OSG获取模型坐标点、索引、法向量、纹理等数据
(文章很长,如果想直接看源码不想听我啰嗦的话,请直接跳到最后下载源码)
如果要做针对模型的算法,获取模型中所有图元(由于OSG多边形只支持三角形图元,而且自己做的科研也是针对三角网模型的,本文就针对三角形模型来说明)的坐标、纹理、法向量等数据,然后再进行处理是非常重要的,但是网上关于获取图元属性的教程实在太少,而且有的说的也不是很清楚,自己在做科研的过程中,探索以后,记录在此,希望能帮助到有需要的同学。
首先要知道,在osg中几何图元是被几何体(osg::Geometry)管理的,osg::Geometry提供了管理几何图元osg::PrimitiveSet的数组,用来添加和删除这些图元,这些图元共同构成了几何体对象。要访问图元的属性,应该就要在geometry中找,查看geometry的函数,发现有两个访问者函数:
virtual void accept(PrimitiveFunctor& pf) const;
virtual void accept(PrimitiveIndexFunctor& pf) const;根据命名我们可以看出,这两个函数对应着图元的访问和图元索引的访问。Geometry的父类Drawable也有这两个函数。因为在Node中,我们很容易拿到Drawable,所以我们要获取图元的属性,应该是要给Drawable传入访问器,然后在访问器的apply中获取图元的属性了。
通过查文档,我们发现Drawale支持四个visitor来获取Drawable的信息,分别是:
virtual void accept(AttributeFunctor&);
virtual void accept(ConstAttributeFunctor&) const;
virtual void accept(PrimitiveFunctor&) const;
virtual void accept(PrimitiveIndexFunctor&) const;我们要访问图元的属性和索引,主要用到的是AttributeFunctor还有PrimitiveIndexFunctor。首先看AttributeFunctor类的定义:
class AttributeFunctor
{
public:
virtual ~AttributeFunctor() {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,GLbyte*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,GLshort*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,GLint*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,GLubyte*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,GLushort*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,GLuint*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,float*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec2*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec3*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec4*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec4ub*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,double*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec2d*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec3d*) {}
virtual void apply(AttributeType,unsigned int,Vec4d*) {}
};
不出所料,就是在不同的apply函数中,可以获取不同类型的属性信息。
再看PrimitiveIndexFunctor的实现:
class PrimitiveIndexFunctor
{
public:
virtual ~PrimitiveIndexFunctor() {}
virtual void setVertexArray(unsigned int count,const Vec2* vertices) = 0;
virtual void setVertexArray(unsigned int count,const Vec3* vertices) = 0;
virtual void setVertexArray(unsigned int count,const Vec4* vertices) = 0;
virtual void setVertexArray(unsigned int count,const Vec2d* vertices) = 0;
virtual void setVertexArray(unsigned int count,const Vec3d* vertices) = 0;
virtual void setVertexArray(unsigned int count,const Vec4d* vertices) = 0;
virtual void drawArrays(GLenum mode,GLint first,GLsizei count) = 0;
virtual void drawElements(GLenum mode,GLsizei count,const GLubyte* indices) = 0;
virtual void drawElements(GLenum mode,GLsizei count,const GLushort* indices) = 0;
virtual void drawElements(GLenum mode,GLsizei count,const GLuint* indices) = 0;
virtual void begin(GLenum mode) = 0;
virtual void vertex(unsigned int pos) = 0;
virtual void end() = 0;
void useVertexCacheAsVertexArray()
{
setVertexArray(_vertexCache.size(),&_vertexCache.front());
}
std::vector _vertexCache;
bool _treatVertexDataAsTemporary;
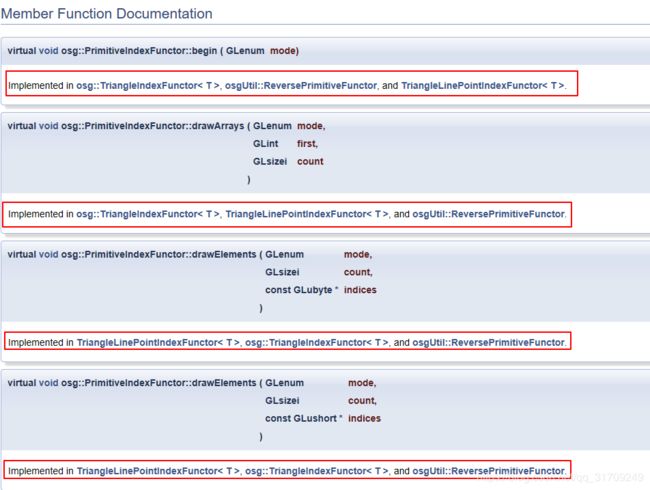
}; 可以看到,里面有函数drawElements函数,有openGL知识的通过应该知道这个函数时用来使用索引绘图的,里面通过各类参数应该可以拿到顶点的信息。但是在文档中我们看发现这个类是一个类中的函数都没有实现(如下图所示)
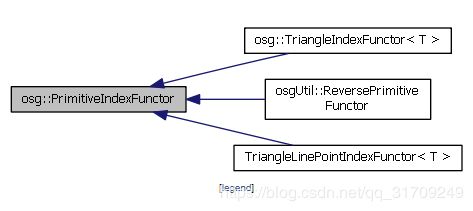
所以我们再去看看他的子类是否有实现,进一步看文档我们可以发现,PrimitiveIndexFunctor类有以下三个子类:
我们要处理的是三角形,再去看看TriangleIndexFunctor,
virtual void setVertexArray (unsigned int, const Vec2 *)
virtual void setVertexArray (unsigned int, const Vec3 *)
virtual void setVertexArray (unsigned int, const Vec4 *)
virtual void setVertexArray (unsigned int, const Vec2d *)
virtual void setVertexArray (unsigned int, const Vec3d *)
virtual void setVertexArray (unsigned int, const Vec4d *)
virtual void begin (GLenum mode)
virtual void vertex (unsigned int vert)
virtual void end ()
virtual void drawArrays (GLenum mode, GLint first, GLsizei count)
virtual void drawElements (GLenum mode, GLsizei count, const GLubyte *indices)
virtual void drawElements (GLenum mode, GLsizei count, const GLushort *indices)
virtual void drawElements (GLenum mode, GLsizei count, const GLuint *indices)
我们发现里面仍然有drawElements函数,所以我们就直接用这个类来获取模型中三角形索引的信息。从文档中得知:TriangleIndexFunctor是一个类模板,而且它继承自自身模板参数T,在模板参数中必须实现T::operator()(const unsigned& v1, const unsigned& v2, const unsigned& v3)这个函数,每绘制一个三角形,都会调用一次这个函数。这个函数中,很明显可以猜到,v1,v2,v3就是三角形三个顶点的索引。现在好办了。
1.首先定义类TriangleIndex作为TriangleIndexFunctor的模板参数T。
头文件:
#include
#include
#include
class TriangleIndex
{
public:
osg::ref_ptr indexs;//所有的索引
int triangleNum;//三角形的数量
TriangleIndex();
~TriangleIndex();
void operator()(const unsigned int& v1, const unsigned int& v2, const unsigned int& v3);
}; cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "TriangleIndex.h"
#include
TriangleIndex::TriangleIndex()
{
indexs = new osg::UIntArray;
triangleNum = 0;
}
TriangleIndex::~TriangleIndex()
{
}
void TriangleIndex::operator()(const unsigned& v1, const unsigned& v2, const unsigned& v3)
{
if (v1 == v2 || v1 == v3 || v2 == v3)
return;
indexs->push_back(v1);
indexs->push_back(v2);
indexs->push_back(v3);
triangleNum++;
} 这个函数在operator()函数中存储了所有的三角形索引的值以及三角形的数量。
2.定义类ModelAttributeFunctor继承自osg::Drawable::AttributeFunctor来获取顶点属性
上面已经说过,要获取顶点的属性,应该在AttributeFunctor函数中来获取。我们要获取顶点坐标位置和纹理坐标,顶点位置是osg::Vec3类型,而纹理坐标是osg::Vec2类型(此处不考虑三维和一维纹理)。那就应该重写以下两个函数:
virtual void apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType, unsigned, osg::Vec2*) ;
virtual void apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType, unsigned, osg::Vec3*) ;OK,我们定义类ModelAttributeFunctor继承自osg::Drawable::AttributeFunctor,然后重写上面的两个函数,然后将得到的信息保存下来。
头文件:
#include
class ModelAttributeFunctor
:public osg::Drawable::AttributeFunctor
{
public:
osg::ref_ptr vertexList;//存储顶点的数组
osg::ref_ptr normalList;//存储法向量
osg::ref_ptr textCoordList;//纹理坐标
virtual void apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType, unsigned, osg::Vec2*) override;
virtual void apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType, unsigned, osg::Vec3*) override;
ModelAttributeFunctor();
~ModelAttributeFunctor();
};
cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ModelAttributeFunctor.h"
#include
using namespace std;
ModelAttributeFunctor::ModelAttributeFunctor()
{
vertexList = new osg::Vec3Array;
normalList = new osg::Vec3Array;
textCoordList = new osg::Vec2Array;
}
ModelAttributeFunctor::~ModelAttributeFunctor()
{
}
void ModelAttributeFunctor::apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType type, unsigned size, osg::Vec2* front)
{
if (type==osg::Drawable::TEXTURE_COORDS_0)
{
for (unsigned i=0;ipush_back(*(front + i));
}
}
}
void ModelAttributeFunctor::apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType type, unsigned size, osg::Vec3* front)
{
if (type == osg::Drawable::VERTICES)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; ipush_back(*(front + i));
}
}
else if (type == osg::Drawable::NORMALS)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; ipush_back(*(front + i));
}
}
}
可以看到,在不同类型的apply函数中,获取了不同的数据,并分别存储在vertexList,normalList,textCoordList中。此处需要注意的是,apply函数中,有一个参数是osg::Drawable::AttributeType,利用这个参数可以判断是哪种类型的数据,比如法向量和顶点坐标都是osg::Vec3类型,所以在上面的void ModelAttributeFunctor::apply(osg::Drawable::AttributeType type, unsigned size, osg::Vec3* front)函数中做了判断。
3.定义存储顶点信息,三角形信息以及Node信息的类
为了存储读取得到的顶点,三角形以及三角形构成的模型部件,我定义了三个类:Vertex类用来存储顶点信息,Triangle类用来存储三角形信息,Geom类用来存储模型部件(这个在4中详细说)。
3.1定义Vertex类
头文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/**
* 顶点类,记录模型中顶点的各类信息,包括顶点坐标、法向量、纹理坐标等
*/
class Vertex
{
public:
osg::Vec3 coor;//顶点坐标
osg::Vec3 normal;//法向量
osg::Vec2 texCoor;//纹理坐标
int index;//该顶点在数组中的下标
vector neighborTriangle;//顶点相邻的三角形
Vertex();
~Vertex();
}; cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Vertex.h"
Vertex::Vertex()
{
}
Vertex::~Vertex()
{
}3.2定义Triangle类存储三角形信息
头文件:
#include
#include
#include
class Trianngle
{
public:
void init();
Trianngle();
~Trianngle();
int vertexIndexs[3];//顶点索引
osg::Vec3 normal;//法向量
int index;//该三角形在数组中的索引
std::vector neighborTriangles;//相邻的三角形的索引
}; cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Trianngle.h"
Trianngle::Trianngle()
{
init();
}
Trianngle::~Trianngle()
{
}
void Trianngle::init()
{
this->vertexIndexs[0] = this->vertexIndexs[1] = this->vertexIndexs[2] = -1;
this->normal.set(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
}3.3定义Geom类存储模型中的部件
Geom类中自己以前写了自己科研过程中创建三角形及顶点之间索引的一些函数,这里就不删除了。此外,Geom中自己写了一个函数osg::ref_ptr
头文件:
#include
#include "Vertex.h"
#include "Trianngle.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Geom
{
public:
vector vertices;//一个geom中所有的顶点信息
vector trianngles;//一个geom中的所有三角形信息
osg::BoundingBox boundingBox;//包围盒
bool isTwoTriangleNeighbor(int triangle1Index,int triangle2Index);//两个三角形是否相邻
void createTriangleTopo();//创建三角形之间的拓扑关系
void createVertexTopo();//创建顶点之间的拓扑
osg::ref_ptr createOsgNode(osg::Vec4 color);
Geom();
~Geom();
}; cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Geom.h"
#include
#include
#include "Utility.h"
#include
using namespace std;
Geom::Geom()
{
}
Geom::~Geom()
{
for (Vertex* vertex : vertices)
delete vertex;
for (Trianngle* trianngle : trianngles)
delete trianngle;
}
/**
* 判断两个三角形是否相邻
*/
bool Geom::isTwoTriangleNeighbor(int triangle1Index, int triangle2Index)
{
Trianngle* trianngle1 = trianngles.at(triangle1Index);
Trianngle* trianngle2 = trianngles.at(triangle2Index);
osg::Vec3 pnt11 = vertices.at(trianngle1->vertexIndexs[0])->coor;
osg::Vec3 pnt12 = vertices.at(trianngle1->vertexIndexs[1])->coor;
osg::Vec3 pnt13 = vertices.at(trianngle1->vertexIndexs[2])->coor;
osg::Vec3 pnt21 = vertices.at(trianngle2->vertexIndexs[0])->coor;
osg::Vec3 pnt22 = vertices.at(trianngle2->vertexIndexs[1])->coor;
osg::Vec3 pnt23 = vertices.at(trianngle2->vertexIndexs[2])->coor;
if ((Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt21) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt22))//第一条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt22) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt21))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt22) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt23))//第二条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt23) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt22))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt21) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt23))//第三条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt23) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt21))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt21) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt22))//第一条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt22) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt21))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt22) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt23))//第二条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt23) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt22))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt21) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt23))//第三条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt12, pnt23) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt21))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt21) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt22))//第一条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt22) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt21))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt22) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt23))//第二条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt23) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt22))
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt21) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt23))//第三条边
|| (Utility::isVec3Same(pnt11, pnt23) && Utility::isVec3Same(pnt13, pnt21)))
return true;
return false;
}
/**
* 创建模型的三角形之间的拓扑
*/
void Geom::createTriangleTopo()
{
cout << "开始创建三角形之间的拓扑关系:" << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; ineighborTriangles.push_back(j);
triannglej->neighborTriangles.push_back(i);
}
}
cout << "\t当前进度" << int(i*100.0 / trianngles.size()) << "%\r";
}
cout << endl;
}
/**
* 创建顶点之间的拓扑
*/
void Geom::createVertexTopo()
{
//点周围的三角形
for (size_t i=0;ivertexIndexs[0]);
vertex1->neighborTriangle.push_back(i);
Vertex *vertex2 = (Vertex*)vertices.at(trianngles.at(i)->vertexIndexs[1]);
vertex2->neighborTriangle.push_back(i);
Vertex *vertex3 = (Vertex*)vertices.at(trianngles.at(i)->vertexIndexs[2]);
vertex3->neighborTriangle.push_back(i);
cout << " 点周围的三角形:" << int(i*1.0 / trianngles.size() * 100) << "%\r";
}
}
/**
* 将Geom中的数据创建成osg节点
*/
osg::ref_ptr Geom::createOsgNode(osg::Vec4 color)
{
osg::ref_ptr geode = new osg::Geode;
osg::ref_ptr geometry = new osg::Geometry;
//顶点、法向量
osg::ref_ptr vertexArray = new osg::Vec3Array;
osg::ref_ptr normalArray = new osg::Vec3Array;
osg::ref_ptr colorArray = new osg::Vec4Array;
for (Vertex* vertex : vertices)
{
vertexArray->push_back(vertex->coor);
normalArray->push_back(vertex->normal);
}
//颜色
colorArray->push_back(color);
//索引
osg::ref_ptr indexs = new osg::DrawElementsUInt(osg::PrimitiveSet::TRIANGLES, 0);
for (Trianngle* trianngle : trianngles)
{
indexs->push_back(trianngle->vertexIndexs[0]);
indexs->push_back(trianngle->vertexIndexs[1]);
indexs->push_back(trianngle->vertexIndexs[2]);
}
geometry->setVertexArray(vertexArray);
geometry->setNormalArray(normalArray, osg::Array::BIND_PER_VERTEX);
geometry->setColorArray(colorArray, osg::Array::BIND_OVERALL);
geometry->addPrimitiveSet(indexs);
geode->addDrawable(geometry);
return geode;
} 4.创建节点访问器遍历节点,获取模型的各类数据
OK,在3中定义了那么多类,终于要开始获取节点的信息了。我们知道osg中,其实说到底,有两类节点非常重要:一个是Geode,另一个是Group。其他类的节点基本都是从这两类中继承或者封装得到的。我们在上面说过,Drawable使用accept函数,传入访问器参数,在访问器中就可以拿到模型的坐标等各类信息。那获取Drawable的话,我们知道Geode有一个函数是getDrawable,所以我们应该拿到osg场景中的所有Geode节点,然后获取其Drawable,然后应用访问器即可。获取所有Geode节点的话,就要用到OSG中的节点访问器了。关于节点访问器,我这里就不赘述了,自己可以查资料,我以后如果有时间,也想写一个关于节点访问器的博客,感兴趣的话,可以关注我的博客。我在这里定义了一个类PositionVisitor函数继承自osg::NodeVisitor,直接贴代码:
头文件:
#include
#include
#include "ModelAttributeFunctor.h"
#include
#include "TriangleIndex.h"
#include "Geom.h"
#include
using namespace std;
class PositionVisitor
:public osg::NodeVisitor
{
protected:
vector allGeom;//所有的geom
osg::Vec4 geomColor;//geom的颜色
string modelName;//模型名称
osg::BoundingBox boundingBox;//包围盒
public:
virtual void apply(osg::Geode& node) override;
void dealTriangleInfo(ModelAttributeFunctor attributeFunctor,osg::TriangleIndexFunctor indexFunctor);//处理访问器得到的信息,构建三角形关系
osg::ref_ptr createOsgNode(osg::Vec4 color,int order);//根据指定的颜色,将geom中的数据创建成osg节点
osg::ref_ptr createRandomColorOsgNode(int order);//将geom中的数据创建成osg节点,颜色随机
osg::ref_ptr createTipText(short direction);//创建提示文字
PositionVisitor(string ModelName);
~PositionVisitor();
}; cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "PositionVisitor.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include "Geom.h"
#include
#include "Trianngle.h"
#include "Vertex.h"
#include
#include
#include
PositionVisitor::PositionVisitor(string ModelName)
{
this->modelName = ModelName;
setTraversalMode(osg::NodeVisitor::TRAVERSE_ALL_CHILDREN);
}
PositionVisitor::~PositionVisitor()
{
for (Geom* geom:allGeom)
{
delete geom;
}
}
void PositionVisitor::apply(osg::Geode& node)
{
for (size_t i=0;i drawable = node.getDrawable(i);
ModelAttributeFunctor functor;
drawable->accept(functor);
osg::TriangleIndexFunctor triangleIndex;
drawable->accept(triangleIndex);
dealTriangleInfo(functor, triangleIndex);
}
}
void PositionVisitor::dealTriangleInfo(ModelAttributeFunctor attributeFunctor, osg::TriangleIndexFunctor indexFunctor)
{
Geom *geom = new Geom;
if (attributeFunctor.textCoordList->size()!=0
&&attributeFunctor.textCoordList->size()!=attributeFunctor.vertexList->size())
{
cout << "纹理坐标和顶点数量不匹配" << endl;
return;
}
//处理顶点信息
for (size_t i=0;isize();i++)
{
Vertex* vertex=new Vertex;
vertex->coor = attributeFunctor.vertexList->at(i);
vertex->index = i;
vertex->normal = attributeFunctor.normalList->at(i);
if (i< attributeFunctor.textCoordList->size())
vertex->texCoor = attributeFunctor.textCoordList->at(i);
geom->vertices.push_back(vertex);
}
//处理三角形信息
for (int i=0;iindex = i;
trianngle->vertexIndexs[0] = indexFunctor.indexs->at(i * 3);
trianngle->vertexIndexs[1] = indexFunctor.indexs->at(i * 3+1);
trianngle->vertexIndexs[2] = indexFunctor.indexs->at(i * 3+2);
//计算法向量
osg::Vec3 edge1 = geom->vertices.at(trianngle->vertexIndexs[1])->coor - geom->vertices.at(trianngle->vertexIndexs[0])->coor;
osg::Vec3 edge2 = geom->vertices.at(trianngle->vertexIndexs[2])->coor - geom->vertices.at(trianngle->vertexIndexs[0])->coor;
osg::Vec3 triangleNormal = edge1^edge2;
triangleNormal.normalize();
trianngle->normal = triangleNormal;
geom->trianngles.push_back(trianngle);
}
allGeom.push_back(geom);
}
osg::ref_ptr PositionVisitor::createOsgNode(osg::Vec4 color, int order)
{
this->geomColor = color;
short direction = order % 4;
osg::ref_ptr result = new osg::Group;
if (allGeom.size()>0&&allGeom.size()==1)
{
osg::ref_ptr geode= allGeom[0]->createOsgNode(color);
this->boundingBox = geode->getBoundingBox();
result->addChild(geode);
}
else
{
for (Geom* geom : allGeom)
result->addChild(geom->createOsgNode(color));
osg::ComputeBoundsVisitor boundsVisitor;
result->accept(boundsVisitor);
this->boundingBox = boundsVisitor.getBoundingBox();
}
result->addChild(createTipText(direction));
return result;
}
osg::ref_ptr PositionVisitor::createRandomColorOsgNode(int order)
{
//创建一个随机颜色
osg::Vec4 color = osg::Vec4(rand()%10*0.1, rand() % 10 * 0.1, rand() % 10 * 0.1, 1.0f);
this->geomColor = color;
return createOsgNode(color,order);
}
osg::ref_ptr PositionVisitor::createTipText(short direction)
{
osg::ref_ptr font = osgText::readFontFile("fonts/simhei.ttf");
osg::ref_ptr text = new osgText::Text;
text->setFont(font);//设置字体
text->setCharacterSize(5);//字体大小
//对每个组件设置不同的朝向,避免所有的提示文字都在一个朝向
osg::Vec3 tipPosition;
float halfX = (boundingBox.xMax() + boundingBox.xMin()) / 2;
float halfY = (boundingBox.yMax() + boundingBox.yMin()) / 2;
float halfZ = (boundingBox.zMax() + boundingBox.zMin()) / 2;
switch (direction)
{
case 0://左
tipPosition =osg::Vec3 (halfX, boundingBox.yMin()-1, halfZ);
text->setAxisAlignment(osgText::Text::XZ_PLANE);//文字对称方式
break;
case 1://右
tipPosition = osg::Vec3(halfX, boundingBox.yMax()+1, halfZ);
text->setAxisAlignment(osgText::Text::REVERSED_XZ_PLANE);//文字对称方式
break;
case 2://前
tipPosition = osg::Vec3(boundingBox.xMax()+1, halfY, halfZ);
text->setAxisAlignment(osgText::Text::YZ_PLANE);//文字对称方式
break;
case 3://后
tipPosition = osg::Vec3(boundingBox.xMin()-1, halfY, halfZ);
text->setAxisAlignment(osgText::Text::REVERSED_YZ_PLANE);//文字对称方式
break;
}
text->setPosition(tipPosition);//字体位置
text->setColor(this->geomColor);//字体颜色
text->setAutoRotateToScreen(false);//跟随视角不断变化,距离越远,文字越小
text->setBackdropType(osgText::Text::OUTLINE);//文件描边
text->setBackdropColor(osg::Vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0));//文字描边的颜色
text->setDrawMode(osgText::Text::TEXT | osgText::Text::BOUNDINGBOX);//添加文字边框
text->setText(modelName);
return text;
} PositionVisitor函数中,我定义了vector
1.在构造函数中一定要写上setTraversalMode(osg::NodeVisitor::TRAVERSE_ALL_CHILDREN)这一句,这样节点访问器才能遍历所有节点。
2.在PositionVisitor::apply(osg::Geode& node)函数中,可以拿到所有的Geode节点(其实说到其,一个场景,到最后,都是Geode节点组成的,所以我们只需要写这一个apply函数,就可以拿到模型的所有部分了)。因为一个Geode节点中,可能有多个Drawable,所以我定义了Geom类来存储一个Drawable。
5.工具类
上面的代码中,有一些是我写的工具类中的函数,故把工具类的定义也贴在这里吧。
头文件:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Utility
{
public:
static bool isVec3Same(osg::Vec3 v1, osg::Vec3 v2);//比较两个三维向量是否相等
static string getFileNameFromPath(string path);//从模型路径中获取明名称
static void string_replace(std::string &strBig, const std::string &strsrc, const std::string &strdst);
Utility();
~Utility();
}; cpp文件:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Utility.h"
#include
Utility::Utility()
{
}
Utility::~Utility()
{
}
/**
* 比较两个三维向量是否相同
*/
bool Utility::isVec3Same(osg::Vec3 v1, osg::Vec3 v2)
{
return (v1.x() == v2.x()) && (v1.y() == v2.y()) && (v1.z() == v2.z());
}
/**
* 用一个字符替换原字符中的另一个字符
*/
void Utility::string_replace(std::string& strBig, const std::string& strsrc, const std::string& strdst)
{
std::string::size_type pos = 0;
std::string::size_type srclen = strsrc.size();
std::string::size_type dstlen = strdst.size();
while ((pos = strBig.find(strsrc, pos)) != std::string::npos)
{
strBig.replace(pos, srclen, strdst);
pos += dstlen;
}
}
/**
* 从路径中获取文件名(不包括后缀名)
*/
string Utility::getFileNameFromPath(string path)
{
if(path.empty())
{
return "";
}
string_replace(path, "/", "\\");
std::string::size_type iPos = path.find_last_of('\\') + 1;
std::string::size_type dPos = path.find_last_of('.') + 1;
if (dPos == 0)
dPos = path.length();
return path.substr(iPos, dPos - iPos-1);
}
6.调用
调用就很简单了,只需要给节点传入Visitor就好了,然后在visitor的allGeom函数中拿到Geom对象,就可以获取模型的诸如顶点坐标,法向量,纹理坐标等各类属性了。调用示例如下:
string name = "此处是模型的路径”;
osg::ref_ptr node = osgDB::readNodeFile(name);
string modelName = Utility::getFileNameFromPath(name);
PositionVisitor visitor = PositionVisitor(modelName);
node->accept(visitor);
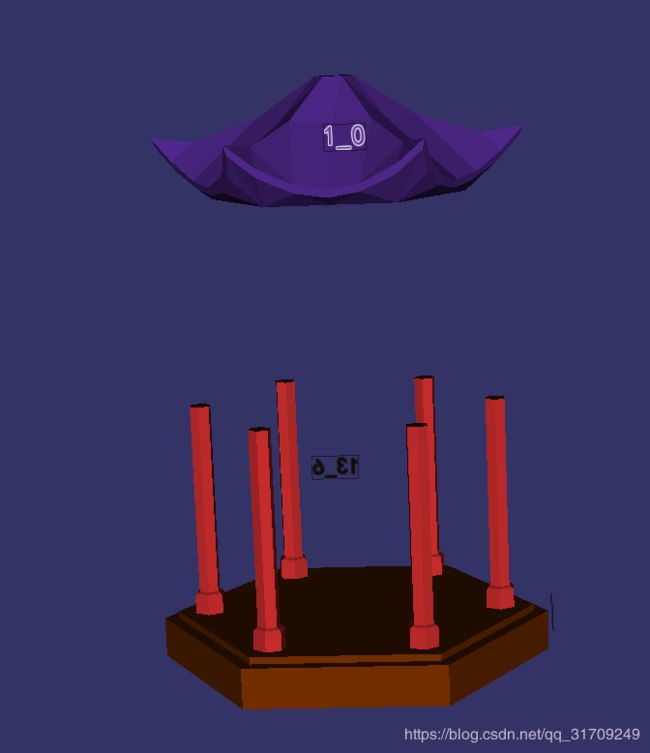
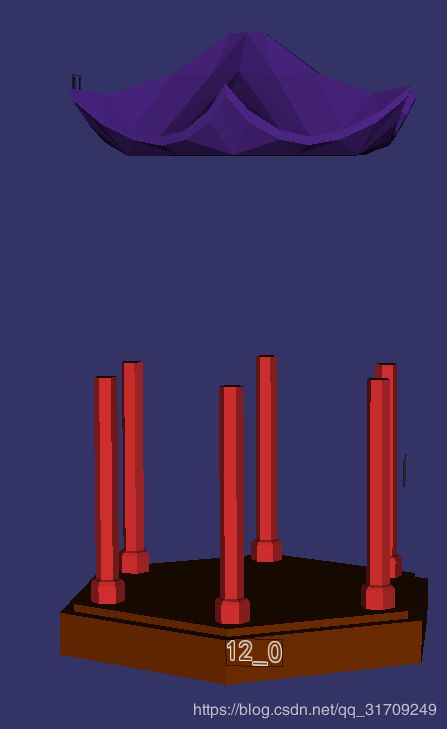
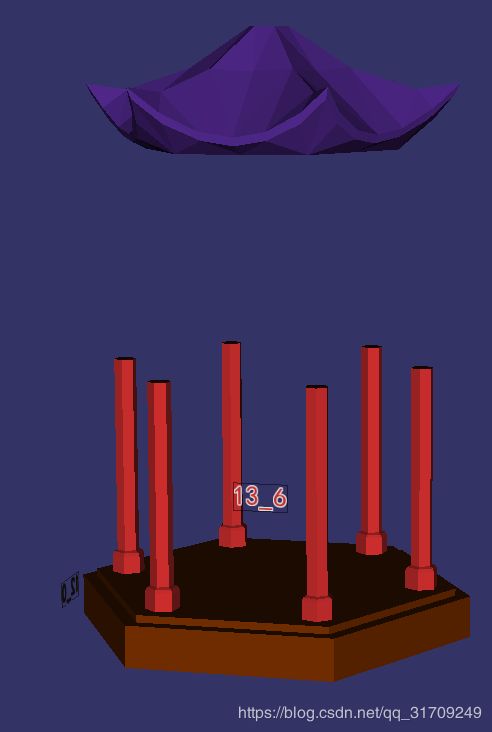
root->addChild(visitor.createRandomColorOsgNode(i)); OK,因为我要同时加载多个模型并且查看模型之间的关系,但是osg中的cmd的osgviewer命令一次只能查看一个模型,非常不方便,所以这个程序是自己写的可以同时查看多个模型的一个小工具。程序会将每个模型用一个随机的颜色纯色绘制出来,而且用相同颜色的文字显示模型的名称。效果如下:
7.源代码
源码为自己做的这个小工具的源码,如果自己想读取模型的各类属性然后自己使用的话,直接把我的类拷贝到自己的项目中使用即可。下载后,记得修改osg库目录的位置为自己的位置。
源码地址:https://github.com/MeteorCh/ModelViewer(觉得好的话记得给个star)
8.问题
我的代码应该是可以满足大部分的读取模型坐标、法向量的问题了。但是,由于自己水平有限,有些东西肯定还是会存在考虑不到的情况(比如纹理类型没有考虑完全,比如有些顶点没有纹理坐标只有颜色,本文没有考虑),有意见建议或者问题可以在评论下说明,我会尽力解答。
9. 更新日记
- 2019.08.30更新:针对模型大小不同,统一设置提示字体大小可能会出现的提示文字过大或过小的问题,添加进入程序先输入文字大小,再绘制模型的功能。当文字不合适时,可以关闭程序重新启动,多测试几次直到找到合适的文字大小。
- 2019.09.01更新:增加坐标轴显示功能。如下所示: