使用ROS MoveIt!控制真实五自由度机械臂
使用ROS MoveIt!控制diy五自由度机械臂
写在前面
环境:Ubuntu16.04+ROS Kinetic
准备工作一定要有,参见前面几篇博客,尤其是使用MoveIt!+Arbotix控制六自由度机械臂,里面涉及到控制器配置文件的编写、launch文件修改等。
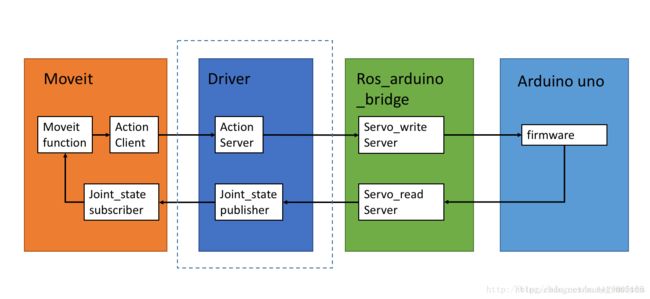
了解驱动的原理:
重点理解前两个模块的内容,moveit实际上是通过action这种交互机制来控制机械臂的,并且moveit只提供action client,因此driver中的action server需要自己编写,两者的接口类型为FollowJointTrajectoryAction。
我没有使用ros_arduino_brige,直接在arduino IDE中编写ros节点订阅driver发送过来的关节信息,然后驱动机械臂。
有机会我也要试试ros_arduino_brige~
修改功能包中相关文件
编写myrobot_controllers.yaml文件
经过moveit setup assistant设置之后,可以在myrobot_moveit_config包的config文件夹下找到一个fake_controllers.yaml文件,这个是虚拟控制器配置文件,仅供仿真使用,如果要驱动真实机械臂,就要编写自己的controller.yaml(可参见使用MoveIt!+Arbotix控制六自由度机械臂)以取代fake的那个。
myrobot_controllers.yaml格式如下,注意yaml文件对格式要求比较严格,要用空格代替tab!!
controller_list:
- name: arm_controller
action_ns: follow_joint_trajectory
type: FollowJointTrajectory
default: true
joints:
- joint1
- joint2
- joint3
- joint4
- joint5
- name: gripper_controller
action_ns: gripper_action
type: GripperCommand
default: true
joints:
- finger_joint1
- finger_joint2
修改launch文件
在demo.launch文件中,重点关注如下嵌套关系:
- demo.launch
- move_group.launch
- trajectory_execution.launch.xml
- $(arg moveit_controller_manager)_moveit_controller_manager.launch.xml
- trajectory_execution.launch.xml
- move_group.launch
一般新建的包,会以你自己的robot名自建一个空的xxx_moveit_controller_manager.launch.xml,我的就是myrobot_moviet_controller_manager.launch.xml。该文件的主要作用就是加载你自己编写的控制器yaml文件,通用格式如下:
<launch>
<arg name="moveit_controller_manager" default="moveit_simple_controller_manager/MoveItSimpleControllerManager" />
<param name="moveit_controller_manager" value="$(arg moveit_controller_manager)" />
<rosparam file="$(find myrobot_moveit_config)/config/myrobot_controllers.yaml" />
launch>
需要注意,在demo演示时,机械臂的joint_states是通过/move_group/fake_controller_joint_states这个话题发出到/joint_states话题,而驱动真实机械臂时,从上面的Driver模块中可以看出,需要自己编写一个joint_states_pulisher发布/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states话题。在demo.launch文件中进行修改:
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher">
<param name="use_gui" value="$(arg use_gui)"/>
<rosparam param="source_list">[/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states]rosparam>
node>
myrobot_driver.cpp
综上,自建的/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states话题+上文提到的action server = myrobot_driver节点,即自定义的Driver节点。另外,我手头上的机械臂只是简单的舵机驱动,没有角度反馈,所以可以通过获取movie规划得到的最后一组数据作为机械臂运动输出后的实际状态(没有闭环反馈就是很low……),代码如下
/* myrobot_driver.cpp */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*------只是arm group部分,因此只有五个舵机-----*/
//换算舵机PWM值与弧度之间的关系
//舵机运动范围PWM500-2500,对应角度0°-270°,中间状态为1500(设定为偏置)
//关节弧度范围-2.36-2.36,0rad对应舵机中间状态1500
//换算得到每变化1rad,PWM变化423
#define scaler 423
#define offset 1500
using namespace std;
class FollowJointTrajectoryAction
{
protected:
sensor_msgs::JointState js;
std_msgs::Float64 joint1_pos, joint2_pos, joint3_pos, joint4_pos, joint5_pos;
ros::NodeHandle nh;
std::string action_name_;
ros::Publisher pub_joint;//给move_group识别的publisher,代替joint_state_publisher,发布joint_states
ros::Publisher pub_joint1;//给下位机arduino识别的publiser
ros::Publisher pub_joint2;//同上
ros::Publisher pub_joint3;//同上
ros::Publisher pub_joint4;//同上
ros::Publisher pub_joint5;//同上
//与moveit中action client通讯的action server
actionlib::SimpleActionServer as_;
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryActionResult result_;
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryActionGoal goal_;
public:
FollowJointTrajectoryAction(std::string name) :
as_(nh, name, false),
action_name_(name)
{
as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&FollowJointTrajectoryAction::goalCB, this));
as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&FollowJointTrajectoryAction::preemptCB, this));
as_.start();
pub_joint = nh.advertise("/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states", 10);
pub_joint1 = nh.advertise("joint1_value", 100);
pub_joint2 = nh.advertise("joint2_value", 100);
pub_joint3 = nh.advertise("joint3_value", 100);
pub_joint4 = nh.advertise("joint4_value", 100);
pub_joint5 = nh.advertise("joint5_value", 100);
// ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
js.name.resize(5);
js.position.resize(5);
//名字要与关节定义的名字一致
js.name[0] = "joint1";
js.name[1] = "joint2";
js.name[2] = "joint3";
js.name[3] = "joint4";
js.name[4] = "joint5";
ROS_INFO("-------action start!-------");
}
~FollowJointTrajectoryAction(void)
{
}
void goalCB()
{
ROS_INFO("-------goal is receive!-------");
std::vector points_;
double points_end[5];
double Pos_length;
if (as_.isNewGoalAvailable()){
js.position.clear();
points_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->trajectory.points;
Pos_length = points_.size();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
//假设v是一个vector对象,v.at(n)和v[n]是一样的
//但是前者会检查是否越界,后者不会
points_end[i] = points_.at(Pos_length - 1).positions[i];
js.position.push_back(points_end[i]);
}
js.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
//向move_group节点发布规划得到的关节值
pub_joint.publish(js);
//向下位机arduino节点发布规划得到的关节值,直接得到舵机PWM值
//舵机2需要反向
joint1_pos.data = js.position[0] * scaler + offset;
joint2_pos.data = -js.position[1] * scaler + offset;
joint3_pos.data = js.position[2] * scaler + offset;
joint4_pos.data = js.position[3] * scaler + offset;
joint5_pos.data = js.position[4] * scaler + offset;
pub_joint1.publish(joint1_pos);
pub_joint2.publish(joint2_pos);
pub_joint3.publish(joint3_pos);
pub_joint4.publish(joint4_pos);
pub_joint5.publish(joint5_pos);
}else{
ROS_INFO("-------goal is not availabel!-------");
}
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryResult result;
result.error_code = 0;
as_.setSucceeded(result);
}
void preemptCB()
{
ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
as_.setPreempted();
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "myrobot_driver");
FollowJointTrajectoryAction followjointtrajectory("arm_controller/follow_joint_trajectory");//名称要与yaml配置一致
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
加个验证
运行demo,订阅/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states
命令如下:
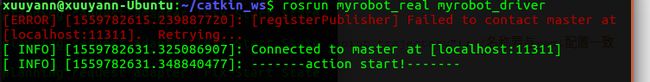
$ rosrun myrobot_real myrobot_driver
$ roslaunch myrobot_moveit_config demo.launch
rqt_graph一下,看看话题/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states加载成功没有,同时如下显示可以知道arm_controller加载成功,Driver中的action server与move_group中的action client也配对成功。
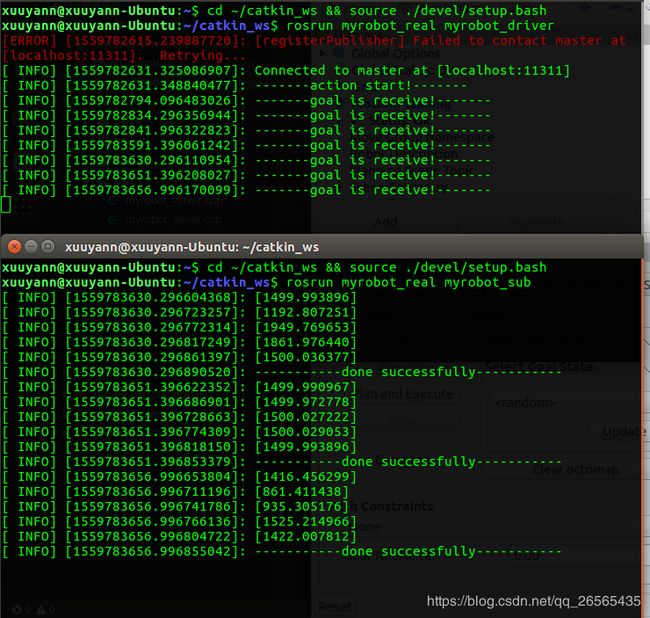
监听话题/move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states,即rostopic echo /move_group/myrobot_controller_joint_states,拖动机械臂并规划执行,可监听到如下数据。目前需要的就是position。
编写一个简单的myrobot_sub.cpp
为了省事,直接撸一个订阅节点,把myrobot_driver.cpp中写的jointX_value全部订阅监听一道,看算的舵机PWM值与弧度值之间是不是正确对应关系,也方便后面测试舵机。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*------只是arm group部分,因此只有五个舵机-----*/
#define scaler 423
#define offset 1500
float jointval[5] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
void callback1(const std_msgs::Float64& pos_msg)
{
jointval[0] = pos_msg.data ;//舵机1
ROS_INFO("[%f] ", jointval[0]);
}
void callback2(const std_msgs::Float64& pos_msg)
{
jointval[1] = pos_msg.data ;//舵机2
ROS_INFO("[%f] ", jointval[1]);
}
void callback3(const std_msgs::Float64& pos_msg)
{
jointval[2] = pos_msg.data ;//舵机3
ROS_INFO("[%f] ", jointval[2]);
}
void callback4(const std_msgs::Float64& pos_msg)
{
jointval[3] = pos_msg.data;//舵机4
ROS_INFO("[%f] ", jointval[3]);
}
void callback5(const std_msgs::Float64&pos_msg)
{
jointval[4] = pos_msg.data ;//舵机5
ROS_INFO("[%f] ", jointval[4]);
ROS_INFO("-----------done successfully-----------");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* code for main function */
ros::init(argc, argv, "ListenJointValue");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber sub1 = nh.subscribe("joint1_value", 1000, callback1);
ros::Subscriber sub2 = nh.subscribe("joint2_value", 1000, callback2);
ros::Subscriber sub3 = nh.subscribe("joint3_value", 1000, callback3);
ros::Subscriber sub4 = nh.subscribe("joint4_value", 1000, callback4);
ros::Subscriber sub5 = nh.subscribe("joint5_value", 1000, callback5);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
$ rosrun myrobot_real myrobot_sub
成功~
arduino端节点
模仿上面的myrobot_sub.cpp可以很快的写出arduino程序,只需要加个舵机初始化和驱动程序即可,简单来说就是订阅监听+驱动。
我试了下,舵机速度超快,震得桌子咚咚响,不行不行太吵了。我之前写了个控制舵机速度的程序,以1rad/s的速度改改正好可以拿来用Arduino学习(4)——串口发送指令控制舵机速度。
代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define USE_USBCON
#define SERVO_NUM 5
#define init 1500
#define SERVO_TIME_PERIOD 20 //每隔20ms处理一次(累加)舵机的PWM增量
Servo myservo[SERVO_NUM];
const byte servo_pin[SERVO_NUM] = {10, A2, A3, A0, A1};
float jointval[SERVO_NUM] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
//float buf[SERVO_NUM] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
bool check = false;//check为true才表示订阅到消息
typedef struct { //舵机结构体变量声明
unsigned int aim = 1500; //舵机目标值
float cur = 1500.0; //舵机当前值
float inc= 8.48; //舵机值增量,以20ms为周期
}duoji_struct;
duoji_struct servo_do[SERVO_NUM]; //用结构体变量声明一个舵机变量组
ros::NodeHandle nh;
void joint1_callback(const std_msgs::Float64& msg){
jointval[0] = msg.data;
//buf[0] = jointval[0];
//myservo[0].writeMicroseconds((int)jointval[0]);
check = true;
}
void joint2_callback(const std_msgs::Float64& msg){
jointval[1] = msg.data;
//buf[1] = jointval[1];
//myservo[1].writeMicroseconds((int)jointval[1]);
}
void joint3_callback(const std_msgs::Float64& msg){
jointval[2] = msg.data;
//buf[2] = jointval[2];
//myservo[2].writeMicroseconds((int)jointval[2]);
}
void joint4_callback(const std_msgs::Float64& msg){
jointval[3] = msg.data;
//buf[3] = jointval[3];
//myservo[3].writeMicroseconds((int)jointval[3]);
}
void joint5_callback(const std_msgs::Float64& msg){
jointval[4] = msg.data;
//buf[4] = jointval[4];
//myservo[4].writeMicroseconds((int)jointval[4]);
}
ros::Subscriber sub1("joint1_value", joint1_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub2("joint2_value", joint2_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub3("joint3_value", joint3_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub4("joint4_value", joint4_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub5("joint5_value", joint5_callback);
void AttachServosAndInit()
{
for (byte i = 0; i < SERVO_NUM; i++){
myservo[i].attach(servo_pin[i]);
myservo[i].writeMicroseconds(init);
}
}
void subscribeToAll()
{
nh.subscribe(sub1);
nh.subscribe(sub2);
nh.subscribe(sub3);
nh.subscribe(sub4);
nh.subscribe(sub5);
}
/*
时间处理函数,第一个参数是上一次处理时间点, 第二个参数是处理时间间隔,
到达时间间隔返回0,否则返回1
*/
bool handleTimePeriod( unsigned long *ptr_time, unsigned int time_period) {
if((millis() - *ptr_time) < time_period) {//millis()返回Arduino开始运行当前程序以来经历的毫秒数
return 1;
} else{
*ptr_time = millis();
return 0;
}
}
//解析订阅得到的PWM
void analyJoint()
{
for (byte i = 0; i < SERVO_NUM; i++)
servo_do[i].aim = (int)jointval[i];
}
//舵机PWM增量处理函数,每隔SERVO_TIME_PERIOD毫秒处理一次,这样就实现了舵机的连续控制
void handleServo()
{
static unsigned long systick_ms_bak = 0;
if(handleTimePeriod(&systick_ms_bak, SERVO_TIME_PERIOD))return; //20ms处理一次,不到20ms则返回不处理
for(byte i = 0; i < SERVO_NUM; i++) {
if(abs( servo_do[i].aim - servo_do[i].cur) <= abs (servo_do[i].inc) ) {//这里就体现了这个程序的精度,SERVO_TIME_PERIOD越小精度越高
myservo[i].writeMicroseconds(servo_do[i].aim);
} else {
if (servo_do[i].aim < servo_do[i].cur )
servo_do[i].cur -= servo_do[i].inc;
else
servo_do[i].cur += servo_do[i].inc;
myservo[i].writeMicroseconds((int)servo_do[i].cur);
}
}
}
void setup(){
nh.initNode();
subscribeToAll();
AttachServosAndInit();
}
void loop(){
nh.spinOnce();
analyJoint();
if (check){//保证起始状态为中间位置
handleServo();
}
}
效果图
运行命令rosrun rosserial_python serial_node.py /dev/ttyUSB0
rqt_graph

附上一张定妆照
参考
ros之真实驱动diy6自由度机械臂
ros之真实驱动diy6自由度机械臂(moveit中controller源码)
ROS进阶——通过MoveIt!控制实体机械臂PC层
MoveIt!