动态规划-树形DP
文章目录
- 树形DP
- HDU-1520
- HDU-2196
树形DP
树形DP,顾名思义是在「树」这种数据结构上进行的DP,往往给定一棵树,通过指定操作求最小代价或最大收益等。
一般方向主要分①从子节点向根节点传递信息,②根节点向子节点传递
树操作一般利用递归和搜索,如树的遍历等,用dfs编程会比较简单,但往往状态转移方程不好设计,常常比较难(主要是我太菜了 ),令人头秃。做题步骤一般是:建树、树的遍历、DP。

HDU-1520
HDU-1520Anniversary party
Problem Description
There is going to be a party to celebrate the 80-th Anniversary of the Ural State University. The University has a hierarchical structure of employees. It means that the supervisor relation forms a tree rooted at the rector V. E. Tretyakov. In order to make the party funny for every one, the rector does not want both an employee and his or her immediate supervisor to be present. The personnel office has evaluated conviviality of each employee, so everyone has some number (rating) attached to him or her. Your task is to make a list of guests with the maximal possible sum of guests’ conviviality ratings.
Input
Employees are numbered from 1 to N. A first line of input contains a number N. 1 <= N <= 6 000. Each of the subsequent N lines contains the conviviality rating of the corresponding employee. Conviviality rating is an integer number in a range from -128 to 127. After that go T lines that describe a supervisor relation tree. Each line of the tree specification has the form:
L K
It means that the K-th employee is an immediate supervisor of the L-th employee. Input is ended with the line
0 0
Output
Output should contain the maximal sum of guests’ ratings.
Sample Input
7
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 3
2 3
6 4
7 4
4 5
3 5
0 0
Sample Output
5
题意: 树上每个结点都有一个权值,相邻的父节点和子节点只能选择一个,求最大权值和。
定义 d p [ i ] [ j ] dp[i][j] dp[i][j]代表以第 i i i个节点为根的子树能得到的最大值, j = 0 j=0 j=0代表选 i i i, j = 1 j =1 j=1代表不选 i i i。考虑将从子节点向跟节点传递的顺序,每个结点都有两种选择:选和不选,复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
①如果不选,那么它的子节点可选可不选,取最大值即可;
- d p [ u ] [ 0 ] + = m a x ( d p [ s o n ] [ 1 ] , d p [ s o n ] [ 0 ] ) dp[u][0]+=max(dp[son][1],dp[son][0]) dp[u][0]+=max(dp[son][1],dp[son][0])
②如果选,那么它的子结点就不能选了;
- d p [ u ] [ 1 ] + = d p [ s o n ] [ 0 ] dp[u][1]+=dp[son][0] dp[u][1]+=dp[son][0]
#includeHDU-2196
HDU-2196Computer
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer’s id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
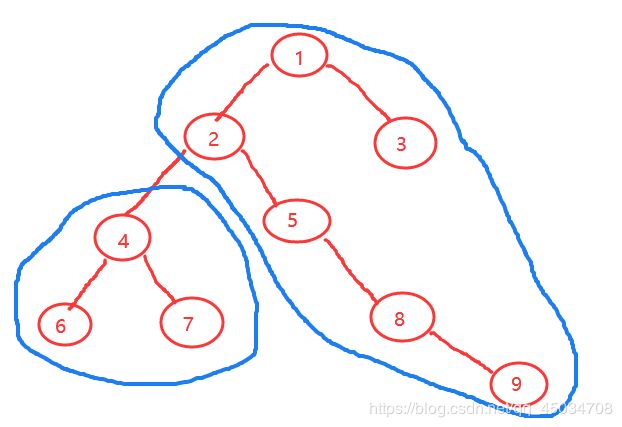
**题意:**给定一棵树若干结点间的距离,对其中任意结点,求离它最远的结点的距离。
① 以4为顶点的子树(左半篮圈),距4最远距离 L 1 L_1 L1,那么对它的子树做一次dfs即可求 L 1 L_1 L1,同样的,求所有结点的 L 1 L_1 L1,可以从根节点 1 1 1开始dfs,在返回过程中记录最大深度,即该结点 L 1 L_1 L1的值(实际编程算了最长距离 l 1 l_1 l1,次长距离 l 2 l_2 l2)。
② 设剩下右半篮圈部分到结点 4 4 4的最优距离为 L 2 L_2 L2,那么 L 2 = L_2= L2=父结点2的最长距离+dist[2][4],dist[2][4]表示结点2和4的距离,剩下关键是求父结点2的最长距离。分为2种情况:
- 从结点2往上走,即路径2-1-3,可以用dfs更新。
- 从结点2往下走(子树的最长距离 x x x),即路径2-5-8-9。若结点4在父结点2的最长子树上, x = l 2 + d i s t [ 2 ] [ 4 ] x=l_2+dist[2][4] x=l2+dist[2][4];若在, x = l 1 + d i s t [ 2 ] [ 4 ] x=l_1+dist[2][4] x=l1+dist[2][4]。
综上,距离结点4的最远距离是 m a x ( L 1 , L 2 ) max(L_1,L_2) max(L1,L2),用dfs1()实现①,dfs2()实现②,dfs1和dfs2的复杂度都是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- d p [ i ] [ 0 ] dp[i][0] dp[i][0]表示结点 i i i往下走的最长距离
- d p [ i ] [ 1 ] dp[i][1] dp[i][1]表示结点 i i i往下走的次长距离
- d p [ i ] [ 2 ] dp[i][2] dp[i][2]表示结点 i i i往上走的最长距离
#include原创不易,请支持正版。(百度发现我的好多博客被抄袭
qswl)
博主首页:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45034708
你的点赞将会是我最大的动力,关注一波