sklearn不够用?尝试更高级的机器学习扩展库:mlxtend
机器学习
Author:louwill
mlxtend是一款高级的机器学习扩展库,可用于日常机器学习任务的主要工具,也可以作为sklearn的一个补充和辅助工具。
mlxtend主要包括以下模块:
分类器
聚类器
数据
评估方法
特征提取
特征选择
文件读写
关联算法
常见概念
图像
数学
绘图
预处理
回归器
文本
下面分别从分类器、图像、绘图和预处理等几个模块来展示mlxtend的强大功能。
分类器
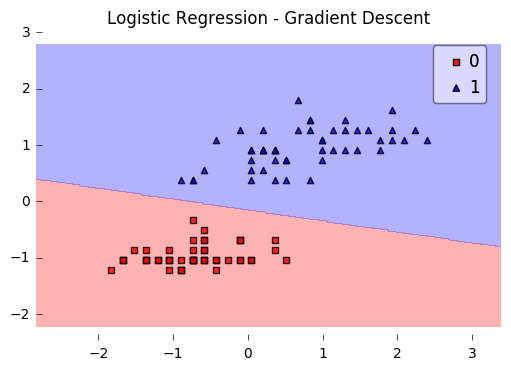
mlxtend提供了多种分类和回归算法api,包括多层感知机、stacking分类器、逻辑回归等。以逻辑回归为例:
from mlxtend.data import iris_data
from mlxtend.plotting import plot_decision_regions
from mlxtend.classifier import LogisticRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Loading Data
X, y = iris_data()
X = X[:, [0, 3]] # sepal length and petal width
X = X[0:100] # class 0 and class 1
y = y[0:100] # class 0 and class 1
# standardize
X[:,0] = (X[:,0] - X[:,0].mean()) / X[:,0].std()
X[:,1] = (X[:,1] - X[:,1].mean()) / X[:,1].std()
lr = LogisticRegression(eta=0.1,
l2_lambda=0.0,
epochs=100,
minibatches=1, # for Gradient Descent
random_seed=1,
print_progress=3)
lr.fit(X, y)
plot_decision_regions(X, y, clf=lr)
plt.title('Logistic Regression - Gradient Descent')
plt.show()
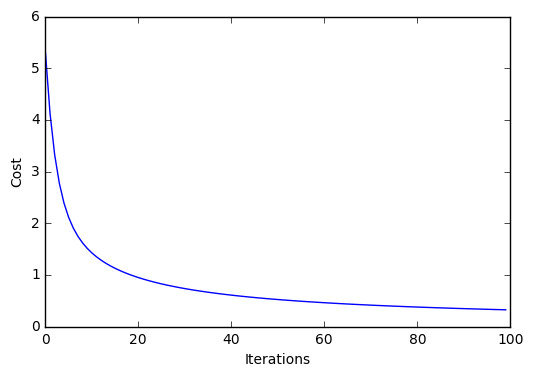
plt.plot(range(len(lr.cost_)), lr.cost_)
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.show()
图像
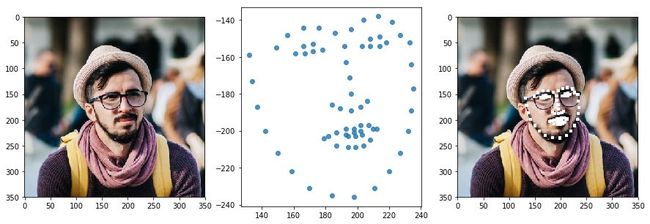
图像模块提供了人脸特征点提取的api,示例如下:
import imageio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mlxtend.image import extract_face_landmarks
img = imageio.imread('test-face.png')
landmarks = extract_face_landmarks(img)
print(landmarks.shape)
print('\n\nFirst 10 landmarks:\n', landmarks[:10])
可视化展示:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 1)
ax.imshow(img)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 2)
ax.scatter(landmarks[:, 0], -landmarks[:, 1], alpha=0.8)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3)
img2 = img.copy()
for p in landmarks:
img2[p[1]-3:p[1]+3,p[0]-3:p[0]+3,:] = (255, 255, 255)
ax.imshow(img2)
plt.show()
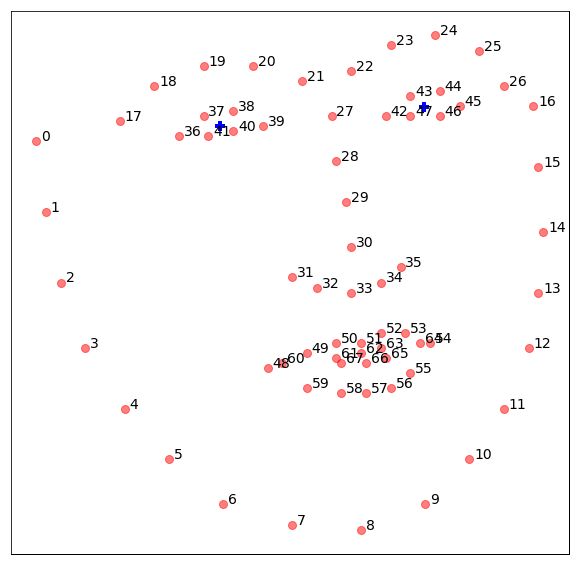
展示人脸特征点:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
left = np.array([36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41])
right = np.array([42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.plot(landmarks[:,0], -landmarks[:,1], 'ro', markersize=8, alpha = 0.5)
for i in range(landmarks.shape[0]):
plt.text(landmarks[i,0]+1, -landmarks[i,1], str(i), size=14)
left_eye = np.mean(landmarks[left], axis=0)
right_eye = np.mean(landmarks[right], axis=0)
print('Coordinates of the Left Eye: ', left_eye)
print('Coordinates of the Right Eye: ', right_eye)
plt.plot([left_eye[0]], [-left_eye[1]],
marker='+', color='blue', markersize=10, mew=4)
plt.plot([right_eye[0]], [-right_eye[1]],
marker='+', color='blue', markersize=10, mew=4)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
Coordinates of the Left Eye: [169.33333333 156. ]
Coordinates of the Right Eye: [210.83333333 152.16666667]
绘图
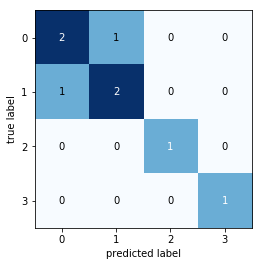
mlxtend的绘图模块提供了各种机器学习辅助绘图工具,比如分类散点图、热图、决策边界图、多分类混淆矩阵图等等。以多分类混淆矩阵图为例,sklearn的plot_confusion模块只提供了绘制二分类的混淆矩阵图,如果想绘制多分类的混淆矩阵,尝试使用mlxtend的plot_confusion_matrix函数。示例如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mlxtend.evaluate import confusion_matrix
from mlxtend.plotting import plot_confusion_matrix
y_target = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 3]
y_predicted = [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 3]
cm = confusion_matrix(y_target=y_target,
y_predicted=y_predicted,
binary=False)
fig, ax = plot_confusion_matrix(conf_mat=cm)
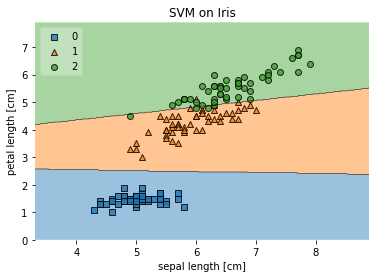
plt.show()再来看如何绘制模型的决策边界图。比如我们想看看SVM在iris数据集上的分类效果,尝试绘制其决策边界图:
from mlxtend.plotting import plot_decision_regions
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Loading some example data
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, [0, 2]]
y = iris.target
# Training a classifier
svm = SVC(C=0.5, kernel='linear')
svm.fit(X, y)
# Plotting decision regions
plot_decision_regions(X, y, clf=svm, legend=2)
# Adding axes annotations
plt.xlabel('sepal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('petal length [cm]')
plt.title('SVM on Iris')
plt.show()
预处理
mlxtend预处理模块提供了各种数据标准化和归一化方法,这里以分类变量的one-hot编码为例。mlxtend下的one_hot可对列表或numpy数组的数据进行转换:
from mlxtend.preprocessing import one_hot
import numpy as np
# numpy array
y = np.array([0, 1, 2, 1, 2])
one_hot(y)
from mlxtend.preprocessing import one_hot
# list
y = [0, 1, 2, 1, 2]
one_hot(y)mlxtend其他模块和更多功能参考官方文档:
http://rasbt.github.io/mlxtend/
GitHub源码地址:
https://github.com/rasbt/mlxtend
参考资料:
http://rasbt.github.io/mlxtend/user_guide
往期精彩: