recastdemo 源码详解 001
介绍
在学习recast的过程中看了很多别人的博客,感觉没有很好的贴近demo的博客,然后准备自己动手写一个。
recastdemo git链接 https://github.com/recastnavigation/recastnavigation
recastdemo 编译方法 https://blog.csdn.net/memory_nothing/article/details/83589287
博客跳过了sample_solemesh和sample_tilemesh的介绍,直接从sample_tempobstacle开始(todo这三个的区别)
1 网格数据的读取
关键类 Sample_TempObstacles.InputGeom.rcMeshLoaderObj
这个类是封装的用于读取网格数据的。在Input Mesh里面选择网格模型之后,调用load接口读取网格数据。
2 构造配置表
关键类 Sample_TempObstacles
调用handleBuild方法来生成寻路网格,后面的操作也都是在这个方法里面
if (!m_geom || !m_geom->getMesh())
{
m_ctx->log(RC_LOG_ERROR, "buildTiledNavigation: No vertices and triangles.");
return false;
}
m_tmproc->init(m_geom);
// Init cache
const float* bmin = m_geom->getNavMeshBoundsMin();
const float* bmax = m_geom->getNavMeshBoundsMax();
int gw = 0, gh = 0;
rcCalcGridSize(bmin, bmax, m_cellSize, &gw, &gh);
const int ts = (int)m_tileSize;
const int tw = (gw + ts-1) / ts;
const int th = (gh + ts-1) / ts;
// Generation params.
rcConfig cfg;
memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(cfg));
cfg.cs = m_cellSize;
cfg.ch = m_cellHeight;
cfg.walkableSlopeAngle = m_agentMaxSlope;
cfg.walkableHeight = (int)ceilf(m_agentHeight / cfg.ch);
cfg.walkableClimb = (int)floorf(m_agentMaxClimb / cfg.ch);
cfg.walkableRadius = (int)ceilf(m_agentRadius / cfg.cs);
cfg.maxEdgeLen = (int)(m_edgeMaxLen / m_cellSize);
cfg.maxSimplificationError = m_edgeMaxError;
cfg.minRegionArea = (int)rcSqr(m_regionMinSize); // Note: area = size*size
cfg.mergeRegionArea = (int)rcSqr(m_regionMergeSize); // Note: area = size*size
cfg.maxVertsPerPoly = (int)m_vertsPerPoly;
cfg.tileSize = (int)m_tileSize;
cfg.borderSize = cfg.walkableRadius + 3; // Reserve enough padding.
cfg.width = cfg.tileSize + cfg.borderSize*2;
cfg.height = cfg.tileSize + cfg.borderSize*2;
cfg.detailSampleDist = m_detailSampleDist < 0.9f ? 0 : m_cellSize * m_detailSampleDist;
cfg.detailSampleMaxError = m_cellHeight * m_detailSampleMaxError;
rcVcopy(cfg.bmin, bmin);
rcVcopy(cfg.bmax, bmax);
ts代表像素块大小,ts代表一个title在x,z轴上面包含的像素块数,tw和th即地信息网格包含的在x,z轴划分的块数。
3 dtTileCache 初始化
// Tile cache params.
dtTileCacheParams tcparams;
memset(&tcparams, 0, sizeof(tcparams));
rcVcopy(tcparams.orig, bmin);
tcparams.cs = m_cellSize;
tcparams.ch = m_cellHeight;
tcparams.width = (int)m_tileSize;
tcparams.height = (int)m_tileSize;
tcparams.walkableHeight = m_agentHeight;
tcparams.walkableRadius = m_agentRadius;
tcparams.walkableClimb = m_agentMaxClimb;
tcparams.maxSimplificationError = m_edgeMaxError;
tcparams.maxTiles = tw*th*EXPECTED_LAYERS_PER_TILE;
tcparams.maxObstacles = 128;
dtFreeTileCache(m_tileCache);
m_tileCache = dtAllocTileCache();
if (!m_tileCache)
{
m_ctx->log(RC_LOG_ERROR, "buildTiledNavigation: Could not allocate tile cache.");
return false;
}
status = m_tileCache->init(&tcparams, m_talloc, m_tcomp, m_tmproc);
if (dtStatusFailed(status))
{
m_ctx->log(RC_LOG_ERROR, "buildTiledNavigation: Could not init tile cache.");
return false;
}
关键类 dtTileCache
这个类可以认为是把把每个title的寻路网格数据缓存。
4 dtNavMesh 初始化
dtFreeNavMesh(m_navMesh);
m_navMesh = dtAllocNavMesh();
if (!m_navMesh)
{
m_ctx->log(RC_LOG_ERROR, "buildTiledNavigation: Could not allocate navmesh.");
return false;
}
dtNavMeshParams params;
memset(¶ms, 0, sizeof(params));
rcVcopy(params.orig, bmin);
params.tileWidth = m_tileSize*m_cellSize;
params.tileHeight = m_tileSize*m_cellSize;
params.maxTiles = m_maxTiles;
params.maxPolys = m_maxPolysPerTile;
status = m_navMesh->init(¶ms);
if (dtStatusFailed(status))
{
m_ctx->log(RC_LOG_ERROR, "buildTiledNavigation: Could not init navmesh.");
return false;
}
关键类 dtNavMesh
dtNavMesh就是最终的寻路网格数据
生成寻路网格数据
m_cacheLayerCount = 0;
m_cacheCompressedSize = 0;
m_cacheRawSize = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < th; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < tw; ++x)
{
TileCacheData tiles[MAX_LAYERS];
memset(tiles, 0, sizeof(tiles));
int ntiles = rasterizeTileLayers(x, y, cfg, tiles, MAX_LAYERS);
for (int i = 0; i < ntiles; ++i)
{
TileCacheData* tile = &tiles[i];
status = m_tileCache->addTile(tile->data, tile->dataSize, DT_COMPRESSEDTILE_FREE_DATA, 0);
if (dtStatusFailed(status))
{
dtFree(tile->data);
tile->data = 0;
continue;
}
m_cacheLayerCount++;
m_cacheCompressedSize += tile->dataSize;
m_cacheRawSize += calcLayerBufferSize(tcparams.width, tcparams.height);
}
}
}
首先用rasterizeTileLayers函数对原始的网格数据进行光栅化。
Sample_TempObstacles::rasterizeTileLayers 光栅化

创建高度场(heightfiedl)
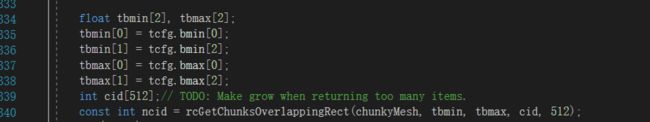

这里我也不是很清楚(todo)
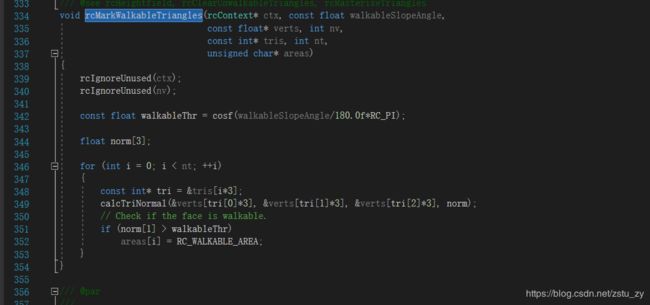
这个函数通过计算三角形平面的法向量来和可行走角度(walkableSlopeAngle)来判断平面是否可行走

rcRasterzeTriangles函数用于对地形数据进行光栅化,光栅化就是把原地图数据切成小长方体,每一个长方体被称为体素,
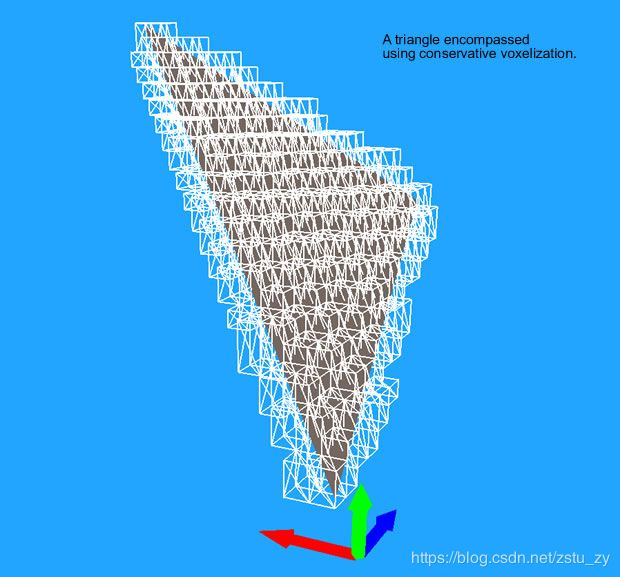
图片来源http://www.critterai.org/projects/cainav/doc/html/e72bd1ee-04b0-4bbb-a21d-d8d7ecaa11af.htm
上面的图片就是一个三角形被体素化后的样子,
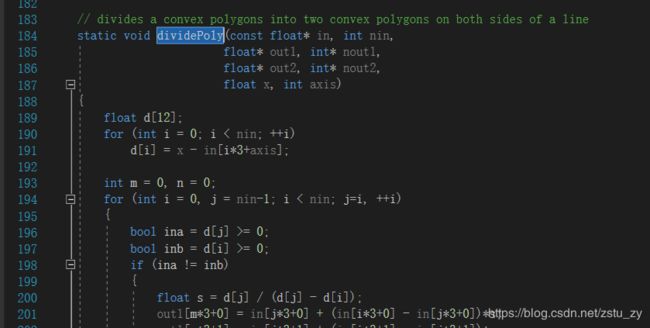
先来介绍一下这个函数,它的功能我脑补成对三维空间的一个三角形平面进行x,z平面切割,具体可以参考下面我给出的图片进行理解

这个图片显示的是在z轴对这个三角形平面进行切割,剩下图中5个点围成的平面,把剩余平面称为res平面,然后在对x轴上对res平面进行切割,


然后就可以根据切割后的多边形的在y轴的最大值和最小值,就可以得到这个三角形平面在上图白色框框这个地方可以被切成的体素了,好了上面就是体素化过程了,