一个文件实现横向纵向拉拽刷新
今天分享一个非常轻量级的拉拽刷新控件,源码已上传到github:
https://github.com/huzenan/EasyPullLayout
再老的司机也难免遇到这样的场景,产品跑过来大声对我说:首页要加刷新,下拉刷新非侵入式,上拉加载为侵入式,头部轮播图片最左边向右继续拖拽进入xx页,最右边向左继续拖拽进入xx页!噢,xx页再加一个从中间下拉刷新吧!噢,设计已经出好了刷新的动画和规范,照着做就好了。
(╯‵□′)╯︵┻━┻ 顿时有了掀桌子的小心情,怎么办,写一个统一的刷新的库?太重了而且方法数爆了怎么办?
然而,现在我有了EasyPullLayout,你想加什么随便加就是了,上拉、下拉、左拉、右拉,任何姿势我都能给,整个控件只有一个文件,不到500行代码,支持横向纵向,侵入非侵入,自定义拉拽行为以及刷新内容,ListView、RecyclerView、ViewPager等等什么内容都能包裹进来,再也不用导入这样那样的库来支持各种各样的刷新了。
看看效果
纵向
横向
一共5个demo,其余的都传了效果图到github上,其中变形金刚动画用到了我写的另一个轻量级的控件EasyPath,使用方法很简单,传送门:
https://github.com/huzenan/EasyPath
用法
1.布局
接着在布局文件中,在需要刷新的地方用EasyPullLayout包裹起来(例如根布局),并为EasyPullLayout下的子View声明layout_type属性,使得子View可以被EasyPullLayout识别,分别可以为content(必选)、edge_top、edge_bottom、edge_left和edge_right:
<com.hzn.lib.EasyPullLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/epl"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<com.hzn.easypulllayout.TransformerView
android:id="@+id/topView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_type="edge_top" />
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_type="content"
tools:listitem="@layout/item"
/>
com.hzn.lib.EasyPullLayout>因为layout_type属性是EasyPullLayout提供的,所以不要忘记加入自定义的命名空间(如上为app)。
上面我们的边缘视图(TransformerView)是自定义的一个视图,我们可以通过EasyPullLayout提供的接口来动态改变它的行为。
EasyPullLayout本身也提供属性可选,用于控制拉拽行为和距离等,详细可以参考github中的“属性”一栏。
2.监听
EasyPullLayout的设计遵从单一职责原则,只负责处理拉拽相关的操作,其他的均交给外部进行处理,因此其子View可以是任何一种View,这有点类似于RecyclerView只负责使用和回收操作。
EasyPullLayout有3个监听可以设置,分别为:
OnEdgeListener:
可选,用于通知EasyPullLayout当前是否到达边缘,到达边缘后EasyPullLayout会拦截触摸事件,开始拉拽行为,默认会自动监听layout_type为content的子View是否到达边缘。
OnPullListener:
可选,用于EasyPullLatout向外通知当前拉拽的一些参数(例如拉拽进度),我们可以利用这些参数来改变我们的边缘视图的行为,例如调整变形金刚矢量动画当前的执行位置。
OnTriggerListener:
必选,用于EasyPullLayout在触发边缘动作后向外通知,此时EasyPullLayout会一直停留在STATE_TRIGGERING(触发中)的状态,我们做一些耗时操作后,需要调用stop方法让其回到STATE_IDLE(闲置)状态,这样才完成整个过程。
原理
在看了安卓的SwipeRefreshLayout,以及一些开源的刷新库的源码后,有了一些思路,总结起来,控件主要处理的问题有:
1、为EasyPullLayout的子View提供layout_type属性
2、如何摆放子View
3、在什么时机进行拉拽(即处理事件分发)
处理了这3个问题后,剩下的例如拉拽过程,以及触发事件都很好实现了。
1.提供layout_type属性
EasyPullLayout需要辨别子View的类型,因此需要子View声明自己的类型,我们在ViewGroup的generateLayoutParams方法中,返回我们自己的LayoutParams:
// 返回LayoutParmas
override fun generateLayoutParams(attrs: AttributeSet?): ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
return LayoutParams(context, attrs)
}
// 自定义LayoutParams
class LayoutParams : ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
// layout_type默认为NONE
var type = TYPE_NONE
constructor(c: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : super(c, attrs) {
//...
// 在构造函数中,获取layout_type属性,存储起来
type = it?.getInt(R.styleable.EasyPullLayout_LayoutParams_layout_type, TYPE_NONE)
//...
}
constructor(width: Int, height: Int) : super(width, height)
constructor(source: MarginLayoutParams?) : super(source)
constructor(source: ViewGroup.LayoutParams?) : super(source)
}这样我们便可以通过子View的LayoutParams对象获取到这个type值。
2.如何摆放子View
EasyPullLayout继承自ViewGroup,在完成xml解析后,即onFinishInflate方法中,获取到子View后用一个HashMap来存储,key对应View,value对应View的一些参数,接着再设置默认的OnEdgeListener:
override fun onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate()
// 遍历子View
var i = 0
while (i < childCount) {
getChildAt(i++).let {
val lp = it.layoutParams as LayoutParams
childViews.getByType(lp.type)?.let {
throw Exception("Each child type can only be defined once!")
} ?: childViews.put(it, ChildViewAttr()) // 存储子View
}
}
// 确保有一个子View的layout_type为content
val contentView = childViews.getByType(TYPE_CONTENT) ?:
throw Exception("Child type \"content\" must be defined!")
// 设置默认的OnEdgeListener,可以被覆盖
setOnEdgeListener {
// 若存在左侧的边缘视图
childViews.getByType(TYPE_EDGE_LEFT)?.let {
// 此时判断content是否能向左滚动
if (!contentView.canScrollHorizontally(-1))
// 若已经不能滚动,则返回TYPE_EDGE_LEFT表示已经到达了左侧边缘
return@setOnEdgeListener TYPE_EDGE_LEFT
}
// 其余3个方向实现方法也一样
// 若都不满足,则说明没有到达边缘,返回NONE
TYPE_NONE
}
}然后做测量,遍历子View,对每个子View进行测量,然后记录下边缘视图的一些参数,以及根据这些参数初始化EasyPullLayout自身的一些参数:
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
// 遍历子View
for ((childView, childViewAttr) in childViews) {
// 要求该子View进行测量
measureChildWithMargins(childView,
widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0)
// 得到子View的LayoutParams对象
val lp = childView.layoutParams as LayoutParams
when (lp.type) {
// 类型为横向的子View
TYPE_EDGE_LEFT, TYPE_EDGE_RIGHT -> {
// 把子View的size值记录下来,在摆放子View时会用到
// 横向size对应为宽度加左右margin
// 纵向size对应为高度加上下margin
childViewAttr.size =
childView.measuredWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
// 初始化EasyPullLayout的属性,例如拖拽距离等
}
// 纵向的实现方式也一样
}
}
}然后开始摆放,根据测量时记录的参数,我们将边缘视图分别摆放到四周:
override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, l: Int, t: Int, r: Int, b: Int) {
// 首先获取content,得到宽高用于给其他子View做参考
val contentView = childViews.getByType(TYPE_CONTENT)
val contentWidth = contentView?.measuredWidth
?: throw Exception("子View必须包含一个content")
val contentHeight = contentView.measuredHeight
for ((childView, childViewAttr) in childViews) {
// 首先计算出子View的位置
// 此时还未进行偏移,左上角都位于(0,0)
val lp = childView.layoutParams as LayoutParams
var left: Int = paddingLeft + lp.leftMargin
var top: Int = paddingTop + lp.topMargin
var right: Int = left + childView.measuredWidth
var bottom: Int = top + childView.measuredHeight
when (lp.type) {
TYPE_EDGE_LEFT -> {
// 左侧的子View应该向左偏移,摆放在左侧
left -= childViewAttr.size
right -= childViewAttr.size
}
// 其他3个方向的实现方式也一样
}
childViewAttr.set(left, top, right, bottom) // child views' initial location
childView.layout(left, top, right, bottom)
}
// 若设置了左侧拖拽时固定
if (fixed_content_left)
// 改变左侧边缘视图z-order,使其在顶部
childViews.getByType(TYPE_EDGE_LEFT)?.bringToFront()
}可以看到最后我们还把子View的当前摆放位置记录下来,因为EasyPullLayout是通过改变View的x和y属性来达到位移效果的, 因此需要参考子View的初始位置。另外这样做的好处是,我们可以不通过onLayout来重置位置,避免回调onLayout。
3.处理事件分发
首先要在onInterceptTouchEvent中适当地对事件进行拦截,在ACTION_MOVE事件中回调了OnEdgeListener,这样就把是否进行拦截的判断操作交给了外部进行处理,只要返回正确的类型,则开始对触摸事件进行拦截:
override fun onInterceptTouchEvent(ev: MotionEvent?): Boolean {
// 不为闲置状态时不处理触摸事件
if (currentState != STATE_IDLE)
return false
when (ev?.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
// 记录按下位置
downX = ev.x
downY = ev.y
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
// 回调OnEdgeListener,得到type值
val type = onEdgeListener.invoke()
currentType = type
val dx = ev.x - downX
val dy = ev.y - downY
return when (type) {
// 边缘监听返回的是左侧,若向右拉拽且横向比纵向偏移大
// 则返回值为true,表示开始拦截触摸事件
TYPE_EDGE_LEFT -> ev.x > downX && Math.abs(dx) > Math.abs(dy)
// 另外3个方向处理规则相同
TYPE_NONE -> false
else -> false
}
}
}
return false
}拦截了触摸事件后,开始进行拉拽操作,在onTouchEvent中,ACTION_MOVE事件对必要的子View进行偏移(设置了对应的fixed选项后,content不会进行偏移,达到侵入式效果),ACTION_CANCEL、ACTION_UP事件则将子View位置还原:
override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent?): Boolean {
// 不为闲置状态时不处理触摸事件
if (currentState != STATE_IDLE)
return false
when (event?.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
val x = event.x
val y = event.y
// 当前偏移值,sticky_factor参数使得拖拽时有黏着效果
offsetX = (x - downX) * (1 - sticky_factor * 0.75f)
offsetY = (y - downY) * (1 - sticky_factor * 0.75f)
var pullFraction = 0f
when (currentType) {
TYPE_EDGE_LEFT -> {
// 限制offsetX的最小和最大值
offsetX = "..."
// 计算出当前拖拽进度,未拖拽时为0,到达触发位置时为1
pullFraction = "..."
}
}
// 是否经过触发位置,使用该参数可以只在经过触发位置时进行更新
val changed =
!(lastPullFraction < 1f && pullFraction < 1f ||
lastPullFraction == 1f && pullFraction == 1f)
// 回调OnPullListener
onPullListener?.invoke(currentType, pullFraction, changed)
lastPullFraction = pullFraction
when (currentType) {
TYPE_EDGE_LEFT ->
for ((childView, childViewAttr) in childViews)
if ("如果设置了对应的fixed,且为content,则不偏移")
// 子View偏移
childView.x = childViewAttr.left + offsetX
// 其他3个方向规则相同
}
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL, MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> {
currentState = STATE_ROLLING
// 松开手指,还原子View位置
when (currentType) {
TYPE_EDGE_LEFT, TYPE_EDGE_RIGHT -> rollBackHorizontal()
TYPE_EDGE_TOP, TYPE_EDGE_BOTTOM -> rollBackVertical()
}
}
}
return true
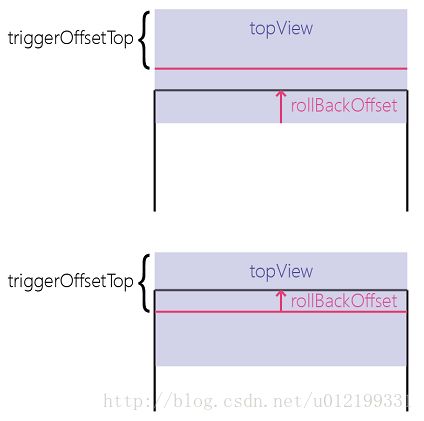
}还原子View位置时,我们通过ValueAnimator,在一段时间内将子View还原,还原后的位置分2种情况,第一种还没超过触发偏移量,则还原回到初始位置,第二种已经超过了触发偏移量,则回到触发偏移量的位置,看图比较直观:
rollback分为横向和纵向,下面贴出横向的大致的流程:
private fun rollBackHorizontal() {
// 需要还原的偏移量
val rollBackOffset = "..."
// 触发位置的偏移量
val triggerOffset = "..."
// 动画,值从1->0
horizontalAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1f, 0f).apply {
duration = roll_back_duration
interpolator = DecelerateInterpolator()
// 动画更新
addUpdateListener {
//...
for ((childView, childViewAttr) in childViews)
// 通过rollBackOffset和triggerOffset,以及animatedValue计算得出x
childView.x = "..."
}
// 动画结束后,还原一些参数,回调监听
addListener(object : AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
override fun onAnimationEnd(animation: Animator?) {
if (triggerOffset != 0 && currentState == STATE_ROLLING) {
// 还原到触发位置
currentState = STATE_TRIGGERING
offsetX = triggerOffset.toFloat()
// 回调触发监听
onTriggerListener?.invoke(currentType)
} else {
// 还原到初始位置
currentState = STATE_IDLE
offsetX = 0f
}
}
})
start()
}
}最后
因为是Kotlin写的库,所以没有使用kotlin的项目,通过直接gradle直接导入后是看不到源码的,不过不要慌,已经写了一个简单的java版本demo(下面有地址),可以直接用。嗯,随便用,稳稳的。写了好长,逻辑也是已经凌乱了,感谢大伙的围观,谢谢了!
https://github.com/huzenan/EasyPullLayoutJavaDemo