keras集成学习二-回归问题
keras集成学习二-回归问题
- 数据描述
- keras普通实现
- 模型结构
- 模型输出
- 模型损失曲线
- keras集成学习-平均法
- 模型结构
- 模型输出
- 模型损失曲线
- keras-scikit_learn集成学习
- 模型输出
- keras集成学习-学习法
- 模型结构
- 模型输出
- 模型损失曲线
- 代码位置
文档完整位置:https://docs.nn.knowledge-precipitation.site/ji-chu-zhi-shi/guo-ni-he/jichengxuexi-ensemble/huigui-keras
- keras集成学习一
- keras集成学习二-回归问题
- keras集成学习三-分类问题
数据描述
波士顿房价数据集(Boston House Price Dataset)(https://www.kaggle.com/c/boston-housing)
boston_housing数据集对房价数据进行回归分析,数据来自1970年代,波斯顿周边地区的房价,是用于机器学习的经典数据集。该数据集很小,共计506条数据
每条数据包含房屋以及房屋周围的详细信息。其中包含城镇犯罪率,一氧化氮浓度,住宅平均房间数,到中心区域的加权距离以及自住房平均房价等等。
- CRIM:城镇人均犯罪率。
- ZN:住宅用地超过 25000 sq.ft. 的比例。
- INDUS:城镇非零售商用土地的比例。
- CHAS:查理斯河空变量(如果边界是河流,则为1;否则为0)。
- NOX:一氧化氮浓度。
- RM:住宅平均房间数。
- AGE:1940 年之前建成的自用房屋比例。
- DIS:到波士顿五个中心区域的加权距离。
- RAD:辐射性公路的接近指数。
- TAX:每 10000 美元的全值财产税率。
- PTRATIO:城镇师生比例。
- B:1000(Bk-0.63)^ 2,其中 Bk 指代城镇中黑人的比例。
- LSTAT:人口中地位低下者的比例。
- MEDV:自住房的平均房价,以千美元计。
keras普通实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def load_data():
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = boston_housing.load_data()
x = np.vstack((x_train,x_test))
y = np.concatenate((y_train, y_test))
x = StandardScaler().fit_transform(x)
y = StandardScaler().fit_transform(y.reshape(-1, 1))
x_train = x[1:401, :]
x_test = x[401:, :]
y_train = y[1:401, :]
y_test = y[401:, :]
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
def draw_train_history(history):
# summarize history for loss
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('model loss')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
def build_model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(13,)))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='linear'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_data()
model = build_model()
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', patience=10)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs=500,
batch_size=64,
validation_split=0.2,
callbacks=[early_stopping])
draw_train_history(history)
loss = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=64)
print("test loss: {}".format(loss))
模型结构
模型输出
test loss: 0.20772670450664701
模型损失曲线
keras集成学习-平均法
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, average
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def load_data():
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = boston_housing.load_data()
x = np.vstack((x_train,x_test))
y = np.concatenate((y_train, y_test))
x = StandardScaler().fit_transform(x)
y = StandardScaler().fit_transform(y.reshape(-1, 1))
x_train = x[1:401, :]
x_test = x[401:, :]
y_train = y[1:401, :]
y_test = y[401:, :]
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
def draw_train_history(history):
# summarize history for loss
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('model loss')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
def build_model():
inputs = Input(shape=(13, ))
model1_1 = Dense(64, activation='relu')(inputs)
model2_1 = Dense(128, activation='relu')(inputs)
model3_1 = Dense(32, activation='relu')(inputs)
model1_2 = Dense(32, activation='relu')(model1_1)
model2_2 = Dense(64, activation='relu')(model2_1)
model3_2 = Dense(16, activation='relu')(model3_1)
model1_out = Dense(1, activation='linear')(model1_2)
model2_out = Dense(1, activation='linear')(model2_2)
model3_out = Dense(1, activation='linear')(model3_2)
out = average([model1_out, model2_out, model3_out])
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=out)
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_data()
model = build_model()
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', patience=10)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs=500,
batch_size=64,
validation_split=0.2,
callbacks=[early_stopping])
draw_train_history(history)
model.save("regression-average-ensemble.h5")
loss = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=64)
print("test loss: {}".format(loss))
模型结构
模型输出
test loss: 0.14132633038929532
模型损失曲线
keras-scikit_learn集成学习
import numpy as np
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasRegressor
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingRegressor
from sklearn.externals import joblib
def load_data():
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = boston_housing.load_data()
x = np.vstack((x_train,x_test))
y = np.concatenate((y_train, y_test))
x = StandardScaler().fit_transform(x)
y = StandardScaler().fit_transform(y.reshape(-1, 1))
x_train = x[1:401, :]
x_test = x[401:, :]
y_train = y[1:401, :]
y_test = y[401:, :]
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
def build_model1():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu', input_shape=(13, )))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='linear'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
def build_model2():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(13, )))
model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='linear'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
def build_model3():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu', input_shape=(13, )))
model.add(Dense(16, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='linear'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_data()
model1 = KerasRegressor(build_fn=build_model1, epochs=100, batch_size=64)
model1._estimator_type = "regressor"
model2 = KerasRegressor(build_fn=build_model2, epochs=100, batch_size=64)
model2._estimator_type = "regressor"
model3 = KerasRegressor(build_fn=build_model3, epochs=100, batch_size=64)
model3._estimator_type = "regressor"
cls = VotingRegressor(estimators=[
('model1', model1),
('model2', model2),
('model3', model3)
])
cls.fit(x_train, y_train)
joblib.dump(cls, "sklearn-regressor.h5")
print("score: ", cls.score(x_test, y_test))
这里我们使用scikit_learn中的VotingRegressor作为模型集成的工具,在sklearn的文档中是这样描述VotingRegressor的
A voting regressor is an ensemble meta-estimator that fits several base regressors, each on the whole dataset. Then it averages the individual predictions to form a final prediction.
也就是它会将每个基学习器的输出结果做平均作为最后的输出结果。
如果我们使用StackingRegressor做模型集成工具的话,他会将每个基学习器的输出再放进一个regressor中做最后的预测,也就是下面我们要实现的学习法。我们来看一下文档中的描述
Stacked generalization consists in stacking the output of individual estimator and use a regressor to compute the final prediction. Stacking allows to use the strength of each individual estimator by using their output as input of a final estimator.
模型输出
score: 0.8482947319781606
keras集成学习-学习法
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, concatenate
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def load_data():
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = boston_housing.load_data()
x = np.vstack((x_train,x_test))
y = np.concatenate((y_train, y_test))
x = StandardScaler().fit_transform(x)
y = StandardScaler().fit_transform(y.reshape(-1, 1))
x_train = x[1:401, :]
x_test = x[401:, :]
y_train = y[1:401, :]
y_test = y[401:, :]
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
def draw_train_history(history):
# summarize history for loss
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('model loss')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
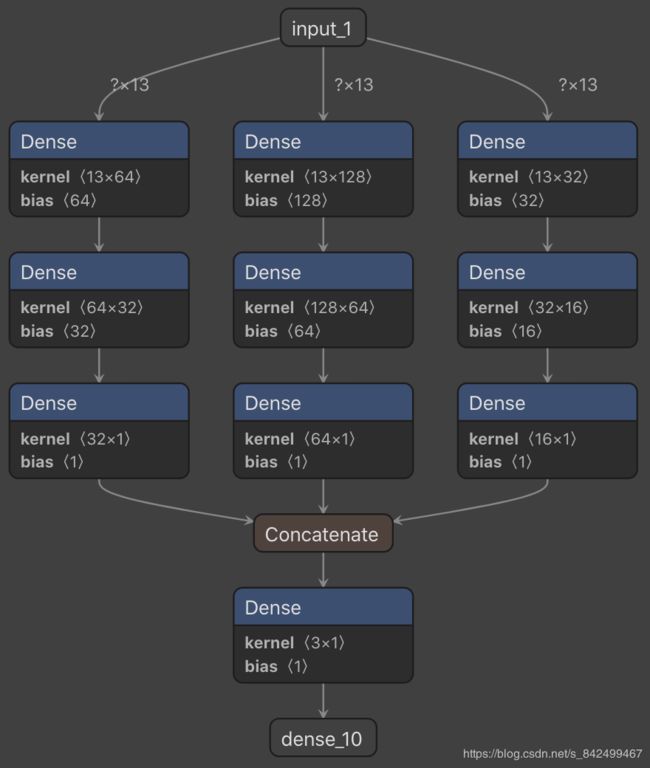
def build_model():
inputs = Input(shape=(13, ))
model1_1 = Dense(64, activation='relu')(inputs)
model2_1 = Dense(128, activation='relu')(inputs)
model3_1 = Dense(32, activation='relu')(inputs)
model1_2 = Dense(32, activation='relu')(model1_1)
model2_2 = Dense(64, activation='relu')(model2_1)
model3_2 = Dense(16, activation='relu')(model3_1)
model1_3 = Dense(1, activation='linear')(model1_2)
model2_3 = Dense(1, activation='linear')(model2_2)
model3_3 = Dense(1, activation='linear')(model3_2)
con = concatenate([model1_3, model2_3, model3_3])
output = Dense(1, activation='linear')(con)
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=output)
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_data()
model = build_model()
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', patience=10)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs=500,
batch_size=64,
validation_split=0.2,
callbacks=[early_stopping])
draw_train_history(history)
model.save("regression-ensemble.h5")
loss = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=64)
print("test loss: {}".format(loss))
模型结构
模型输出
test loss: 0.16616634471075875
模型损失曲线
代码位置
https://github.com/Knowledge-Precipitation-Tribe/Neural-network/tree/master/code/Ensemble-Learning