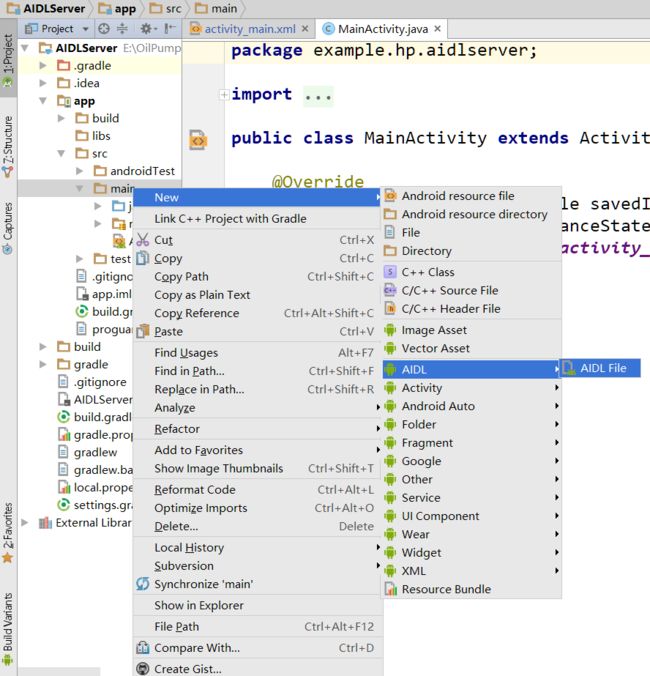
AIDL实现两个进程通信
前言
aidl是用于Android 进程间通信的一种方式,通过使用aidl,A进程可以调用B进程的Service中的方法,从而实现数据传递和通信。
下面用一个简单实例一步步实现aidl通信,此次实例需要一个Server项目和一个Client项目,我们想实现的是,Client进程可以从Server进程中获取数据。
Server端实现
输入aidl文件名之后,Android studio会自动把aidl文件放到一个和Android 项目的java文件相同包名的文件夹下,如图所示:
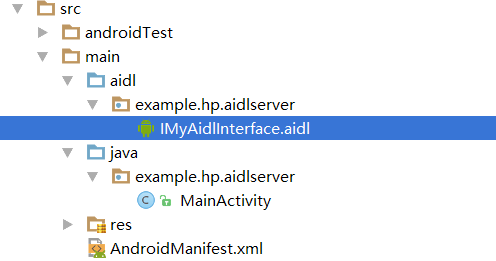
生成的aidl文件我们命名为IMyAidlInterface.aidl,它的包名为example.hp.aidlserver,和java文件对应的包名是一模一样的。
将IMyAidlInterface.aidl的文件内容修改如下:
package example.hp.aidlserver;
interface IMyAidlInterface {
int getValue(); //自定义的抽象方法,供cilent进程调用
}此时把Server项目运行一下,就会发现在Build目录下生成了IMyAidlInterface.java文件:

打开这个IMyAidlInterface.java文件,可以看到这个Java类内容如下,
下面的代码都是项目自动生成的:
package example.hp.aidlserver;
public interface IMyAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface {
/**
* Local-side IPC implementation stub class.
*/
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface";
/**
* Construct the stub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface))) {
return ((example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface) iin);
}
return new example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getValue: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _result = this.getValue();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
private static class Proxy implements example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public int getValue() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getValue, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_getValue = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
}
public int getValue() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
其中有个Stub内部类非常重要,它就是我们实现aidl通信的关键,它继承了Binder类,并实现了IMyAidlInterface接口。
接下来,我们要在Server项目里定义一个Service,供Client进程通过bindService的方式进行调用。这个Service建立在java目录下,命名为MyService.class:
package example.hp.aidlserver;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class MyService extends Service {
IMyAidlInterface.Stub stub = new IMyAidlInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public int getValue() throws RemoteException {
return 99;
}
};
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return stub;
}
}可以看到,我们在MyService的onBind方法里返回了一个IMyAidlInterface.Stub的对象,这个对象实现了aidl接口定义的getValue()方法,返回值为99。
Client端实现
新建Client项目,然后把Server项目的aidl整个文件夹拷贝过来,放到Client项目里。注意是完全拷贝,不用做任何修改,拷贝过来后的Client项目结构如下:
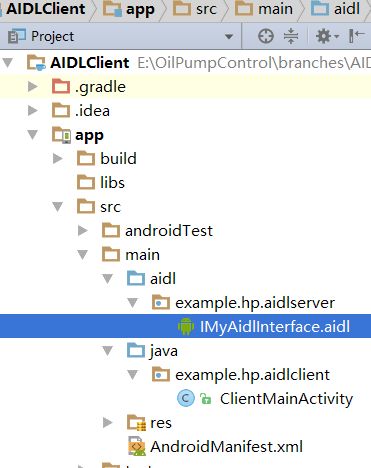
然后我们就可以在Client端的activity里,通过bindServer的方式拿到Server端的Binder实例,从而可以调用getValue()方法,具体怎么做呢?如下是Client端的activity代码,我们让页面打开的时候从Server端获取数据:
package example.hp.aidlclient;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import example.hp.aidlserver.IMyAidlInterface;
public class ClientMainActivity extends Activity {
private boolean mBound = false;
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceConnected");
mBound = true;
IMyAidlInterface iface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
try {
int value = iface.getValue();
Log.d(TAG, "get value: " + value);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_client_main);
Intent intent = new Intent();
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName("example.hp.aidlserver", "example.hp.aidlserver.MyService");
intent.setComponent(componentName);
bindService(intent, connection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (mBound) {
unbindService(connection);
}
}
}先运行Server,再运行Client,运行后打印结果为:
02-28 22:18:35.566 29647-29647/example.hp.aidlclient D/MyService: onServiceConnected
02-28 22:18:35.566 29647-29647/example.hp.aidlclient D/MyService: get value: 99可见Client进程已经成功地获取到了Server进程的数据。