上采样方法大PK(Upsample,Interpolate,resize,Transposed convolution,deconv,Unpool,Pixelshuffle)
目录
Upsample:
Interpolate,resize:
Transposed convolution,deconv:
Unpool:
Pixelshuffle:
Upsample:
Pytorch example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.arange(1, 5).view(1, 1, 2, 2).float()
print(input)
#tensor([[[[1., 2.],
# [3., 4.]]]])
upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
print(upsample(input))
#tensor([[[[1., 1., 2., 2.],
# [1., 1., 2., 2.],
# [3., 3., 4., 4.],
# [3., 3., 4., 4.]]]])
upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
print(upsample(input))
#tensor([[[[1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 2.0000],
# [1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 2.5000],
# [2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 3.5000],
# [3.0000, 3.2500, 3.7500, 4.0000]]]])
tensorflow example:
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random_normal((1, 4,4,9))
print(x.get_shape().as_list()) #[1, 4, 4, 9]
y = tf.keras.layers.UpSampling2D(size=(1, 2))(x)
print(y.get_shape().as_list())#[1, 4, 8, 9]
Interpolate,resize:
Pytorch example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.arange(1, 5).view(1, 1, 2, 2).float()
print(input)
#tensor([[[[1., 2.],
# [3., 4.]]]])
upsample = F.interpolate(input, size=(4, 4), mode='nearest')
print(upsample)
#tensor([[[[1., 1., 2., 2.],
# [1., 1., 2., 2.],
# [3., 3., 4., 4.],
# [3., 3., 4., 4.]]]])
upsample = F.interpolate(input, size=(4, 4), mode='bilinear')
print(upsample)
#tensor([[[[1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 2.0000],
# [1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 2.5000],
# [2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 3.5000],
# [3.0000, 3.2500, 3.7500, 4.0000]]]])
tensorflow example:
import tensorflow as tf
image = tf.constant([
[1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1],
])
image = image[tf.newaxis, ..., tf.newaxis]# Add "batch" and "channels" dimensions
print(image.shape.as_list()) # [1, 5, 5, 1]
resized_image = tf.image.resize_images(image, [3,5]) #tf1.9.0
print(resized_image.get_shape().as_list())#[1, 3, 5, 1]
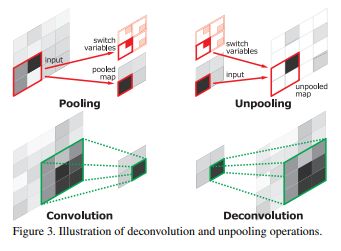
Transposed convolution,deconv:
出自论文,Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation
Pytorch example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 6, 6)
upsample = nn.ConvTranspose2d(3, 16, 3, stride=2, padding=1)
output = upsample(input, output_size=(1,16,12,12))
print(output.size()) #torch.Size([1, 16, 12, 12])
tensorflow example:
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
input = tf.random_normal((1, 4,4,9))
print(input.get_shape().as_list()) #[1, 4, 4, 9]
pred = slim.conv2d_transpose(input, 16, kernel_size=[3, 3], stride=2)# tf 1.15.3
print(pred.get_shape().as_list())#[1, 8, 8, 16]
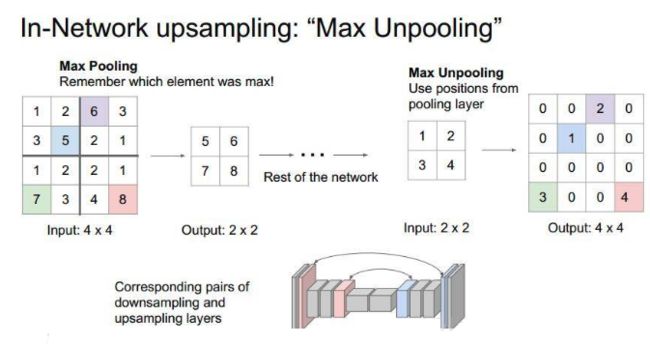
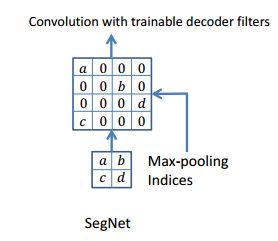
Unpool:
出自论文,
Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks
SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation
Pytorch example:
import torch
from torch import nn
input = torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]).view(1,1,4,4)
print(input)
downsample ,index= nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2,return_indices=True)(input)
out = nn.MaxUnpool2d(kernel_size =2, stride=2)(downsample,index)
print(out)
“””
tensor([[[[ 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8.],
[ 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[13., 14., 15., 16.]]]])
tensor([[[[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 6., 0., 8.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 14., 0., 16.]]]])
“””
Pixelshuffle:
出自论文:Real-Time Single Image and Video Super-Resolution Using an Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network
Pytorch example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(3)
input = torch.randn(1, 9, 4, 4)
output = pixel_shuffle(input)
print(output.size()) #torch.Size([1, 1, 12, 12])
tensorflow example:
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random_normal((1, 4,4,9))
print(x.shape) #(1, 4, 4, 9)
y = tf.depth_to_space(x,3)
with tf.Session() as sess:
z = sess.run(y)
print(z.shape) #(1, 12, 12, 1)