Mac开发-10.14获取文件操作权限-管理员权限获取
文章目录
- 使用NSAppleScript来操作
- 使用Security框架来获取权限
- ServiceManagement注册LaunchdDaemon
Mac os 10.14以及
Mac os 10.15之后,系统对部分文件夹下的操作权限判断更加严格,需要获得管理员权限,在输入命令行时,我们通常加上
sudo来进行获取权限,同时输入密码。在Mac os开发中,也面临这样的问题,就需要主动获取权限。
我的场景是做
MacOS的更新功能,需要替换
Application下的应用程序(先删除再移动新app到
Application目录)。在Mac os 10.14以上版本中,需要获得管理员权限。
使用NSAppleScript来操作
使用 NSTask 不能获取相关权限,所以使用NSAppleScript来进行权限获取的同时,执行脚本。
Boolean runProcessAsAdministrator( NSString *scriptPath, NSArray *arguments,BOOL isAdmin, NSString **output,NSString **errorDescription)
{
NSString * allArgs = [arguments componentsJoinedByString:@" "];
NSString *isAdminPre = @"";
if (isAdmin) {
isAdminPre = @"with administrator privileges";
}
NSString * fullScript = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", scriptPath, allArgs];
NSDictionary *errorInfo = [NSDictionary new];
NSString *script = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"do shell script \"%@\" %@", fullScript,isAdminPre];
NSLog(@"script = %@",script);
NSAppleScript *appleScript = [[NSAppleScript new] initWithSource:script];
NSAppleEventDescriptor * eventResult = [appleScript executeAndReturnError:&errorInfo];
// Check errorInfo/var/tmp
if (! eventResult)
{
// Describe common errors
*errorDescription = nil;
if ([errorInfo valueForKey:NSAppleScriptErrorNumber])
{
NSNumber * errorNumber = (NSNumber *)[errorInfo valueForKey:NSAppleScriptErrorNumber];
if ([errorNumber intValue] == -128)
*errorDescription = @"The administrator password is required to do this.";
}
// Set error message from provided message
if (*errorDescription == nil)
{
if ([errorInfo valueForKey:NSAppleScriptErrorMessage])
*errorDescription = (NSString *)[errorInfo valueForKey:NSAppleScriptErrorMessage];
}
return NO;
}
else
{
// Set output to the AppleScript's output
*output = [eventResult stringValue];
return YES;
}
}
runProcessAsAdministrator(脚本路径,参数数组,是否管理员权限运行,输出结果,错误描述)
使用方法
NSString *output = nil;
NSString *errorDescription = nil;
runProcessAsAdministrator(@"",@[@"/usr/bin/unzip",@"-u", @"-d",
unzipFolder, zipPath],YES,&output,&errorDescription);
值得注意的是需要自己判断是否没有权限,没有权限才传入YES,以管理员身份运行,并会要求用户输入用户密码。
使用Security框架来获取权限
Security.framework包含权限获取的功能,通过使用AuthorizationExecuteWithPrivileges函数来获取所需要的权限。
char * const GSFileOpRemoveCommand = "rm";
char * const GSFileOpMoveCommand = "mv";
//这里进行预授权,如果能获取权限,则进行下一步
- (BOOL)_acquireAuthorizationWithError:(NSError *__autoreleasing *)error {
NSLog(@"AuthHelperTool executing self-repair");
OSStatus myStatus;
myStatus = AuthorizationCreate(NULL, kAuthorizationEmptyEnvironment, kAuthorizationFlagDefaults, &_auth);
if (myStatus != errAuthorizationSuccess){
_auth = NULL;
NSLog(@"AuthHelperTool AuthorizationCreate failed");
return NO;
}
AuthorizationItem rightItems[] = {
// The right that allows us to run tools as root user
{.name = kAuthorizationRightExecute, .valueLength = 0, .value = NULL, .flags = 0}
};
AuthorizationRights rights = {
.count = sizeof(rightItems) / sizeof(*rightItems),
.items = rightItems
};
AuthorizationFlags flags =
(AuthorizationFlags)(kAuthorizationFlagDefaults | kAuthorizationFlagInteractionAllowed| kAuthorizationFlagExtendRights | kAuthorizationFlagPreAuthorize);
myStatus = AuthorizationCopyRights (_auth, &rights, kAuthorizationEmptyEnvironment, flags, NULL);
if (myStatus != errAuthorizationSuccess) {
AuthorizationFree(_auth, kAuthorizationFlagDefaults);
_auth = NULL;
NSLog(@"AuthHelperTool AuthorizationCopyRights failed");
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
//这里进行命令操作,同时进行授权
- (BOOL)_authorizeAndExecuteCommand:(char *)command sourcePath:(char *)sourcePath destinationPath:(char *)destinationPath error:(NSError * __autoreleasing *)error
{
NSError *acquireError = nil;
if (![self _acquireAuthorizationWithError:&acquireError]) {
if (error != NULL) {
*error = acquireError;
}
return NO;
}
char *arguments[] = { command, sourcePath, destinationPath, NULL };
char toolPath[PATH_MAX] = {0};
//这里由于是更新程序的授权,所以取的是系统缓存目录中的Unix可执行文件
NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *genseePath = [[paths objectAtIndex:0]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"gensee"];
NSString* updaterFolder = [genseePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"update"];
[[NSFileManager defaultManager]createDirectoryAtPath:updaterFolder withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:NULL error:NULL];
NSString* updaterPath =[updaterFolder stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Updater.app"];
NSString* bundleName = [[NSBundle mainBundle] objectForInfoDictionaryKey:@"CFBundleName"];
NSString* fileOperationToolPath =[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/Contents/MacOS/%@",updaterPath,bundleName];
//这里取到需要获取权限的Unix执行文件程序路径
NSLog(@"fileOperationToolPath (%@) ",fileOperationToolPath);
if (![fileOperationToolPath getFileSystemRepresentation:toolPath maxLength:sizeof(toolPath)]) {
NSLog(@"File to author folder permission (%@) cannot be represented as a valid file name.",fileOperationToolPath);
return NO;
}
FILE *pipe = NULL;
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
//这里值得注意的就是第二个参数是可执行文件路径,就是需要获取权限的程序路径,例如Test.app,则是Test.app/Content/MacOS/Test执行文件
OSStatus runStatus = AuthorizationExecuteWithPrivileges(_auth, toolPath, kAuthorizationFlagDefaults, arguments, &pipe);
if (runStatus != errAuthorizationSuccess) {
NSLog(@"AuthorizationExecuteWithPrivileges not success");
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
正常使用中我们需要先使用NSFileManager进行删除和移动操作,当获取的错误码为
NSFileReadNoPermissionError和NSFileWriteNoPermissionError时,就进行权限获取逻辑
#define NS_HAS_PERMISSION_ERROR(error) (error.code == NSFileReadNoPermissionError || error.code == NSFileWriteNoPermissionError)
例如如下:
sself是因为我在子线程中执行的,使用了GCD的block块
NSError* error;
if ([[NSFileManager defaultManager]fileExistsAtPath:applicationPath]){
BOOL result = [[NSFileManager defaultManager]removeItemAtPath:applicationPath error:&error];
if (!result) {
NSLog(@"[Appdelegate] removeItemAtPath : %@ error : %@",applicationPath,error.description);
if(NS_HAS_PERMISSION_ERROR(error)){
char rmPath[PATH_MAX] = {0};
if (![applicationPath getFileSystemRepresentation:rmPath maxLength:sizeof(rmPath)]) {
NSLog(@"File to remove (%@) cannot be represented as a valid file name.", applicationPath.lastPathComponent);
return;
}
// rm
NSError *executeError = nil;
BOOL success = [sself _authorizeAndExecuteCommand:GSFileOpRemoveCommand sourcePath:rmPath destinationPath:NULL error:&executeError];
if (!success) {
NSLog(@"File to remove (%@) _authorizeAndExecuteCommand", applicationPath.lastPathComponent);
// return;
}
}
}
}
BOOL result = [[NSFileManager defaultManager] moveItemAtPath:unzipPath toPath:applicationPath error:&error];
if (!result) {
NSLog(@"[Appdelegate] moveItemAtPath : %@ to %@ error : %@",unzipPath,applicationPath,error.description);
if (NS_HAS_PERMISSION_ERROR(error)) {
//do new version handler
if ([[NSFileManager defaultManager]fileExistsAtPath:applicationPath]){
}
//mv
char sourcePath[PATH_MAX] = {0};
if (![unzipPath getFileSystemRepresentation:sourcePath maxLength:sizeof(sourcePath)]) {
NSLog(@"File to move (%@) cannot be represented as a valid file name.", applicationPath.lastPathComponent);
return;
}
char destinationPath[PATH_MAX] = {0};
if (![applicationPath getFileSystemRepresentation:destinationPath maxLength:sizeof(destinationPath)]) {
NSLog(@"File to remove (%@) cannot be represented as a valid file name.", applicationPath.stringByDeletingLastPathComponent);
return;
}
NSError *executeError = nil;
BOOL success = [sself _authorizeAndExecuteCommand:GSFileOpMoveCommand sourcePath:sourcePath destinationPath:destinationPath error:&executeError];
if (!success) {
NSLog(@"File to move (%@) sourcPath %s destinationPath %s", applicationPath.lastPathComponent,sourcePath,destinationPath);
// return;
}
}
}
ServiceManagement注册LaunchdDaemon
细心的小伙伴可能已经发现AuthorizationExecuteWithPrivileges已经废除,苹果推荐另一种新的权限获取方式。
大概就是将你的app需要root权限的操作独立到另一个helper tool中,通过给与这个helper tool高级权限,来完成你的操作。这样你的app也不会在高权限下运行,且权限获取只需要一次。
ServiceManagement是在10.6就出现的framework,下面就具体介绍一下如何使用相关的API来注册高权限的LaunchdDaemon。
即使用 SMJobBless 方法,这里贴出 官方文档Demo
使用这个需要如下几点需求:
- 调用应用程序和目标可执行工具都必须签名。
- App中的plist必须包含
SMPrivilegedExecutables字符串字典。key必须全局唯一
<key>SMPrivilegedExecutables</key>
<dict>
<key>com.apple.bsd.SMJobBlessHelper</key>
<string>anchor apple generic and identifier "com.apple.bsd.SMJobBlessHelper" and (certificate leaf[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.1.9] /* exists */ or certificate 1[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.2.6] /* exists */ and certificate leaf[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.1.13] /* exists */ and certificate leaf[subject.OU] = xxxxxxxxxx)</string>
</dict>
如图,在主app的plist文件中
![]()
3. helper tool必须plist文件必须包含"SMAuthorizedClients"的字符数组,来表示用于标识可加载或卸载它的主程序。
即在helper tool的plist文件中

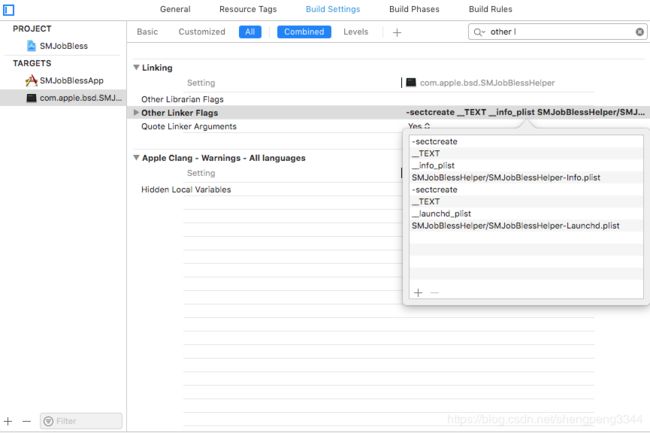
4. helper tool还需要一个launchd plist文件,这个plist文件仅包含一个Label key,和使用 launchctl工具加载plist文件 不同,这里不需要指定Program or ProgramArguments,这个plist必须嵌入到二进制文件的_ text,_ launchd_plist部分。
在helper toolplist文件中
-sectcreate __TEXT __info_plist SMJobHelper/SMJobHelper-Info.plist
-sectcreate __TEXT __launchd_plist SMJobHelper/SMJobHelper-Launchd.plist
5.helper tool必须驻留在应用程序包内的Contents/Library/LaunchServices目录中,其名称必须是其SMPrivilegedExecutables中设置的label,即com.apple.bsd.SMJobBlessHelper。