LeakCanary-源码篇
本篇主要介绍LeakCanary的执行流程,一些具体代码不做详解。
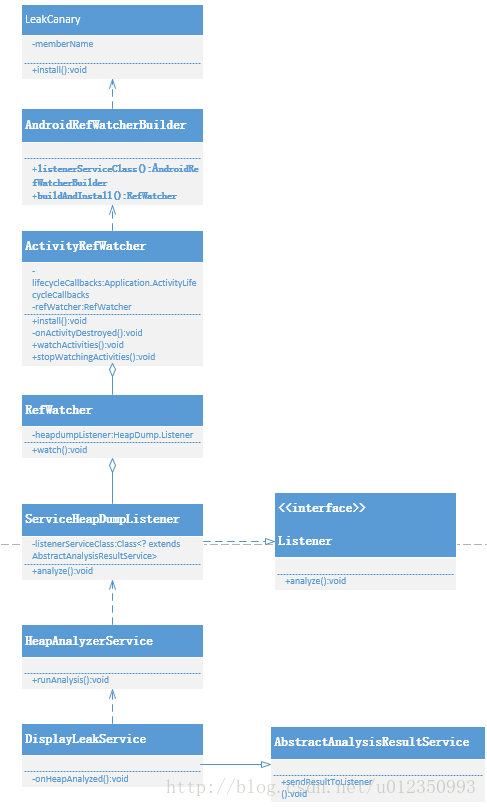
1. LeakCanary涉及类图关系解析
2. LeakCanary执行序列图解析
![]()
注:图片出自https://www.jianshu.com/p/0049e9b344b0
3. LeakCanary执行流程解析
/**
*所属类:ExampleApplication.java
*/
protected void setupLeakCanary() {
if (LeakCanary.isInAnalyzerProcess(this)) {
// This process is dedicated to LeakCanary for heap analysis.
// You should not init your app in this process.
return;
}
enabledStrictMode();
LeakCanary.install(this);
}安装LeakCanary前先判断当前进程是否是HeapAnalyzerService所在的远程分析进程,如果是分析进程就直接返回,否则调用LeakCanary的install()方法,该方法就是入口。
/**
* Creates a {@link RefWatcher} that works out of the box, and starts watching activity
* references (on ICS+).
* 所属类:LeakCanary.java
*/
public static RefWatcher install(Application application) {
return refWatcher(application).listenerServiceClass(DisplayLeakService.class)
.excludedRefs(AndroidExcludedRefs.createAppDefaults().build())
.buildAndInstall();
}创建一个RefWatcher,开始监听activity引用,注:如果需要监听fragment,需要手动进行监听。refWatcher(application)方法返回AndroidRefWatcherBuilder对象,listenerServiceClass(DisplayLeakService.class)对解析结果做回调监听此处为display service,excludedRefs(AndroidExcludedRefs.createAppDefaults().build())设置需要过滤的内存泄露,一般为已知的sdk内存泄露以及第三方库内存泄露。然后调用buildAndInstall()。
/**
* Creates a {@link RefWatcher} instance and starts watching activity references (on ICS+).
* 所属类:AndroidRefWatcherBuilder.java
*/
public RefWatcher buildAndInstall() {
RefWatcher refWatcher = build();
if (refWatcher != DISABLED) {
LeakCanary.enableDisplayLeakActivity(context);
ActivityRefWatcher.install((Application) context, refWatcher);
}
return refWatcher;
}builid调用父类方法创建RefWatcher, 然后调用ActivityRefWatcher.install((Application) context, refWatcher);开始监控activity。首先,看下父类build()方法:
/**
*Creates a {@link RefWatcher}.
* 所属类:RefWatcherBuilder.java
*/
public final RefWatcher build() {
if (isDisabled()) {
return RefWatcher.DISABLED;
}
ExcludedRefs excludedRefs = this.excludedRefs;
if (excludedRefs == null) {
excludedRefs = defaultExcludedRefs();
}
HeapDump.Listener heapDumpListener = this.heapDumpListener;
if (heapDumpListener == null) {
heapDumpListener = defaultHeapDumpListener();
}
DebuggerControl debuggerControl = this.debuggerControl;
if (debuggerControl == null) {
debuggerControl = defaultDebuggerControl();
}
HeapDumper heapDumper = this.heapDumper;
if (heapDumper == null) {
heapDumper = defaultHeapDumper();
}
WatchExecutor watchExecutor = this.watchExecutor;
if (watchExecutor == null) {
watchExecutor = defaultWatchExecutor();
}
GcTrigger gcTrigger = this.gcTrigger;
if (gcTrigger == null) {
gcTrigger = defaultGcTrigger();
}
return new RefWatcher(watchExecutor, debuggerControl, gcTrigger, heapDumper, heapDumpListener,
excludedRefs);
}调用子类AndroidRefWatcherBuilder.java方法defaultHeapDumpListener(),创建ServiceHeapDumpListener赋值heapDumpListener(ServiceHeapDumpListener用于回调HeapAnalyzerService进行解析.hprof源文件),进行defaultHeapDumper()创建AndroidHeapDumper赋值heapDumper(AndroidHeapDumper用于dump .hprof源文件),初始化各个参数之后创建RefWatcher。回头看下ActivityRefWatcher.install((Application) context, refWatcher);
/**
* 所属类:ActivityRefWatcher.java
*/
public static void install(Application application, RefWatcher refWatcher) {
new ActivityRefWatcher(application, refWatcher).watchActivities();
}开始监控activity,具体看下watchActivities()实现。
/**
* 所属类:ActivityRefWatcher.java
*/
public void watchActivities() {
// Make sure you don't get installed twice.
stopWatchingActivities();
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(lifecycleCallbacks);
}注册application回调,具体看下lifecycleCallbacks,
/**
* 所属类:ActivityRefWatcher.java
*/
private final Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks lifecycleCallbacks =
new Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override public void onActivityCreated(Activity activity, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
}
@Override public void onActivityStarted(Activity activity) {
}
@Override public void onActivityResumed(Activity activity) {
}
@Override public void onActivityPaused(Activity activity) {
}
@Override public void onActivityStopped(Activity activity) {
}
@Override public void onActivitySaveInstanceState(Activity activity, Bundle outState) {
}
@Override public void onActivityDestroyed(Activity activity) {
ActivityRefWatcher.this.onActivityDestroyed(activity);
}
};再看下ActivityRefWatcher.this.onActivityDestroyed(activity);具体实现,
/**
* 所属类:ActivityRefWatcher.java
*/
void onActivityDestroyed(Activity activity) {
refWatcher.watch(activity);
}这里自动对activity做了监控,所以为什么我们不用手动监控activity,而要手动监控fragment的原因就是这个了。下面我们看下refWatcher是如何实现对引用对象进行监听判断是否是内存泄露的,跟进去看下具体实现代码。
/**
* Watches the provided references and checks if it can be GCed. This method is non blocking,
* the check is done on the {@link WatchExecutor} this {@link RefWatcher} has been constructed
* with.
*
* @param referenceName An logical identifier for the watched object.
* 所属类:RefWatcher.java
*/
public void watch(Object watchedReference, String referenceName) {
if (this == DISABLED) {
return;
}
checkNotNull(watchedReference, "watchedReference");
checkNotNull(referenceName, "referenceName");
final long watchStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
String key = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
retainedKeys.add(key);
final KeyedWeakReference reference =
new KeyedWeakReference(watchedReference, key, referenceName, queue);
ensureGoneAsync(watchStartNanoTime, reference);
}针对引用object创建对应的weak引用,关联queue队列,queue为ReferenceQueue,所有weak引用被回收都会进入queue,然后调用ensureGoneAsync方法,看下具体实现代码,
/**
* 所属类:RefWatcher.java
*/
@SuppressWarnings("ReferenceEquality") // Explicitly checking for named null.
Retryable.Result ensureGone(final KeyedWeakReference reference, final long watchStartNanoTime) {
long gcStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
long watchDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(gcStartNanoTime - watchStartNanoTime);
//移除已回收的对象
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if (debuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached()) {
// The debugger can create false leaks.
return RETRY;
}
//判断对象是否被回收
if (gone(reference)) {
return DONE;
}
//手动GC
gcTrigger.runGc();
//移除已回收的对象
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if (!gone(reference)) {//如果没有被回收,dump原始信息
long startDumpHeap = System.nanoTime();
long gcDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(startDumpHeap - gcStartNanoTime);
File heapDumpFile = heapDumper.dumpHeap();
if (heapDumpFile == RETRY_LATER) {
// Could not dump the heap.
return RETRY;
}
long heapDumpDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startDumpHeap);
heapdumpListener.analyze(
new HeapDump(heapDumpFile, reference.key, reference.name, excludedRefs, watchDurationMs,
gcDurationMs, heapDumpDurationMs));
}
return DONE;
}移除已回收的对象,判断对应的weak引用是否被回收,如果没有被回收手动触发GC,移除已回收的对象,如果weak引用还存在则dump对应的原始信息,回调解析,heapdumpListener就是之前ServiceHeapDumpListener,看下heapdumpListener.analyze()的具体实现,
/**
* 所属类:ServiceHeapDumpListener.java
*/
@Override public void analyze(HeapDump heapDump) {
checkNotNull(heapDump, "heapDump");
HeapAnalyzerService.runAnalysis(context, heapDump, listenerServiceClass);
}调用解析service,解析源文件,看下里面做了什么,
/**
* 所属类:HeapAnalyzerService.java
*/
@Override protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
if (intent == null) {
CanaryLog.d("HeapAnalyzerService received a null intent, ignoring.");
return;
}
String listenerClassName = intent.getStringExtra(LISTENER_CLASS_EXTRA);
HeapDump heapDump = (HeapDump) intent.getSerializableExtra(HEAPDUMP_EXTRA);
HeapAnalyzer heapAnalyzer = new HeapAnalyzer(heapDump.excludedRefs);
AnalysisResult result = heapAnalyzer.checkForLeak(heapDump.heapDumpFile, heapDump.referenceKey);
AbstractAnalysisResultService.sendResultToListener(this, listenerClassName, heapDump, result);
}调用HeapAnalyzer.checkForLeak()解析源文件,然后通过调用DisplayLeakService父类方法sendResultToListener启动DisplayLeakService,将解析内容通过onHeapAnalyzed(heapDump, result)发送给DisplayLeakService,看下具体实现.
/**
* 所属类:DisplayLeakService.java
*/
@Override protected final void onHeapAnalyzed(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result) {
String leakInfo = leakInfo(this, heapDump, result, true);
CanaryLog.d("%s", leakInfo);
boolean resultSaved = false;
boolean shouldSaveResult = result.leakFound || result.failure != null;
if (shouldSaveResult) {
heapDump = renameHeapdump(heapDump);
resultSaved = saveResult(heapDump, result);
}
PendingIntent pendingIntent;
String contentTitle;
String contentText;
if (!shouldSaveResult) {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_no_leak_title);
contentText = getString(R.string.leak_canary_no_leak_text);
pendingIntent = null;
} else if (resultSaved) {
pendingIntent = DisplayLeakActivity.createPendingIntent(this, heapDump.referenceKey);
if (result.failure == null) {
String size = formatShortFileSize(this, result.retainedHeapSize);
String className = classSimpleName(result.className);
if (result.excludedLeak) {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_leak_excluded, className, size);
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_class_has_leaked, className, size);
}
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_analysis_failed);
}
contentText = getString(R.string.leak_canary_notification_message);
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_could_not_save_title);
contentText = getString(R.string.leak_canary_could_not_save_text);
pendingIntent = null;
}
// New notification id every second.
int notificationId = (int) (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() / 1000);
showNotification(this, contentTitle, contentText, pendingIntent, notificationId);
afterDefaultHandling(heapDump, result, leakInfo);
}生成display所需要的result文件,弹框提示内存泄露信息,至此了解了leakcanary从监控到解析再到展示泄露信息的一个全过程。