JAVA个人学习笔记
(1)导包,智能感应
import java.util.Scanner;
(2)输出语句:
System.out.println("Hello JAVA");
输入语句前导
Scanner in =new Scanner(System.in);//做in这个东西,目前不知道是啥
(3)读用户的输入(应声虫):
System.out.println(in.nextLine());//读入下一行
(4)用+连接两个字符串:
System.out.println("echo:"+in.nextLine());
(5)常量:
final int a=100;
定义一些固定的值
(6)浮点数不能比大小
判断两个浮点数是否相等的办法:
package rrr;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a=1.0;
double b=0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1;
System.out.println(Math.abs(a-b)<1e-6);
}
}
输出结果:true
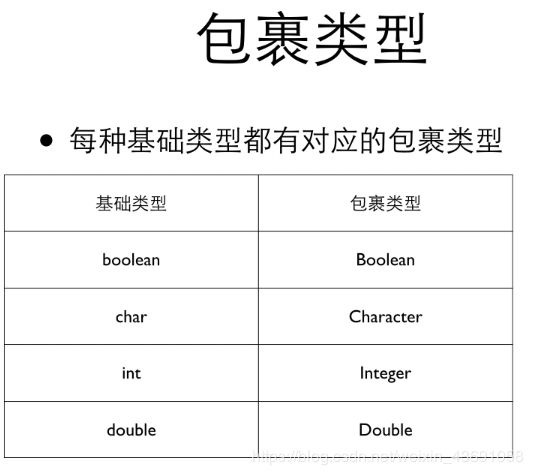
(7)逻辑类型 布尔定义用boolean
(8)break语句是跳出switch、do-while、for、while等循环语句,不能用于跳出if语句。 if中单独使用break是错误用法,除非在一个大循环中使用。
(9)定义数组:
int[] number=new int[101];
(10)对数组做遍历:
for(<类型><变量>:<数组>)

(11)unicode码相关
https://www.cnblogs.com/csguo/p/7401874.html
(12)字符大小写转换:
大写换小写:
char c='A';
char d=(char)(c+'a'-'A');
System.out.println(d);
小写换大写:
char c='a';
char d=(char)(c+'A'-'a');
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Math.abs(-12)); //绝对值
System.out.println(Math.round(10.345)); //四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.random());//随机数[0,1)
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3));//计算次方(double)
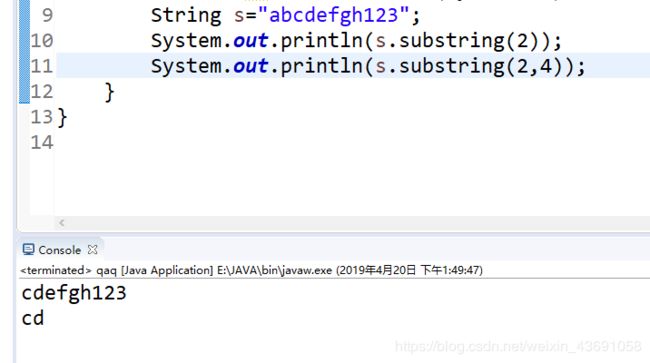
(16)字符串变量:

(17)输入字符串:

(18)字符串判断是否相等:
String s;
s=in.next();
System.out.println(s.equals("abc"));
①比较大小:
s1.compareTo(s2)如果:
s1>s2,返回正数
s1
s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)可以不区分大小写的比较大小
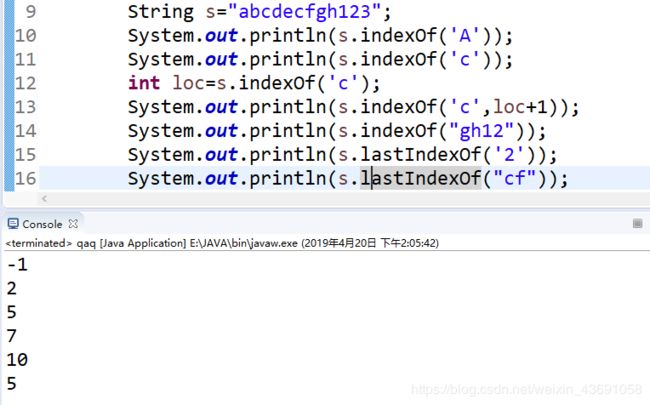
②获得长度
s.length()
③访问单个字符
s1.charAt(0)
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1="abc";
System.out.println(s1.charAt(0));
字符串不能用foreach循环

JAVA中字符串不可变
1.是否以另一个子字符串开头
2.是否以另一个子字符串结尾
3.删除字符串两端空格
4.把字符串中所有c1换成c2
5.把字符串中所有字符换成小写字母
6.把字符串中所有字符换成大写字母
(21)对数组进行排序
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ceshi{
public static void main(String []args){
int[] a={1,8,4,6,12,89,100,85};
Arrays.sort(a);
for(int i=a.length-1;i>=0;i--)
{
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}