栈和递归解决迷宫问题
先给出一个迷宫的模型。0代表通路,1代表墙壁,知道出入口后,找到入口到出口之间的通路。
先给出一个简单迷宫模型

现在令下方为出口方向,[2,0]作为入口寻找通路。将走过的路程标记为2。
此时可以发现迷宫存在一个分叉口,假如以顺时针方向对是否存在通路进行判别,则必定会先走没有出口的那一条死路,而当走进死路时,需要进行回溯。
此时可以开辟一个栈用来维护这条通路,先将入口进行压栈,随后判别通路,将通路压栈,当走到死路的时候,进行一次出栈操作。当回溯到有其他通路时,则进行压栈,保存下一条通路了。
代码实现:
利用递归保证对每一条通路都会进行判别。
#pragma once
#include
#include
class Maze
{
public:
Maze(int maze[][N]); //初始化一个迷宫
void Print(); //打印迷宫
bool CheckAccess(Pos next); //判断该点是否合法
bool GetPath(Pos entry);
protected:
int _maze[M][N];
};
template
Maze::Maze(int maze[][N]) { //初始化迷宫
for (size_t i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++) {
_maze[i][j] = maze[i][j];
}
}
}
template
void Maze::Print() { //打印迷宫
for (size_t i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++) {
cout << _maze[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
template
bool Maze::CheckAccess(Pos next) { //判断该点是否合法
//不溢出或者有通路返回真
if (next._row < M&&next._col < N&&_maze[next._row][next._col] == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
template
bool Maze::GetPath(Pos entry) { //找出口
Pos cur;
cur = entry;
Pos next;
stack 期待的运行方式:

运行结果:

与所期待的运行结果相同。
缺点:不能对有两条通路以上的迷宫求最优解,也不能对带环的迷宫进行求解。
解决求解有两条以上通路以及带环的迷宫的最短路;
对于带有两条以上通路的迷宫:
依然使用栈进行压栈,出栈(回溯)操作,此时在程序内另外开辟一个shortPath用来保存最短路程。path用来保存每一次的通路路程。每找到一条通路就用path和shortPath比较,如果path比shortPath更短,则将path赋值给shortPath。
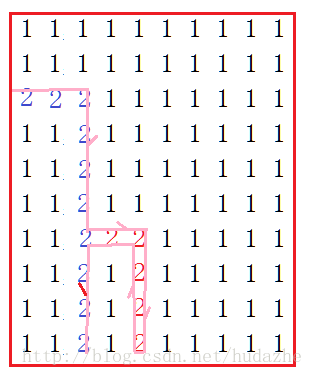
其中蓝色路线是shortPath中所保存的最短路程。
对于带有环的迷宫:
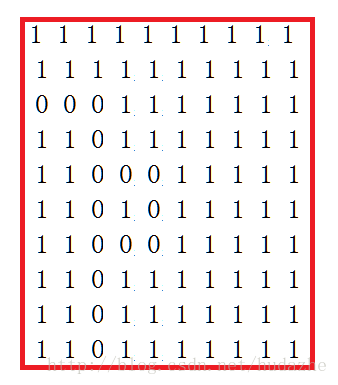
如果用之前的代码会发现,程序保存的最短路程将会是。
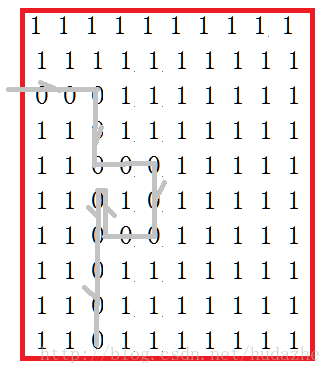
并不是我们所期待的最短路了。
此时之前的2标记法已经不再够用,通路的判别方式也需要改变。
1.现在让入口的标记为2,之后每一个通路点都是前一个点+1。
2.判断通路的条件改为
if (((next._row < M&&next._col < N)&&(_maze[next._row][next._col] == 0))||(_maze[cur._row][cur._col]<_maze[next._row][next._col]))
//不越界&&有通路 || 下一个点的坐标值大于当前点的坐标值此时的通路应该为:

程序走过的路程为:
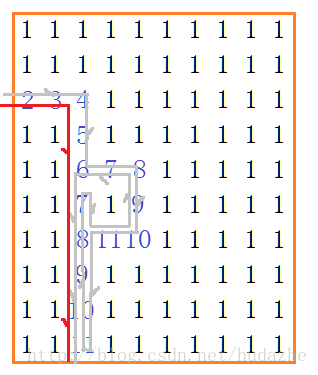
这边是迷宫的最终版本
实现:
template
class Maze
{
public:
Maze(int maze[][N]); //初始化一个迷宫
void Print(); //打印迷宫
bool CheckAccess(Pos cur,Pos next) { //判断该点是否合法
//不溢出或者有通路返回真
if (((next._row < M&&next._col < N)&&(_maze[next._row][next._col] == 0))||(_maze[cur._row][cur._col]<_maze[next._row][next._col]))
return true;
return false;
}
void GetPath(Pos entry, stack
Maze::Maze(int maze[][N]) { //初始化迷宫
for (size_t i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++) {
_maze[i][j] = maze[i][j];
}
}
}
template
void Maze::Print() { //打印迷宫
for (size_t i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++) {
cout << _maze[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
int mazeA[10][10] = {
{ 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 2,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 }, //令入口直接为2更方便
{ 1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 }
};
Maze<10, 10>maze(mazeA);
maze.Print();
Pos entry = { 2,0 };
stack