Python面向对象进阶之闭包
闭包
1. 函数引用
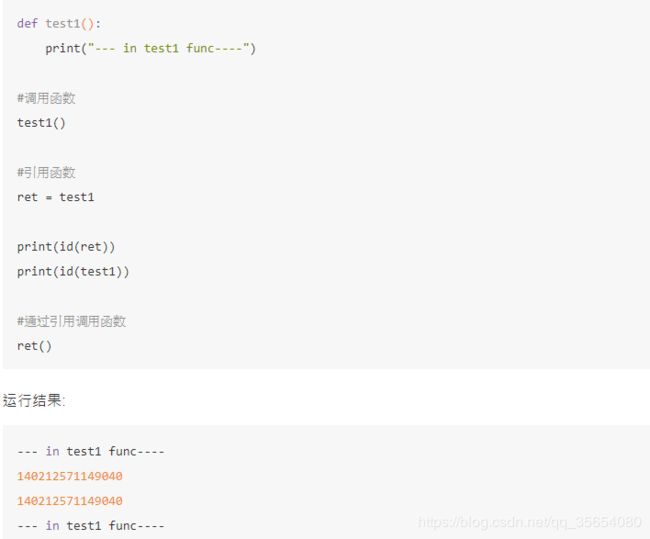
def test1():
print('---start---')
#调用函数
test1()
#引用函数
res=test1
print(id(res))
print(id(test1))
#通过引用调用函数
res()结果:
D:\Anaconda\python.exe E:/pythonwork/黑马/面向对象进阶之闭包.py
---start---
47465744
47465744
---start---
Process finished with exit code 0
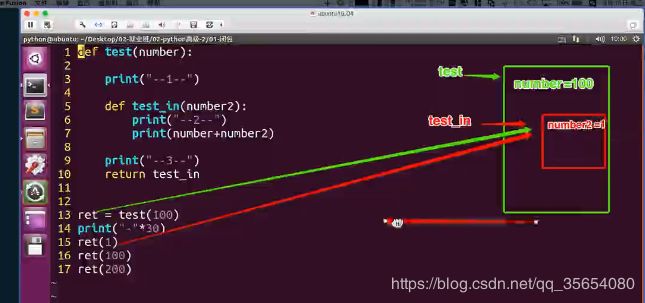
2. 什么是闭包
"""闭包"""
#定义一个函数
def test(number):
#在函数内部再定义一个函数,并且这个函数用到了外边函数的变量,那么将这个函数以及用到的一些变量称之为闭包
def test_in(number_in):
print('in test_in 函数,number_in is %d'%number_in)
return number_in+number
#其实这里返回的就是闭包的结果
return test_in
#给test函数赋值,这个20就是给参数number
res=test(20)
#这里的100其实是给参数number_in
print(res(100))
#这里的200其实是给参数number_in
print(res(200))结果:
D:\Anaconda\python.exe E:/pythonwork/黑马/面向对象进阶之闭包.py
in test_in 函数,number_in is 100
120
in test_in 函数,number_in is 200
220
Process finished with exit code 0
3. 闭包再理解
内部函数对外部函数作用域里变量的引用(非全局变量),则称内部函数为闭包。
"""3.闭包再理解"""
def counter(start=0):
count=[start]
def incr():
count[0]+=1
return count[0]
return incr
c1=counter(5)
print(c1())
print(c1())
print(c1())结果:
D:\Anaconda\python.exe E:/pythonwork/黑马/面向对象进阶之闭包.py
6
7
8
Process finished with exit code 0
nonlocal访问外部函数的局部变量(python3)
"""nonlocal访问外部函数的局部变量"""
def counter(start=0):
def incr():
nonlocal start
start+=1
return start
return incr
c1=counter(5)
print(c1())
print(c1())
c2=counter(50)
print(c2())
print(c2())
print(c1())
print(c1())
print(c2())
print(c2())结果:
D:\Anaconda\python.exe E:/pythonwork/黑马/面向对象进阶之闭包.py
6
7
51
52
8
9
53
54
Process finished with exit code 0
闭包例子
"""闭包例子"""
def line_conf(a,b):
def line(x):
return a*x+b
return line
line1=line_conf(1,1)
print(line1(5))
line2=line_conf(4,5)
print(line2(5))结果:
D:\Anaconda\python.exe E:/pythonwork/黑马/面向对象进阶之闭包.py
6
25
Process finished with exit code 0
这个例子中,函数line与变量a,b构成闭包。在创建闭包的时候,我们通过line_conf的参数a,b说明了这两个变量的取值,这样,我们就确定了函数的最终形式(y = x + 1和y = 4x + 5)。我们只需要变换参数a,b,就可以获得不同的直线表达函数。由此,我们可以看到,闭包也具有提高代码可复用性的作用。
如果没有闭包,我们需要每次创建直线函数的时候同时说明a,b,x。这样,我们就需要更多的参数传递,也减少了代码的可移植性。
闭包思考:
1.闭包似优化了变量,原来需要类对象完成的工作,闭包也可以完成
2.由于闭包引用了外部函数的局部变量,则外部函数的局部变量没有及时释放,消耗内存