docker
参考文档
base 镜像 ubuntu:16.04 ubuntu-16.04.4-server-amd64.iso
docker的安装
卸载旧版本
旧版本的 Docker 称为 docker 或者 docker-engine,使用以下命令卸载旧版本:
$ sudo apt-get remove docker \
docker-engine \
docker.io
Ubuntu 14.04 可选内核模块
从 Ubuntu 14.04 开始,一部分内核模块移到了可选内核模块包 (linux-image-extra-*) ,以减少内核软件包的体积。正常安装的系统应该会包含可选内核模块包,而一些裁剪后的系统可能会将其精简掉。AUFS 内核驱动属于可选内核模块的一部分,作为推荐的 Docker 存储层驱动,一般建议安装可选内核模块包以使用 AUFS。
如果系统没有安装可选内核模块的话,可以执行下面的命令来安装可选内核模块包:
$ sudo apt-get update
sudoapt−getinstall linux−image−extra− s u d o a p t − g e t i n s t a l l l i n u x − i m a g e − e x t r a − (uname -r) \
linux-image-extra-virtual
Ubuntu 16.04 +
Ubuntu 16.04 + 上的 Docker CE 默认使用 overlay2 存储层驱动,无需手动配置。
使用 APT 安装
由于 apt 源使用 HTTPS 以确保软件下载过程中不被篡改。因此,我们首先需要添加使用 HTTPS 传输的软件包以及 CA 证书。
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
software-properties-common
鉴于国内网络问题,强烈建议使用国内源,官方源请在注释中查看。
为了确认所下载软件包的合法性,需要添加软件源的 GPG 密钥。
$ curl -fsSL https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
官方源
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
然后,我们需要向 source.list 中添加 Docker 软件源
$ sudo add-apt-repository \
“deb [arch=amd64] https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable”
官方源
$ sudo add-apt-repository \
“deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable”
以上命令会添加稳定版本的 Docker CE APT 镜像源,如果需要最新或者测试版本的 Docker CE 请将 stable 改为 edge 或者 test。从 Docker 17.06 开始,edge test 版本的 APT 镜像源也会包含稳定版本的 Docker。
安装 Docker CE
更新 apt 软件包缓存,并安装 docker-ce:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce
使用脚本自动安装
在测试或开发环境中 Docker 官方为了简化安装流程,提供了一套便捷的安装脚本,Ubuntu 系统上可以使用这套脚本安装:
curl−fsSLget.docker.com−oget−docker.sh c u r l − f s S L g e t . d o c k e r . c o m − o g e t − d o c k e r . s h sudo sh get-docker.sh –mirror Aliyun
执行这个命令后,脚本就会自动的将一切准备工作做好,并且把 Docker CE 的 Edge 版本安装在系统中。
启动 Docker CE
sudosystemctlenabledocker s u d o s y s t e m c t l e n a b l e d o c k e r sudo systemctl start docker
Ubuntu 14.04 请使用以下命令启动:
$ sudo service docker start
建立 docker 用户组
默认情况下,docker 命令会使用 Unix socket 与 Docker 引擎通讯。而只有 root 用户和 docker 组的用户才可以访问 Docker 引擎的 Unix socket。出于安全考虑,一般 Linux 系统上不会直接使用 root 用户。因此,更好地做法是将需要使用 docker 的用户加入 docker 用户组。
建立 docker 组:
$ sudo groupadd docker
将当前用户加入 docker 组:
sudousermod−aGdocker s u d o u s e r m o d − a G d o c k e r USER
退出当前终端并重新登录,进行如下测试。
测试 Docker 是否安装正确
$ docker run hello-world
Unable to find image ‘hello-world:latest’ locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
ca4f61b1923c: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:be0cd392e45be79ffeffa6b05338b98ebb16c87b255f48e297ec7f98e123905c
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the “hello-world” image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://cloud.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/engine/userguide/
一 docker创建与启动镜像
1 启动docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
2 重启docker
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
3 下载镜像
docker pull centos:7.1.1503
docker pull ubuntu:16.04
4 列表
镜像列表 docker image ls
容器列表 docker ps -a
5 运行镜像
docker run -it –name test –rm –privileged=true ubuntu:16.04 bash (–rm 退出后会删除容器)
docker run -it –name test –privileged=true ubuntu:16.04 bash
docker run -it - –name test -d -privileged=true ubuntu-peach:16.04 bash (-d 后台运行时)
docker run -d –name web -p 80:80 myweb:v1
docker run -it –privileged=true -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb ubuntu:16.04 bash (为了能够使用usb,连接手机,upan等,参考链接)
-v /dev/kvm:/dev/kvm
docker run 的时候加上这个参数 –ulimit core=-1 –security-opt seccomp=unconfined 的功能:
前者就是把 Core Dump 文件的大小设置为无限制,后者是为了开放 ptrace 系列高权限的系统调用,这样我们才可以在 Docker 里面使用 GDB
echo ‘/tmp/%e.%p.%t.core’ | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
这是因为系统在产生 Core Dump 文件的时候是根据 /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern 的设定。而默认的设定是 |/usr/share/apport/apport %p %s %c %P,也就是用管道传给 apport。然而 Docker 里面的系统不一定有装 apport,并且 /proc 又是直接挂到 Docker 里面的,所以我们就得改成放到固定的位置去,也就是 /tmp。
6 删除镜像
exit 命令 退出镜像
1)先停止容器 docker stop containterID
2)删除容器 docker rm containterID
3)删除镜像 docker image rm 501(id)
二 容器相关操作
0 容器和镜像之间的转换
1)导出容器为一个镜像
docker export 236e2e88bc38(containterID) > ubuntu-peach.tar
2)导入镜像
cat ubuntu-peach.tar | docker import - ubuntu-peach:16.04
1 启动 容器
容器列表 docker ps -a
已启动容器列表 docker container ls 看到最初的状态为 (health: starting)。
查看容器的全ID docker ps –no-trunc
docker start
docker start -i :启动一个container并进入交互模式
docker attach attach进一个已经启动的容器
2 复制文件
docker cp :/root/test.bin ./ //将container中的文件复制到本地。
docker cp test.txt :/root/test. //将本地中的文件复制到本地。
3 查看容器中ip地址
docker inspect
或 docker inspect –format ‘{{ .NetworkSettings.IPAddress }}’
docker inspect –format ‘{{json .State.Health}}’ web | python -m json.tool 可用docker inspect 来查看输出的健康状态。
三 使用dockerfile定制镜像
Dockerfile 中每一个指令都会建立一层镜像。容器就是进程,在启动容器的时候,需要指定所运行的程序及参数。
1 构建镜像
docker build -t ubuntu-peach1:16.04 . //-t跟新的镜像名字 . .代表Dockerfile文件的位置 ,也可用-f ../Dockerfile.php 参数指定某个文件作为 Dockerfile
2 启动镜像
docker run -d –name test -it ubuntu-peach:16.04 //通过Dockerfile构建的镜像,不需要后缀bash
Dockerfile内容
0)创建**文件 touch Dockerfile
1)文件内容
可以添加注释
FROM nginx 导入基础镜像
ENV NODE_VERSION 7.2.0 就像定义了一个宏一样。
WORKDIR <工作目录路径> 指定工作路径:若要改变各层的工作目录的位置,那么应该使用 WORKDIR 指令。
RUN groupadd -r redis && useradd -r -g redis redis
USER redis 切换到指定用户而已,这个用户必须是事先建立好的,否则无法切换。
HEALTHCHECK –interval=30s –timeout=3s \
CMD curl -fs http://localhost/ || exit 1 运行该命令来检查是否正常服务。
RUN \ 换行
COPY package.json /usr/src/app/
CMD [“nginx”, “-g”, “daemon off;”]
ENTRYPOINT [ “curl”, “-s”, “http://ip.cn” ] 可以弥补CMD构建完镜像后,运行docker run 镜像 还要添加参数的问题。
VOLUME /data 将动态文件所保存目录挂载为卷。也可通过docker run -d -v mydata:/data xxxx 命令 -v mydata来覆盖文件中的挂载卷。
四、修改及添加容器配置
docker启动后,在运行docker的虚拟机上运行 systemctl status docker.service 查看docker启动时加载的配置文件。
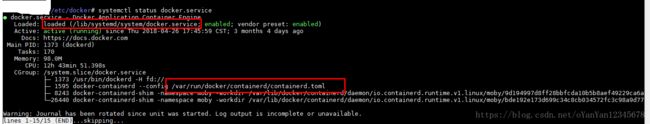
容器运行起来后的配置文件
关闭容器后设置:
vim /var/lib/docker/containers/9d194997d8ff28bbfcda10b5b8aef49229ca6a49efb05a529097d4281ff09c88/hostconfig.json中的 Binds 则对应的设置参数 -v /dev/kvm:/dev/kvm
“Binds”:[
“/dev/kvm:/dev/kvm”
]
但是发现重启容器后,新添加的配置没有加进来。????
保存镜像
docker save alpine | gzip > alpine-latest.tar.gz
到另一台主机上加载镜像
docker load -i alpine-latest.tar.gz
Loaded image: alpine:latest
也可用下面一条命令直接会加载到另一台主机上:docker save <镜像名> | bzip2 | pv | ssh <用户名>@<主机名> ‘cat | docker load’
docker exec -dit
其他参考文档