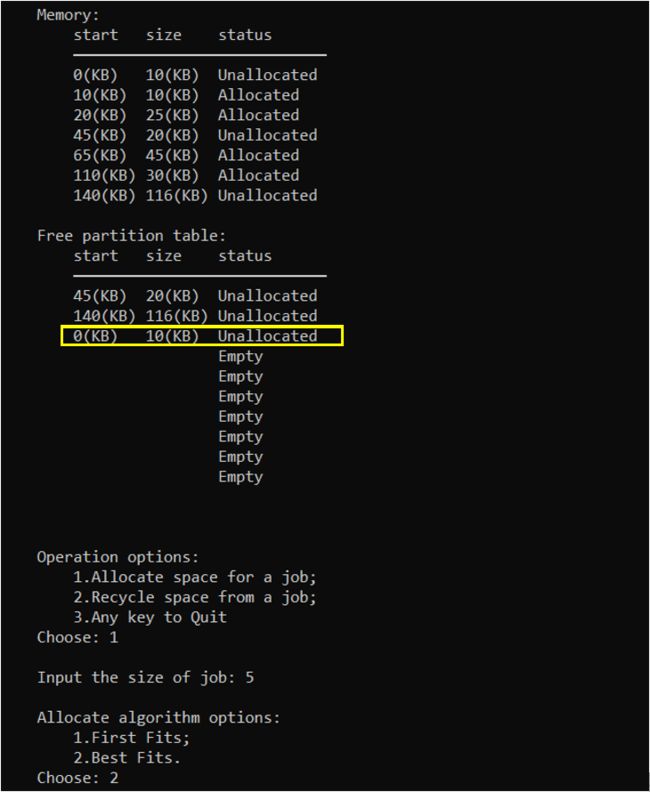
操作选择,输入1,为作业分配空间;这里输入作业大小为5(KB);算法选择,输入2,首次适应算法。
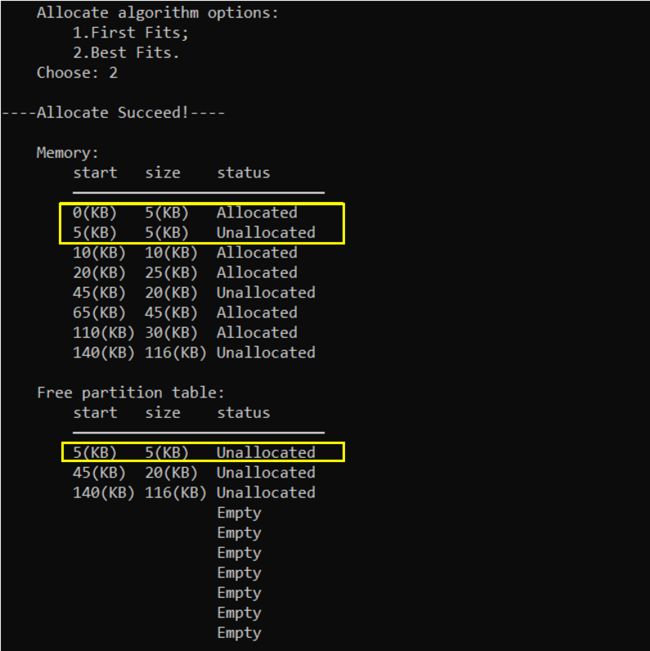
分配成功后的主存和空闲分区表:(从起始地址为0KB的分区分配了5KB给作业)
3.4 回收:逐个回收被分配出去的分区。
成功回收起始地址为0KB的分区(高地址邻接)
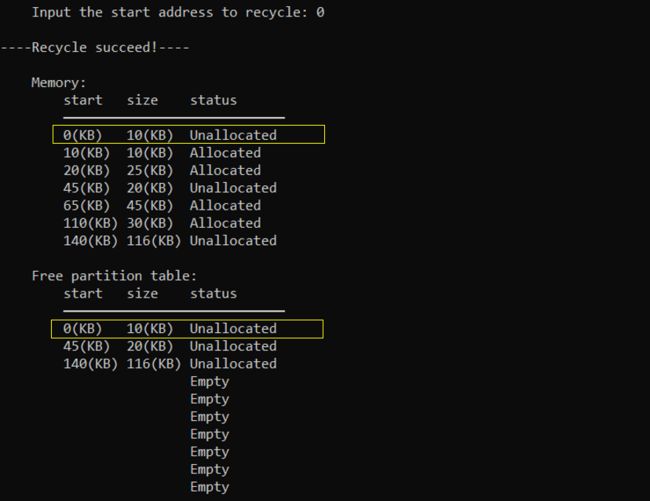
成功回收起始地址为10KB的分区(低地址邻接)
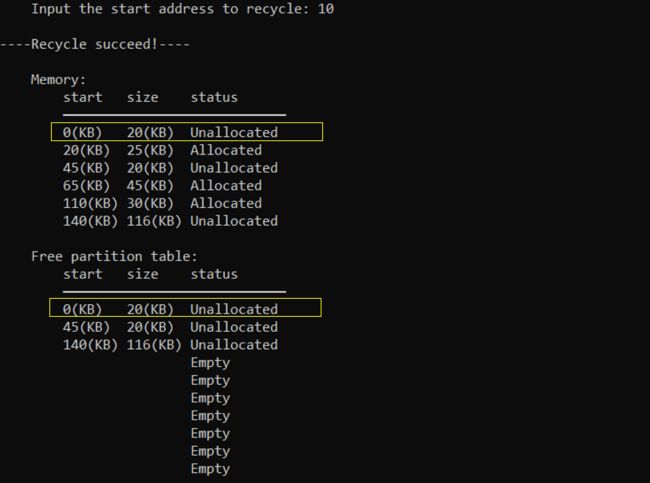
成功回收起始地址为110KB的分区(高地址邻接)
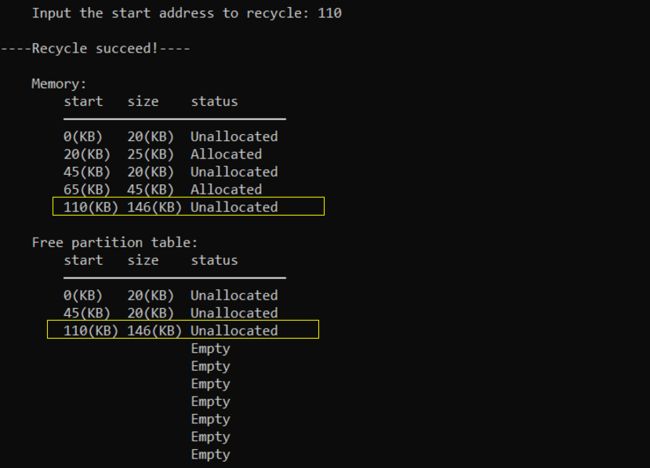
成功回收起始地址为20KB的分区(低地址、高地址都邻接)

成功回收起始地址为65KB的分区(低地址、高地址都邻接)
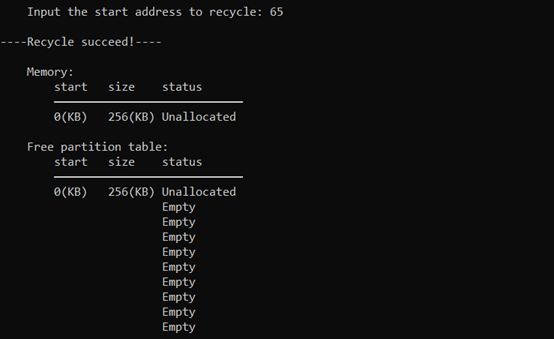
3.5 退出
【小结或讨论】
实验过程中,发现首次适应算法和最佳适应算法的流程中,唯一区别在于最佳适应算法在分配前将空闲分区表按升序排列(即先分配空间小的分区),所以将两个算法合并在同一个allocate()函数中,通过与用户交互来选择分配方法。