Vue 源码详解之生命周期
Vue 生命周期详解
注意!!! 本文是以
vue v2.6版本进行讲解。 源码地址
前言
在学习
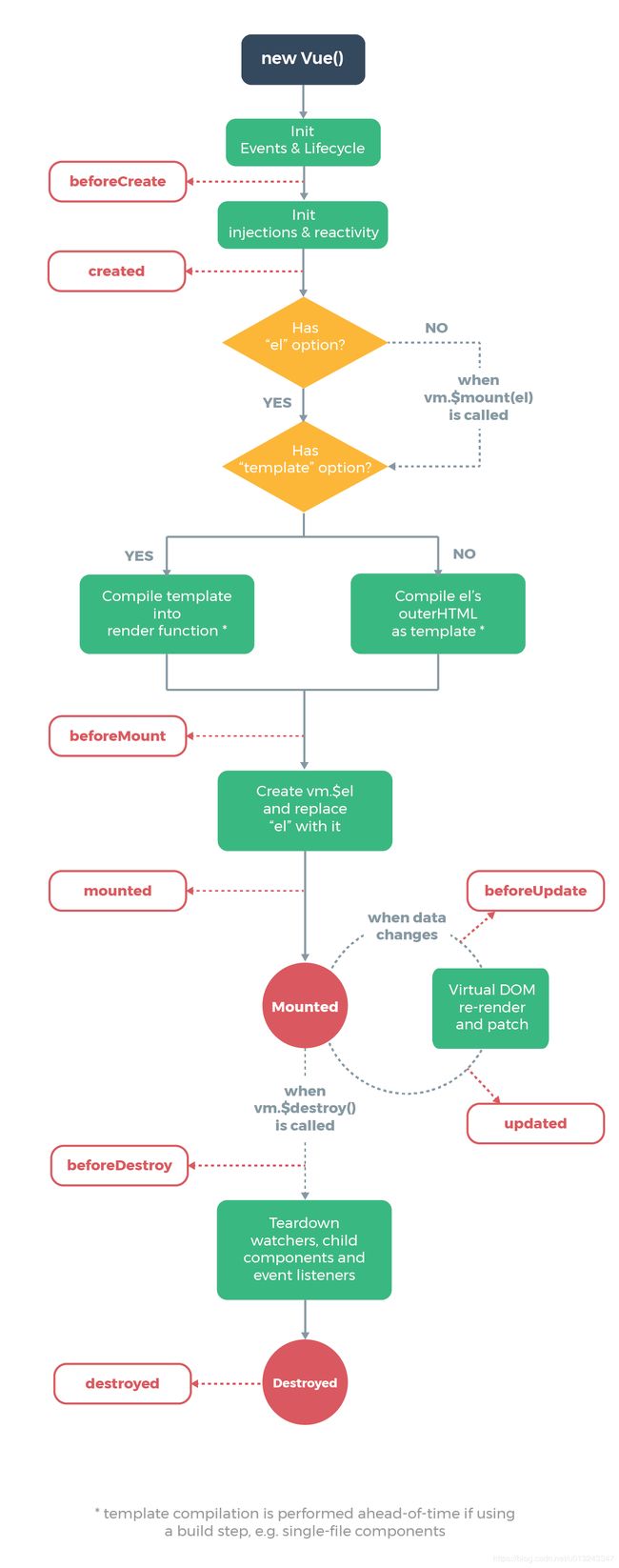
Vue的时候,应该或多或少了解过它的生命周期图示。
基本可以归纳为四个阶段
created【初始化创建阶段】 (beforeCreate、created)mounted【挂载渲染阶段】(beforeMount、mounted)update【数据更新阶段】(beforeUpdate、updated)destroy【组件销毁阶段】(beforeDestroy、destroyed)
钩子函数作用
钩子函数的设计思想是采用了 面向切面编程AOP,即动态地将代码切入到类的指定方法、指定位置上的编程思想就是面向切面的编程。
调用方式形如:
created(){ // ...}
mounted(){ // ...}
updated(){ // ...}
生命周期的表现形式就是一系列钩子函数(hook),而钩子函数分别在其对应的生命周期内被调用。那么,我们来具体分析不同的钩子函数的职责。
生命周期图
1. new Vue
根据 Vue 的源码,我们可以看到 Vue 的本质就是一个 function, new Vue 的过程就是初始化参数、生命周期、事件等一系列过程,下面是简化后的代码:
源码地址
源码路径: src/core/instance/index.js
// Vue 构造函数
function Vue (options) {
// 只有在 new Vue 时才会执行,_init 方法就是 initMixin 中的 _init 方法
this._init(options)
}
// 初始化option相关工作,(<= 此处调用 beforeCreate、created 钩子)
initMixin(Vue)
// 数据绑定核心方法
stateMixin(Vue)
// 事件绑定的核心方法
eventsMixin(Vue)
// 生命周期核心方法
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
// 渲染核心方法,render/Vnode
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
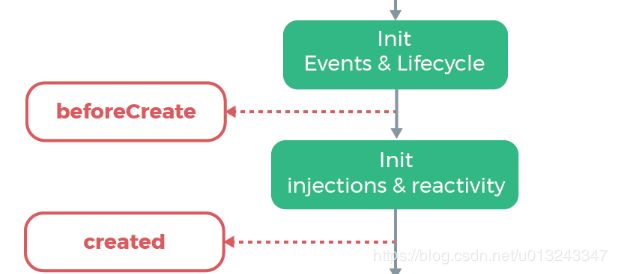
2. beforeCreate、craeted
注意!!! 以下源码分析都是经过简化处理的代码
beforeCreate、created 的调用时机都是在 initMixin(Vue)。
源码地址
源码路径: src/core/instance/init.js
export function initMixin (Vue) {
// 注意此处的 _init 方法,与 Vue 构造函数中的 _init 是同一个方法
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
const vm = this
// 合并options (已简化处理)
vm.$options = mergeOptions(resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),options,vm)
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
// 注意此处!!!
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') // beforeCreate 钩子被执行
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
// 注意此处!!!
callHook(vm, 'created')// created钩子被执行
}
}
由此,可以看到在执行 beforeCreate 钩子函数之前,还会先调用 initLifecycle、initEvents、initRender。
同时, 执行 created 钩子函数之前,会先调用initInjections、initState、initProvide
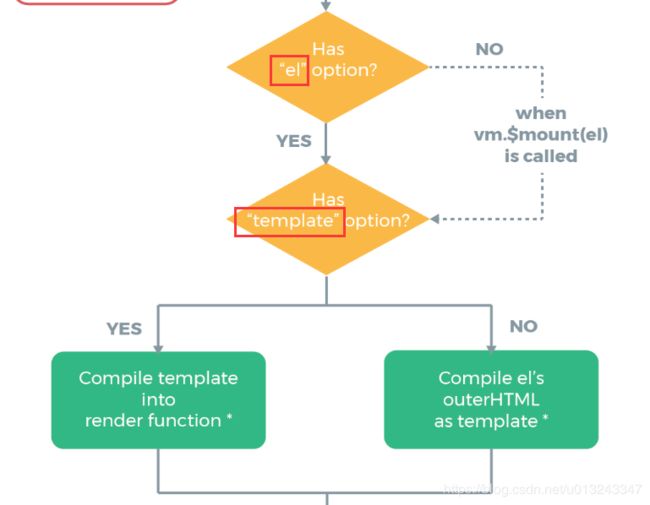
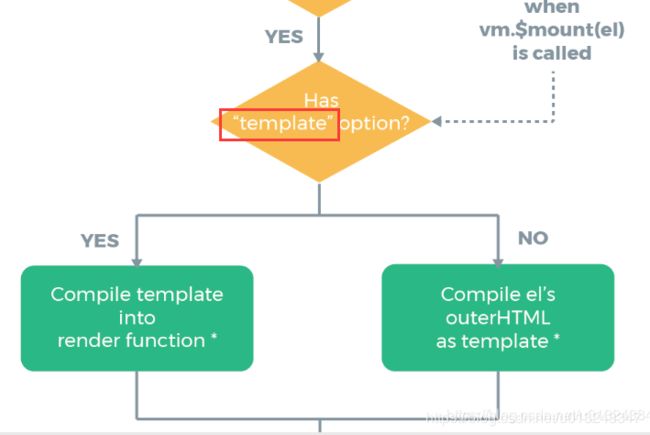
3. $options 检测el、template
注意!!! 以下源码分析都是经过简化处理的代码
源码路径: src/core/instance/init.js
export function initMixin (Vue) {
// 注意此处的 _init 方法,与 Vue 构造函数中的 _init 是同一个方法
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
const vm = this
// 合并options (已简化处理)
vm.$options = mergeOptions(resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),options,vm)
vm._self = vm
// ...
callHook(vm, 'created') // created 钩子被调用
// ...
// 判断el元素
if(vm.$options.el) {
// 挂载该el Dom元素
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}
可以看出,在
created钩子调用之后,首先判断是否存在el元素,如果存在,则执行$mount方法将el元素进行挂载。那么接下来看一下$mount的声明以及执行过程。
源码路径: src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
import Vue from './runtime/index'
// 保存 $mount
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
// 这里采用装饰器设计模式,重写$mount方法
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el, hydrating) {
const options = this.$options
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if(!options.render) {
let template = options.template
// 判断是否存在template方法
if(template) {
if(typeof template === 'string') {
// 通过#id获取dom
template = idToTemplate(template)
} else if(template.nodeType) {
// Dom 节点
template = template.innerHTML
} else {
return this
}
} else if(el) {
// 如果不存在template
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
}
// ...
// 执行旧的 $mount 方法
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
function getOuterHTML(el) {
if(el.outerHTML) {
return el.outerHTML
} else {
const container = document.createElement('div')
container.appendChild(el.cloneNode(true))
return container.innerHTML
}
}
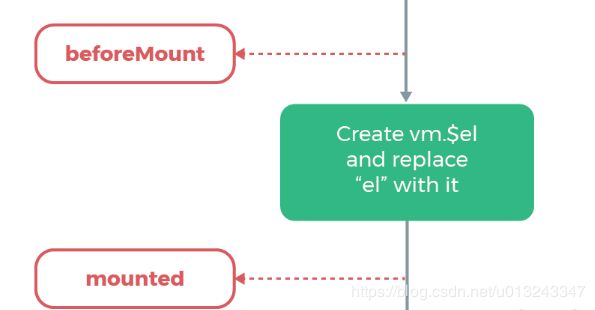
4. beforeMount、mounted (挂载/渲染dom)
注意!!! 以下源码分析都是经过简化处理的代码
源码路径: src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js
import Vue from 'core/index'
import { inBrowser } from 'core/util/index'
import { query } from 'web/util/index'
import { mountComponent } from 'core/instance/lifecycle'
// ...
/**
* $mount
* @params el {Dom} 挂载的Dom元素
* @params hydrating {Boolean} 与服务端渲染有关,web端可以忽略
**/
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el,hydrating) {
// 判断是否存在el 以及在浏览器环境
el = el && isBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
// 调用 mountComponent
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
// 'core/instance/lifecycle'
import { createEmptyVNode } from '../vdom/vnode'
// ...
/**
* 挂载组件
**/
export function mountComponent (vm, el, hydrating) {
// 绑定$el
vm.$el = el
if(!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
}
// 注意此处
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount') // beforeMount 钩子被调用
// ...
if(vm.$vnode === null) {
// 修改当前 vm 的状态
vm._isMounted = true
// 注意此处
callHook(vm, 'mounted') // mounted 钩子被调用
}
return vm
}
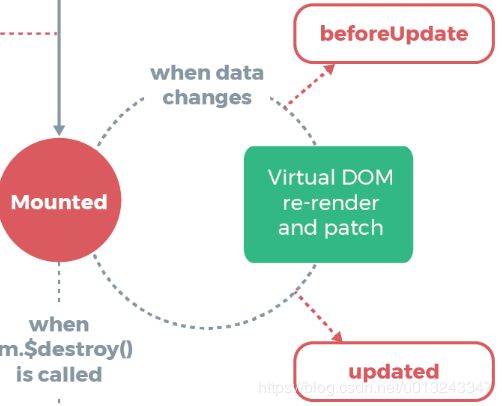
5. beforeUpdate、updated (数据更新)
- beforeUpdate
// src/core/instance/init.js
export function initMixin (Vue) {
// 注意此处的 _init 方法,与 Vue 构造函数中的 _init 是同一个方法
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
// ...
if(vm.$options.el) {
// 1. 调用 $mount 方法
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}
// src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el,hydrating) {
// 2. 调用 mountComponent
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
// src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent (vm, el, hydrating) {
// ...
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount') // 调用 beforeMount 钩子
let updateComponent
updateComponent = _ => {
// 更新视图,第一个参数返回VNode
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before() {
// 判断元素已经被挂载,并且未被销毁
if(vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
// 注意此处
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate') // 调用 beforeUpdate 钩子
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
// ...
}
export function lifecycleMixin (Vue) {
/**
* @params vnode {VNode} 虚拟dom
* @params hydrating {Boolean} 服务端渲染相关
**/
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode, hydrating) {
}
}
- updated
// 此处update 相关逻辑后续会在其他篇章讲解
源码地址: src/core/observer/scheduler.js
function callUpdateHooks (queue) {
let i = queue.length
while(i--) {
const watcher = queue[i]
const vm = watcher.vm
if(vm._wathcer === watcher && vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'updated')
}
}
}
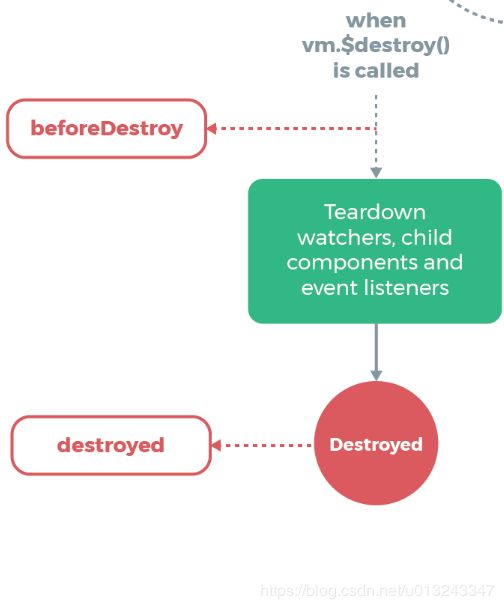
6. beforeDestroye、destroyed
源码地址: src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
export function lifecycleMixin (Vue) {
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {
const vm = this
// 注意此处
callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy') // 调用 beforeDestroy
// 清除wathcer
if(vm._watcher) {
vm._wathcer.teardown()
}
let i = vm._watchers.length
while(i--){
vm._watchers[i].teardown()
}
// 修改vm状态
vm._isDestroyed = true
// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered tree
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)
callHook(vm, 'destroyed')
// 关闭vm实例的listener
vm.$off()
if(vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null
}
if(vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null
}
}
}
参考资料
Vue.js 2.6源码
什么是面向切面编程AOP?
Vue.js 源码解析之前端渲染篇
Vue $mount的挂载入口的奥秘