前面介绍了row hammer,理论上很完美,实际操作的时候会面临很尴尬的问题:内存存储数据最小的单位是cell(就是个电容,充电是1,放电是0),无数个横着的cell组成row,无数个竖着的cell组成colume;数个row和colume组成bank,多个bank组成chip,然后是rank,接着是dimm、channel,总的逻辑包含顺序是:channel->dimm->rank->chip->bak->row/colume->cell;怎么把物理地址映射到具体的cell了?换句话说:比如知道了某个能提权数据位的虚拟地址,linux和windwos都能调用系统API查找到相应的物理地址,又怎么根据物理地址映射到bank/row/colume了? 否则怎么精准hammer?Intel 并未公开映射算法,怎么通过一些逆向的方式、方法猜测出物理地址到dram 的address mapping了?
1、百度的同学公开一种算法,https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1620354 这里有算法的说明,但本人并未找到该工具(自称DRAMDig)的源代码,也未找到该工具下载的地址,未能验证证其效果;为方便理解,整理了一个导图,如下:
通过DRAMDig测试的结果如下,由此可见:不同cpu型号、不同内存大小,对应不同的row、colume、bank function,情况较为复杂;
2、国外有团队做了row hammer测试,根据测试结果猜测出了物理地址映射到DRAM的方法,具体参考:http://lackingrhoticity.blogspot.com/2015/05/how-physical-addresses-map-to-rows-and-banks.html
对应的测试代码:https://github.com/google/rowhammer-test/tree/master/extended_test 下面详细说明代码的思路和倒推映射算法的思路;
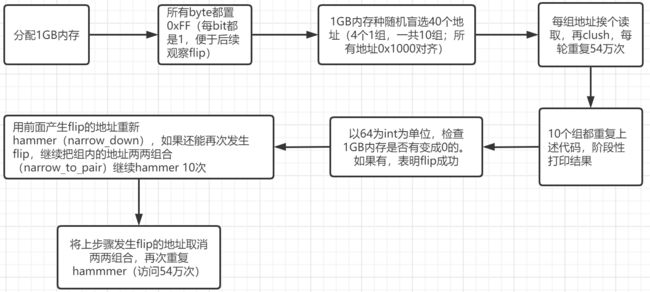
(1)整个流程大致如下: 先分配1GB内存,每个bit全部初始化为1;再盲选40个地址反复hammer,选出成功flip的地址后两两组合继续hammer,再取消两两组合后继续hammer;
(2)新问题来了:作者一开始盲选地址hammer,成功flip后为啥要narrow to pair down后再hammer了?——为了更准确地确认物理地址和反转flip的关系,看看到底是哪个地址导致了哪些cell flip,借此更精确的地逆向address mapping;下面会打印hammer的地址和被flip的地址,然后根据这些信息逆向address mapping;
if (check(&bit_flip_info)) { found = true; printf("RESULT PAIR,0x%" PRIx64 ",0x%" PRIx64 ",0x%" PRIx64 ",%i,%i\n", get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) addr1), get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) addr2), get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) bit_flip_info.victim_virtual_addr), bit_flip_info.bit_number, bit_flip_info.flips_to); }
作者耗费6小时,反转了22个地址,分别如下:
RESULT PAIR,0x6ccc1000,0x6cd59000,0x6cd1f680,40,0 RESULT PAIR,0x708f1000,0x70969000,0x7092ef08,40,0 RESULT PAIR,0x1a1d57000,0x1a1ddc000,0x1a1d9b718,63,0 RESULT PAIR,0x1a14de000,0x72367000,0x72321c20,33,0 RESULT PAIR,0x194d63000,0x194cf8000,0x194d27b30,16,0 RESULT PAIR,0x7b664000,0x7b6ed000,0x7b622d30,47,0 RESULT PAIR,0x72366000,0x61503000,0x72321c20,33,0 RESULT PAIR,0x72366000,0x5e9cf000,0x72321c20,33,0 RESULT PAIR,0x193606000,0x193825000,0x193643c10,2,0 RESULT PAIR,0x171417000,0x171236000,0x171272980,44,0 RESULT PAIR,0x17a644000,0x17a865000,0x17a822f00,49,0 RESULT PAIR,0x80af9000,0x17ebaf000,0x80a34310,4,0 RESULT PAIR,0x1961ec000,0x196165000,0x1961abd10,39,0 RESULT PAIR,0x7248f000,0x72515000,0x724c8d88,45,0 RESULT PAIR,0x1716b7000,0x7eb69000,0x1716f1ea0,36,0 RESULT PAIR,0x16f3d6000,0x16f1f6000,0x16f3930b0,47,0 RESULT PAIR,0x72901000,0x177232000,0x1772775a0,41,0 RESULT PAIR,0x772fc000,0x77277000,0x77231830,36,0 RESULT PAIR,0x7bcf3000,0x7bd69000,0x7bd2ef10,33,0 RESULT PAIR,0x7e275000,0x7e456000,0x7e412a30,39,0 RESULT PAIR,0x1730d7000,0x17305d000,0x1730910a8,35,0 RESULT PAIR,0x80afb000,0x78671000,0x80a34310,4,0
怎么根据这些flip的位反推物理地址和row、colume、bank了?作者cpu是sandy brige,ubuntu系统,4GB内存,先用decode-dimms初步查看了内存信息,如下:
Size 4096 MB Banks x Rows x Columns x Bits 8 x 15 x 10 x 64 Ranks 2
这里有2个rank,8个bank;每个bank包含了2^15 = 32768 rows;每个row的容量 2^10*64=8KB;总容量 = 8 kbytes per row * 32768 rows * 2 ranks * 8 banks = 4GB;通过该命令,初步确认了row、colume和bank的位数;结合上述被filp的地址,连带着各种猜测和不停的尝试,作者把地址做出了以下分解:
result: diff=-39980 addr=0x06cd1f680 -> row=01101100110100 rank=0 bank=011 col_hi=1101101 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (victim) addr=0x06cd59000 -> row=01101100110101 rank=0 bank=011 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x06ccc1000 -> row=01101100110011 rank=0 bank=011 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-3a0f8 addr=0x07092ef08 -> row=01110000100100 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=1011110 channel=0 col_lo=001000 (victim) addr=0x070969000 -> row=01110000100101 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x0708f1000 -> row=01110000100011 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-408e8 addr=0x1a1d9b718 -> row=10100001110110 rank=0 bank=000 col_hi=1101110 channel=0 col_lo=011000 (victim) addr=0x1a1ddc000 -> row=10100001110111 rank=0 bank=000 col_hi=0000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x1a1d57000 -> row=10100001110101 rank=0 bank=000 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-453e0 addr=0x072321c20 -> row=01110010001100 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0111000 channel=0 col_lo=100000 (victim) addr=0x072367000 -> row=01110010001101 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x1a14de000 -> row=10100001010011 rank=0 bank=100 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=2fb30 addr=0x194d27b30 -> row=10010100110100 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=1110110 channel=0 col_lo=110000 (victim) addr=0x194cf8000 -> row=10010100110011 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=0000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x194d63000 -> row=10010100110101 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True unusual? result: diff=-412d0 addr=0x07b622d30 -> row=01111011011000 rank=1 bank=000 col_hi=1011010 channel=0 col_lo=110000 (victim) addr=0x07b664000 -> row=01111011011001 rank=1 bank=000 col_hi=0000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x07b6ed000 -> row=01111011011011 rank=1 bank=000 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-443e0 addr=0x072321c20 -> row=01110010001100 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0111000 channel=0 col_lo=100000 (victim) addr=0x072366000 -> row=01110010001101 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x061503000 -> row=01100001010100 rank=0 bank=100 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-443e0 addr=0x072321c20 -> row=01110010001100 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0111000 channel=0 col_lo=100000 (victim) addr=0x072366000 -> row=01110010001101 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x05e9cf000 -> row=01011110100111 rank=0 bank=100 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=3dc10 addr=0x193643c10 -> row=10010011011001 rank=0 bank=001 col_hi=1111000 channel=0 col_lo=010000 (victim) addr=0x193606000 -> row=10010011011000 rank=0 bank=001 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x193825000 -> row=10010011100000 rank=1 bank=001 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=3c980 addr=0x171272980 -> row=01110001001001 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=1010011 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (victim) addr=0x171236000 -> row=01110001001000 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x171417000 -> row=01110001010000 rank=0 bank=101 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-42100 addr=0x17a822f00 -> row=01111010100000 rank=1 bank=000 col_hi=1011110 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (victim) addr=0x17a865000 -> row=01111010100001 rank=1 bank=000 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x17a644000 -> row=01111010011001 rank=0 bank=000 col_hi=0000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-c4cf0 addr=0x080a34310 -> row=10000000101000 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=0000110 channel=0 col_lo=010000 (victim) addr=0x080af9000 -> row=10000000101011 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x17ebaf000 -> row=01111110101110 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=False unusual? result: diff=-402f0 addr=0x1961abd10 -> row=10010110000110 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1111010 channel=0 col_lo=010000 (victim) addr=0x1961ec000 -> row=10010110000111 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x196165000 -> row=10010110000101 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=39d88 addr=0x0724c8d88 -> row=01110010010011 rank=0 bank=001 col_hi=0011011 channel=0 col_lo=001000 (victim) addr=0x07248f000 -> row=01110010010010 rank=0 bank=001 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x072515000 -> row=01110010010100 rank=0 bank=001 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=3aea0 addr=0x1716f1ea0 -> row=01110001011011 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=0111101 channel=0 col_lo=100000 (victim) addr=0x1716b7000 -> row=01110001011010 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x07eb69000 -> row=01111110101101 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-42f50 addr=0x16f3930b0 -> row=01101111001110 rank=0 bank=010 col_hi=1100001 channel=0 col_lo=110000 (victim) addr=0x16f3d6000 -> row=01101111001111 rank=0 bank=010 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x16f1f6000 -> row=01101111000111 rank=1 bank=010 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=455a0 addr=0x1772775a0 -> row=01110111001001 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1101011 channel=0 col_lo=100000 (victim) addr=0x177232000 -> row=01110111001000 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x072901000 -> row=01110010100100 rank=0 bank=100 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-457d0 addr=0x077231830 -> row=01110111001000 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0110000 channel=0 col_lo=110000 (victim) addr=0x077277000 -> row=01110111001001 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x0772fc000 -> row=01110111001011 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-3a0f0 addr=0x07bd2ef10 -> row=01111011110100 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=1011110 channel=0 col_lo=010000 (victim) addr=0x07bd69000 -> row=01111011110101 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x07bcf3000 -> row=01111011110011 rank=1 bank=111 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=-435d0 addr=0x07e412a30 -> row=01111110010000 rank=0 bank=100 col_hi=1010100 channel=0 col_lo=110000 (victim) addr=0x07e456000 -> row=01111110010001 rank=0 bank=100 col_hi=1000000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x07e275000 -> row=01111110001001 rank=1 bank=100 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True result: diff=340a8 addr=0x1730910a8 -> row=01110011000010 rank=0 bank=110 col_hi=0100001 channel=0 col_lo=101000 (victim) addr=0x17305d000 -> row=01110011000001 rank=0 bank=110 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x1730d7000 -> row=01110011000011 rank=0 bank=110 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=True unusual? result: diff=-c6cf0 addr=0x080a34310 -> row=10000000101000 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=0000110 channel=0 col_lo=010000 (victim) addr=0x080afb000 -> row=10000000101011 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=1100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor1) addr=0x078671000 -> row=01111000011001 rank=1 bank=101 col_hi=0100000 channel=0 col_lo=000000 (aggressor2) fits=False unusual?
仔细观察:(1)aggressor1距离victim更近(22个样本中,20个样本的位数只差1,两个样本差3),大概率是影响victim 的地址 (2)victims和两个aggressor都在同一个bank
进而得出了以下address mapping的结论:
- Bits 0-5: These are the lower 6 bits of the byte index within a row (i.e. the 6-bit index into a 64-byte cache line).
- Bit 6: This is a 1-bit channel number, which selects between the 2 DIMMs.
- Bits 7-13: These are the upper 7 bits of the index within a row (i.e. the upper bits of the column number).
- Bits 14-16: These are XOR'd with the bottom 3 bits of the row number to give the 3-bit bank number.
- Bit 17: This is a 1-bit rank number, which selects between the 2 ranks of a DIMM (which are typically the two sides of the DIMM's circuit board).
- Bits 18-32: These are the 15-bit row number.
- Bits 33+: These may be set because physical memory starts at physical addresses greater than 0.
内存管理器这么映射物理地址,有啥好处了?
- 0~5bit一共有6位,刚好是2^6=64byte 一个cache line的大小,这么做可以让两个channel同时并行访问不同的cache line,提升速度;
- bank 并行:8个bank可以同时并行读写,提升速度
- bank function: bank bit之间的XOR,可以在大范围读取数据时让地址映射到不同的bank,减少thrashing碰撞的概率
(3)最核心的hammer代码如下: 对特定地址读54万次;每次读后cflush清空cache line,强迫cpu每次都去DRAM读取,使得对应地址的row反复充放电,达到hammer的效果;
//inner的每个地址分别读数据,再清除缓存,如此重复54万次; static void row_hammer_inner(struct InnerSet inner) { if (TEST_MODE && inner.addrs[0] == g_inject_addr1 && inner.addrs[1] == g_inject_addr2) { printf("Test mode: Injecting bit flip...\n"); g_mem[3] ^= 1; } uint32_t sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < toggles; i++) {//重复54万次 for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) sum += *inner.addrs[a] + 1;//分别从4个内层地址读数据,可以把这4个地址存储的数据放进rowbuffer,原地址的cell读一次会充放电一次,影响其周边的cell; if (!TEST_MODE) { for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) //上面4个地址的内容从cache line清除,确保下次cpu还是从内存去读,才能保证row hammer的效果 asm volatile("clflush (%0)" : : "r" (inner.addrs[a]) : "memory"); } } // Sanity check. We don't expect this to fail, because reading // these rows refreshes them. if (sum != 0) { printf("error: sum=%x\n", sum); exit(1); } }
完整代码如下:精华都在注释(英文是原作者,中文是我加的)
// Copyright 2015, Google, Inc. // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. // This is required on Mac OS X for getting PRI* macros #defined. #define __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS #include#include #include #include #include #include #include <string.h> #include #include #include #include #include #if !defined(TEST_MODE) # define TEST_MODE 0 #endif const size_t mem_size = 1 << 30;//1GB const int toggles = 540000; char *g_mem; void *g_inject_addr1; void *g_inject_addr2; uint64_t g_address_sets_tried; int g_errors_found; /*从g_mem开始随机选个物理地址,偏移是页的整数倍,大小不超过1GB http://lackingrhoticity.blogspot.com/2015/05/how-physical-addresses-map-to-rows-and-banks.html 原作者自己的硬件环境: Bits 0-5: These are the lower 6 bits of the byte index within a row (i.e. the 6-bit index into a 64-byte cache line). Bit 6: This is a 1-bit channel number, which selects between the 2 DIMMs. Bits 7-13: These are the upper 7 bits of the index within a row (i.e. the upper bits of the column number). 物理地址依次增加0x1000,也就是不同的物理地址低12位是相同的,那么这些物理地址的:1、channel是一样的 2、colume是一样的 3、bank和row可能不同 */ char *pick_addr() { //offset是页(1<<12=4096)的整数倍 size_t offset = (rand() << 12) % mem_size; return g_mem + offset; } //虚拟地址转成物理地址,http://0x4c43.cn/2018/0508/linux-dynamic-link/ 有详细说明 uint64_t get_physical_addr(uintptr_t virtual_addr) { int fd = open("/proc/self/pagemap", O_RDONLY); assert(fd >= 0); int kPageSize = 0x1000; off_t pos = lseek(fd, (virtual_addr / kPageSize) * 8, SEEK_SET); assert(pos >= 0); uint64_t value; int got = read(fd, &value, 8); assert(got == 8); int rc = close(fd); assert(rc == 0); uint64_t frame_num = value & ((1ULL << 54) - 1); return (frame_num * kPageSize) | (virtual_addr & (kPageSize - 1)); } class Timer { struct timeval start_time_; public: Timer() { // Note that we use gettimeofday() (with microsecond resolution) // rather than clock_gettime() (with nanosecond resolution) so // that this works on Mac OS X, because OS X doesn't provide // clock_gettime() and we don't really need nanosecond resolution. int rc = gettimeofday(&start_time_, NULL); assert(rc == 0); } double get_diff() { struct timeval end_time; int rc = gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL); assert(rc == 0); return (end_time.tv_sec - start_time_.tv_sec + (double) (end_time.tv_usec - start_time_.tv_usec) / 1e6); } }; #define ADDR_COUNT 4 #define ITERATIONS 10 struct InnerSet { uint32_t *addrs[ADDR_COUNT];//4个32位的地址 }; struct OuterSet { struct InnerSet inner[ITERATIONS];//10个内层结构,每个内层结构4个32位地址 }; /*g_mem每bit都置1,后续按照一定频率反复读写某些地址的数据。如果发生flip, 会导致其内容不再是1,后续会在check函数检查是否发生了bit flip*/ static void reset_mem() { memset(g_mem, 0xff, mem_size); } //从g_mem开始随机选择40个物理地址保存在set;物理地址的偏移是页的整数倍,大小超过1GB; static void pick_addrs(struct OuterSet *set) { for (int j = 0; j < ITERATIONS; j++) { for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) { set->inner[j].addrs[a] = (uint32_t *) pick_addr(); } } } //inner的每个地址分别读数据,再清除缓存,如此重复54万次; static void row_hammer_inner(struct InnerSet inner) { if (TEST_MODE && inner.addrs[0] == g_inject_addr1 && inner.addrs[1] == g_inject_addr2) { printf("Test mode: Injecting bit flip...\n"); g_mem[3] ^= 1; } uint32_t sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < toggles; i++) {//重复54万次 for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) sum += *inner.addrs[a] + 1;//分别从4个内层地址读数据,可以把这4个地址存储的数据放进rowbuffer,原地址的cell读一次会充放电一次,影响其周边的cell; if (!TEST_MODE) { for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) //上面4个地址的内容从cache line清除,确保下次cpu还是从内存去读,才能保证row hammer的效果 asm volatile("clflush (%0)" : : "r" (inner.addrs[a]) : "memory"); } } // Sanity check. We don't expect this to fail, because reading // these rows refreshes them. if (sum != 0) { printf("error: sum=%x\n", sum); exit(1); } } static void row_hammer(struct OuterSet *set) { Timer timer; for (int j = 0; j < ITERATIONS; j++) { //读取inner的地址、清空缓存,重复54万次; row_hammer_inner(set->inner[j]); g_address_sets_tried++; } // Print statistics derived from the time and number of accesses. double time_taken = timer.get_diff(); printf(" Took %.1f ms per address set\n",//1个set = 1个1inner(一共4个地址),耗时58~59ms,平局每个地址的读取耗时14.5~15ms(每个地址重复了54万次,并且上次读取后清空了缓存); time_taken / ITERATIONS * 1e3); printf(" Took %g sec in total for %i address sets\n", time_taken, ITERATIONS); int memory_accesses = ITERATIONS * ADDR_COUNT * toggles; printf(" Took %.3f nanosec per memory access (for %i memory accesses)\n", time_taken / memory_accesses * 1e9,//每个地址的读取时间在27~29ns之间 memory_accesses); int refresh_period_ms = 64;//内存控制器每64ms刷新一次;每个刷新周期内,每个地址访问53~58万次; printf(" This gives %i accesses per address per %i ms refresh period\n", (int) (refresh_period_ms * 1e-3 * ITERATIONS * toggles / time_taken), refresh_period_ms); } struct BitFlipInfo { uintptr_t victim_virtual_addr; int bit_number; uint8_t flips_to; // 1 if this is a 0 -> 1 bit flip, 0 otherwise. }; static bool check(struct BitFlipInfo *result) { uint64_t *end = (uint64_t *) (g_mem + mem_size); uint64_t *ptr; bool found_error = false; for (ptr = (uint64_t *) g_mem; ptr < end; ptr++) { uint64_t got = *ptr; uint64_t expected = ~(uint64_t) 0;//g_mem每个bit初始都置1 if (got != expected) { printf("error at %p (phys 0x%" PRIx64 "): got 0x%" PRIx64 "\n", ptr, get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) ptr), got); found_error = true; g_errors_found++; if (result) { result->victim_virtual_addr = (uintptr_t) ptr;//保存flip的地址 result->bit_number = -1;//0xff,初始值; for (int bit = 0; bit < 64; bit++) {//上面每次比对取64bit,这里继续看看到底是哪个bit被flip了 if (((got >> bit) & 1) != ((expected >> bit) && 1)) { result->bit_number = bit;//找到了flip的位,最终flip的位=victim_virtual_addr+bit_number; result->flips_to = (got >> bit) & 1; } } assert(result->bit_number != -1); } } } return found_error; } /* 用发生flip的地址两两组合形成新inner地址,缩小范围后继续hammer */ bool narrow_to_pair(struct InnerSet *inner) { bool found = false; for (int idx1 = 0; idx1 < ADDR_COUNT; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = idx1 + 1; idx2 < ADDR_COUNT; idx2++) { //0+1、1+2、2+3组合发生反转的地址 uint32_t *addr1 = inner->addrs[idx1]; uint32_t *addr2 = inner->addrs[idx2]; struct InnerSet new_set; // This is slightly hacky: We reuse row_hammer_inner(), which // always expects to hammer ADDR_COUNT addresses. Rather than // making another version that takes a pair of addresses, we // just pass our 2 addresses to row_hammer_inner() multiple // times. 新的inner分别放这两个发生过flip的地址组合 for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) { new_set.addrs[a] = a % 2 == 0 ? addr1 : addr2; } printf("Trying pair: 0x%" PRIx64 ", 0x%" PRIx64 "\n", get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) addr1), get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) addr2)); reset_mem(); row_hammer_inner(new_set); struct BitFlipInfo bit_flip_info; if (check(&bit_flip_info)) { found = true; printf("RESULT PAIR,0x%" PRIx64 ",0x%" PRIx64 ",0x%" PRIx64 ",%i,%i\n", get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) addr1), get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) addr2), get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) bit_flip_info.victim_virtual_addr), bit_flip_info.bit_number, bit_flip_info.flips_to); } } } return found; } //继续hammer,把发生flip的inner地址保存后 bool narrow_down(struct OuterSet *outer) { bool found = false; for (int j = 0; j < ITERATIONS; j++) { reset_mem(); row_hammer_inner(outer->inner[j]); if (check(NULL)) { printf("hammered addresses:\n"); struct InnerSet *inner = &outer->inner[j];//把发生flip的地址保存在inner结构 for (int a = 0; a < ADDR_COUNT; a++) { printf(" logical=%p, physical=0x%" PRIx64 "\n", inner->addrs[a], get_physical_addr((uintptr_t) inner->addrs[a])); } found = true; printf("Narrowing down to a specific pair...\n"); int tries = 0; while (!narrow_to_pair(inner)) { if (++tries >= 10) { printf("Narrowing to pair: Giving up after %i tries\n", tries); break; } } } } return found; } void main_prog() { printf("RESULT START_TIME,%" PRId64 "\n", time(NULL)); g_mem = (char *) mmap(NULL, mem_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_ANON | MAP_PRIVATE, -1, 0); assert(g_mem != MAP_FAILED); printf("Clearing memory...\n"); reset_mem();//分配的1G内存全部值0xFF Timer t; int iter = 0; for (;;) { printf("Iteration %i (after %.2fs)\n", iter++, t.get_diff()); struct OuterSet addr_set; pick_addrs(&addr_set); if (TEST_MODE && iter == 3) { printf("Test mode: Will inject a bit flip...\n"); g_inject_addr1 = addr_set.inner[2].addrs[0]; g_inject_addr2 = addr_set.inner[2].addrs[1]; } row_hammer(&addr_set); Timer check_timer; bool found_error = check(NULL); printf(" Checking for bit flips took %f sec\n", check_timer.get_diff()); if (iter % 100 == 0 || found_error) { // Report general progress stats: // - Time since start, in seconds // - Current Unix time (seconds since epoch) // - Number of address sets tried // - Number of bit flips found (not necessarily unique ones) printf("RESULT STAT,%.2f,%" PRId64 ",%" PRId64 ",%i\n", t.get_diff(), (uint64_t) time(NULL), g_address_sets_tried, g_errors_found); } if (found_error) { printf("\nNarrowing down to set of %i addresses...\n", ADDR_COUNT); int tries = 0; while (!narrow_down(&addr_set)) { if (++tries >= 10) { printf("Narrowing to address set: Giving up after %i tries\n", tries); break; } } printf("\nRunning retries...\n"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { printf("Retry %i\n", i); reset_mem(); row_hammer(&addr_set); check(NULL); } if (TEST_MODE) exit(1); } } } int main() { // Turn off unwanted buffering for when stdout is a pipe. setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0); // Start with an empty line in case previous output was truncated // mid-line. printf("\n"); if (TEST_MODE) { printf("Running in safe test mode...\n"); } // Fork a subprocess so that we can print the test process's exit // status, and to prevent reboots or kernel panics if we are running // as PID 1. int pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { main_prog(); _exit(1); } int status; if (waitpid(pid, &status, 0) == pid) { printf("** exited with status %i (0x%x)\n", status, status); } if (getpid() == 1) { // We're the "init" process. Avoid exiting because that would // cause a kernel panic, which can cause a reboot or just obscure // log output and prevent console scrollback from working. for (;;) { sleep(999); } } return 0; }
参考:
1、 http://lackingrhoticity.blogspot.com/2015/05/how-physical-addresses-map-to-rows-and-banks.html How physical addresses map to rows and banks in DRAM
2、 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1620354 逆向DRAM地址映射
3、 DRAMDig: A Knowledge-assisted Tool to Uncover DRAM Address Mapping