实战 webpack 4 配置解析四
接上篇: 实战 webpack 4 配置解析三
WEBPACK.PROD.JS 解析
现在让我们看看我们的 webpack.prod.js 配置文件,它包含了我们正在处理项目时用于生产构建的所有设置。它与 webpack.common.js 中的设置合并,形成一个完整的 webpack 配置。
// webpack.prod.js - production builds
const LEGACY_CONFIG = 'legacy';
const MODERN_CONFIG = 'modern';
// node modules
const git = require('git-rev-sync');
const glob = require('glob-all');
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const moment = require('moment');
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
// webpack plugins
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const CreateSymlinkPlugin = require('create-symlink-webpack-plugin');
const CriticalCssPlugin = require('critical-css-webpack-plugin');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const ImageminWebpWebpackPlugin = require('imagemin-webp-webpack-plugin');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
const OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin');
const PurgecssPlugin = require('purgecss-webpack-plugin');
const SaveRemoteFilePlugin = require('save-remote-file-webpack-plugin');
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin');
const WebappWebpackPlugin = require('webapp-webpack-plugin');
const WhitelisterPlugin = require('purgecss-whitelister');
const WorkboxPlugin = require('workbox-webpack-plugin');
// config files
const common = require('./webpack.common.js');
const pkg = require('./package.json');
const settings = require('./webpack.settings.js');
在前面部分,我们还是引入了我们需要的 Node 包,以及我们使用的 webpack 插件。然后我们将 webpack.settings.js 导入设置,以便我们可以访问那里的设置,并将 package.json 作为 pkg 导入,以便访问那里的一些设置。
我们还导入我们的 webpack.common.js 常用 webpack 配置,我们将合并我们的开发设置。
TAILWIND EXTRACTOR
这个类是 Tailwind CSS 的自定义 PurgeCSS 提取器,允许在类名中使用特殊字符。
// Custom PurgeCSS extractor for Tailwind that allows special characters in
// class names.
//
// https://github.com/FullHuman/purgecss#extractor
class TailwindExtractor {
static extract(content) {
return content.match(/[A-Za-z0-9-_:\/]+/g) || [];
}
}
这取自 Tailwind CSS 文档中 Removing unused CSS with PurgeCSS(用 PurgeCSS 删除没用到的 CSS) 这一部分。有关此提取器如何与 PurgeCSS 配合使用以神奇地使 CSS 变得苗条和整洁的详细信息,请参见下文。
CONFIGURATION FUNCTIONS
这是 configureBanner() 的样子:
// Configure file banner
const configureBanner = () => {
return {
banner: [
'/*!',
' * @project ' + settings.name,
' * @name ' + '[filebase]',
' * @author ' + pkg.author.name,
' * @build ' + moment().format('llll') + ' ET',
' * @release ' + git.long() + ' [' + git.branch() + ']',
' * @copyright Copyright (c) ' + moment().format('YYYY') + ' ' + settings.copyright,
' *',
' */',
''
].join('\n'),
raw: true
};
};
这只是为我们构建的每个文件添加了一个包含项目名称,文件名,作者和 git 信息的文件头。
接下来是 configureBundleAnalyzer() 函数:
// Configure Bundle Analyzer
const configureBundleAnalyzer = (buildType) => {
if (buildType === LEGACY_CONFIG) {
return {
analyzerMode: 'static',
reportFilename: 'report-legacy.html',
};
}
if (buildType === MODERN_CONFIG) {
return {
analyzerMode: 'static',
reportFilename: 'report-modern.html',
};
}
};
使用 WebpackBundleAnalyzer 插件为我们的新版和旧版构建生成报告,并且生成一个自包含的交互式 HTML 页面,允许您查看 webpack 打包后的确切内容。
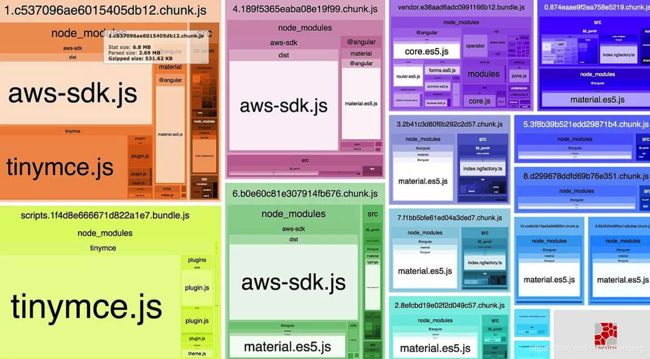
它对保持打包后包的大小很有作用,并且让我确切地了解 webpack 正在构建什么,所以我已经将它作为生产构建过程的一部分。
接下来是 configureCriticalCss():
// Configure Critical CSS
const configureCriticalCss = () => {
return (settings.criticalCssConfig.pages.map((row) => {
const criticalSrc = settings.urls.critical + row.url;
const criticalDest = settings.criticalCssConfig.base + row.template + settings.criticalCssConfig.suffix;
let criticalWidth = settings.criticalCssConfig.criticalWidth;
let criticalHeight = settings.criticalCssConfig.criticalHeight;
// Handle Google AMP templates
if (row.template.indexOf(settings.criticalCssConfig.ampPrefix) !== -1) {
criticalWidth = settings.criticalCssConfig.ampCriticalWidth;
criticalHeight = settings.criticalCssConfig.ampCriticalHeight;
}
console.log("source: " + criticalSrc + " dest: " + criticalDest);
return new CriticalCssPlugin({
base: './',
src: criticalSrc,
dest: criticalDest,
extract: false,
inline: false,
minify: true,
width: criticalWidth,
height: criticalHeight,
})
})
);
};
这使用 CriticalCssPlugin 通过我们的 webpack.settings.js 中的settings.criticalCssConfig.pages 进行分块,为我们的网站生成 CriticalCSS。
需要注意的是,如果传入的页面在任何位置的名字都包含settings.criticalCssConfig.ampPrefix 的值,则会通过传入非常大的高度为整个网页(而不仅仅是上面的折叠内容)生成 CriticalCSS。
我不会在这里详细介绍 CriticalCSS;有关 CriticalCSS 的更多信息,请查看 Implementing Critical CSS on your website 这篇文章。
下来是 configureCleanWebpack():
// Configure Clean webpack
const configureCleanWebpack = () => {
return {
root: path.resolve(__dirname, settings.paths.dist.base),
verbose: true,
dry: false
};
};
这只是使用 CleanWebpackPlugin 删除构建目录。目录配置会从我们的 webpack.settings.js 中读取 settings.paths.dist.base 。
接下来是 configureHtml():
// Configure Html webpack
const configureHtml = () => {
return {
templateContent: '',
filename: 'webapp.html',
inject: false,
};
};
这将 HtmlWebpackPlugin 与 WebappWebpackPlugin(见下文)结合使用,为我们的 favicons 生成 HTML。请注意,我们在 templateContent 中传入一个空字符串,以便输出只是 WebappWebpackPlugin 的原始输出。
接下来是 configureImageLoader():
// Configure Image loader
const configureImageLoader = (buildType) => {
if (buildType === LEGACY_CONFIG) {
return {
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg|webp)$/i,
use: [
{
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
name: 'img/[name].[hash].[ext]'
}
}
]
};
}
if (buildType === MODERN_CONFIG) {
return {
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg|webp)$/i,
use: [
{
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
name: 'img/[name].[hash].[ext]'
}
},
{
loader: 'img-loader',
options: {
plugins: [
require('imagemin-gifsicle')({
interlaced: true,
}),
require('imagemin-mozjpeg')({
progressive: true,
arithmetic: false,
}),
require('imagemin-optipng')({
optimizationLevel: 5,
}),
require('imagemin-svgo')({
plugins: [
{convertPathData: false},
]
}),
]
}
}
]
};
}
};
我们传入 buildType,以便我们可以返回不同的结果,具体取决于它是旧版构建还是新版构建。在这种情况下,我们通过一系列的图像优化处理图像,通过 img-loader 进行新版构建。
我们只对新版本执行此操作,因为花费时间同时对新版本和旧版本做图像优化是没有必要的(图像对于两者都是相同的)。
需要强调的是,这仅适用于我们的 webpack 构建中包含的图像;许多其他图像将来自其他地方(CMS系统,资产管理系统等)。
要让 webpack 优化图像,请将其导入 JavaScript:
import Icon from './icon.png';
有关详细信息,请查看webpack文档的“加载图像”部分。
下面是我们的 configureOptimization():
// Configure optimization
const configureOptimization = (buildType) => {
if (buildType === LEGACY_CONFIG) {
return {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
default: false,
common: false,
styles: {
name: settings.vars.cssName,
test: /\.(pcss|css|vue)$/,
chunks: 'all',
enforce: true
}
}
},
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin(
configureTerser()
),
new OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin({
cssProcessorOptions: {
map: {
inline: false,
annotation: true,
},
safe: true,
discardComments: true
},
})
]
};
}
if (buildType === MODERN_CONFIG) {
return {
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin(
configureTerser()
),
]
};
}
};
这是我们配置 webpack 生产优化的地方。对于旧版构建(两次没有任何意义),我们使用 MiniCssExtractPlugin 将项目范围内使用的所有 CSS 提取到单个文件中。如果您以前使用过 webpack,那么过去可能已经使用了ExtractTextPlugin 来执行此操作;现在不需要了。
然后,我们还使用 OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin 通过删除重复规则来优化生成的CSS,并通过 cssnano 最小化CSS。
最后,我们将 JavaScript 最小化插件设置为 TerserPlugin;这是因为 UglifyJsPlugin 不再支持最小化 ES2015+ JavaScript。由于我们正在生成新版的 ES2015+ 包,所以我们需要它。
接下来是 configurePostcssLoader() :
// Configure Postcss loader
const configurePostcssLoader = (buildType) => {
if (buildType === LEGACY_CONFIG) {
return {
test: /\.(pcss|css)$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 2,
sourceMap: true
}
},
{
loader: 'resolve-url-loader'
},
{
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: true
}
}
]
};
}
// Don't generate CSS for the modern config in production
if (buildType === MODERN_CONFIG) {
return {
test: /\.(pcss|css)$/,
loader: 'ignore-loader'
};
}
};
这看起来非常类似于 configurePostcssLoader() 的 dev 版本,除了对于我们的最终加载器,我们使用 MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader 将我们所有的 CSS 提取到一个文件中。
我们只对旧版构建执行此操作,因为对每个构建执行它没有任何意义(CSS是相同的)。我们使用 ignore-loader 进行新版构建,因此我们的 .css 和 .pcss 文件存在一个加载器,但它什么也没做。
如之前所述,我们使用 PostCSS 处理所有 CSS,包括 Tailwind CSS。我认为它是CSS的 Babel,因为它将各种高级 CSS 功能编译成您的浏览器可以理解的普通旧CSS。
同样,重要的是要注意,对于 webpack 加载器,它们按照它们列出的相反顺序进行处理:
- postcss-loader - 将文件加载并处理为 PostCSS
- resolve-url-loader 将 CSS 中的任何
url()重写为相对公共路径 - css-loader - 解析我们所有的CSS
@import和url() - MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader - 提取所有的生产环境 CSS 到一个文件中
由于这是一个生产版本,我们使用 MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader 提取所有使用的CSS,并将其保存到单个 .css 文件中。CSS也被最小化,并针对生产进行了优化。
我们包含这个告诉 webpack 引入了 CSS:
import styles from '../css/app.pcss';
这在webpack文档的 Loading CSS 部分中有详细讨论。
我们从 App.js 入口点开始;将此视为 PostCSS 的切入点。app.pcss 文件 @import 我们项目使用的所有CSS;稍后将详细介绍。
接下来是 configurePurgeCss():
// Configure PurgeCSS
const configurePurgeCss = () => {
let paths = [];
// Configure whitelist paths
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(settings.purgeCssConfig.paths)) {
paths.push(path.join(__dirname, value));
}
return {
paths: glob.sync(paths),
whitelist: WhitelisterPlugin(settings.purgeCssConfig.whitelist),
whitelistPatterns: settings.purgeCssConfig.whitelistPatterns,
extractors: [
{
extractor: TailwindExtractor,
extensions: settings.purgeCssConfig.extensions
}
]
};
};
Tailwind CSS 是一个出色的实用程序优先的CSS框架,允许快速原型设计,因为在本地开发中,您很少需要实际编写任何 CSS。相反,您只需使用提供的实用程序CSS类。
缺点是生成的CSS可能有点大。这就是 PurgeCSS 的用武之地。它将解析所有HTML/模板/Vue/任何文件,并删除任何未使用的 CSS。
节省的空间可能很大; Tailwind CSS 和 PurgeCSS 是天作之合。我们在 Adam Wathan 播客——Tailwind CSS 实用程序这篇文章中深入探讨了这个问题。
它遍历 settings.purgeCssConfig.paths 中的所有路径 globs,寻找要保留的 CSS 规则;未找到的任何 CSS 规则都会从我们生成的 CSS 构建中删除。
我们还使用 WhitelisterPlugin,当我们知道我们不希望某些 CSS 被剥离时,可以轻松地将整个文件或全局列入白名单。与我们的 settings.purgeCssConfig.whitelist 匹配的所有文件中的 CSS 规则都列入白名单,并且永远不会从生成的构建中剥离。
接下来是 configureTerser():
// Configure terser
const configureTerser = () => {
return {
cache: true,
parallel: true,
sourceMap: true
};
};
这只是配置 TerserPlugin 使用的一些设置,可以最小化我们的旧版和新代 JavaScript 代码。
接下来是 configureWebApp():
// Configure Webapp webpack
const configureWebapp = () => {
return {
logo: settings.webappConfig.logo,
prefix: settings.webappConfig.prefix,
cache: false,
inject: 'force',
favicons: {
appName: pkg.name,
appDescription: pkg.description,
developerName: pkg.author.name,
developerURL: pkg.author.url,
path: settings.paths.dist.base,
}
};
};
这使用 WebappWebpackPlugin 以无数种格式生成我们所有的网站 favicon,以及我们的 webapp manifest.json和其他 PWA 细节。
它与 HtmlWebpackPlugin 结合使用,还可以输出一个 webapp.html 文件,其中包含指向所有生成的 favicons 和相关文件的链接,以包含在我们的 HTML 页面的 中。
接下来是 configureWorkbox():
// Configure Workbox service worker
const configureWorkbox = () => {
let config = settings.workboxConfig;
return config;
};
我们使用 Google 的 WorkboxWebpackPlugin 为我们的网站生成 Service Worker。解释 Service Worker 这超出了本文的内容范围,但您可以查看 Going Offline: Service Workers with Jeremy Keith 的博客作为入门。
配置全部来自 webpack.settings.js 中的 settings.workboxConfig 。除了预先缓存现代构建 manifest.json 中的所有资源之外,我们还包括一个 workbox-catch-handler.js 来配置它以使用回退响应 catch-all 路由。
// fallback URLs
const FALLBACK_HTML_URL = '/offline.html';
const FALLBACK_IMAGE_URL = '/offline.svg';
// This "catch" handler is triggered when any of the other routes fail to
// generate a response.
// https://developers.google.com/web/tools/workbox/guides/advanced-recipes#provide_a_fallback_response_to_a_route
workbox.routing.setCatchHandler(({event, request, url}) => {
// Use event, request, and url to figure out how to respond.
// One approach would be to use request.destination, see
// https://medium.com/dev-channel/service-worker-caching-strategies-based-on-request-types-57411dd7652c
switch (request.destination) {
case 'document':
return caches.match(FALLBACK_HTML_URL);
break;
case 'image':
return caches.match(FALLBACK_IMAGE_URL);
break;
default:
// If we don't have a fallback, just return an error response.
return Response.error();
}
});
// Use a stale-while-revalidate strategy for all other requests.
workbox.routing.setDefaultHandler(
workbox.strategies.staleWhileRevalidate()
);
MODULE.EXPORTS
最后,module.exports 使用 webpack-merge 将 webpack.common.js 中的common.legacyConfig与我们的生产旧版配置合并,并将 common.modernConfig 与我们的生产新版配置合并:
// Production module exports
module.exports = [
merge(
common.legacyConfig,
{
output: {
filename: path.join('./js', '[name]-legacy.[chunkhash].js'),
},
mode: 'production',
devtool: 'source-map',
optimization: configureOptimization(LEGACY_CONFIG),
module: {
rules: [
configurePostcssLoader(LEGACY_CONFIG),
configureImageLoader(LEGACY_CONFIG),
],
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(settings.paths.dist.clean,
configureCleanWebpack()
),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
path: path.resolve(__dirname, settings.paths.dist.base),
filename: path.join('./css', '[name].[chunkhash].css'),
}),
new PurgecssPlugin(
configurePurgeCss()
),
new webpack.BannerPlugin(
configureBanner()
),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin(
configureHtml()
),
new WebappWebpackPlugin(
configureWebapp()
),
new CreateSymlinkPlugin(
settings.createSymlinkConfig,
true
),
new SaveRemoteFilePlugin(
settings.saveRemoteFileConfig
),
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin(
configureBundleAnalyzer(LEGACY_CONFIG),
),
].concat(
configureCriticalCss()
)
}
),
merge(
common.modernConfig,
{
output: {
filename: path.join('./js', '[name].[chunkhash].js'),
},
mode: 'production',
devtool: 'source-map',
optimization: configureOptimization(MODERN_CONFIG),
module: {
rules: [
configurePostcssLoader(MODERN_CONFIG),
configureImageLoader(MODERN_CONFIG),
],
},
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
new webpack.BannerPlugin(
configureBanner()
),
new ImageminWebpWebpackPlugin(),
new WorkboxPlugin.GenerateSW(
configureWorkbox()
),
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin(
configureBundleAnalyzer(MODERN_CONFIG),
),
]
}
),
];
通过在 module.exports 中返回一个数组,我们告诉 webpack 我们需要完成多个编译:一个用于我们的旧版构建,另一个用于我们的新版构建。
请注意,对于旧版构建,我们将处理后的 JavaScript 输出为 [name]-legacy.[hash].js,而新版构建将其输出为 [name].[hash].js。
通过将 mode 设置为 'production',我们告诉 webpack 这是一个生产版本。这样可以实现适合生产构建的许多设置。
通过将 devtool 设置为 'source-map',我们要求将 CSS/JavaScript 的 .map 生成为单独的 .map 文件。这使我们更容易调试实时生产网站,还无需添加资源的文件大小。
这里使用了几个我们尚未涉及的 webpack 插件:
- CreateSymlinkPlugin - 这是我创建的一个插件,允许创建符号链接作为构建过程的一部分。我使用它将生成的
favicon.ico符号链接到/favicon.ico,因为许多Web浏览器在Web根目录中查找。 - SaveRemoteFilePlugin - 这是我创建的插件,用于下载远程文件并将其作为 webpack 构建过程的一部分发出。我用它来下载并在本地提供 Google 的
analytics.js。 - ImageminWebpWebpackPlugin - 此插件创建项目导入的所有 JPEG 和PNG 文件的
.webp变体。
就这样,我们现在为我们的项目提供了一个很好的生产构建,包括所有的花里胡哨。
TAILWIND CSS & POSTCSS CONFIG
为了使 webpack 正确构建 Tailwind CSS 和我们的其他 CSS,我们需要做一些设置。感谢我的伙伴乔纳森梅尔维尔(Jonathan Melville)在构建这方面的工作。首先我们需要一个 postcss.config.js 文件:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-import'),
require('postcss-extend'),
require('postcss-simple-vars'),
require('postcss-nested-ancestors'),
require('postcss-nested'),
require('postcss-hexrgba'),
require('autoprefixer'),
require('tailwindcss')('./tailwind.config.js')
]
};
这可以存储在项目根目录下;PostCSS 将在构建过程中自动查找它,并应用我们指定的 PostCSS 插件。请注意,这里我们包含 tailwind.config.js 文件的位置,以使其成为构建过程的一部分。
最后,我们的 CSS 入口点 app.pcss 看起来像这样:
/**
* app.css
*
* The entry point for the css.
*
*/
/**
* This injects Tailwind's base styles, which is a combination of
* Normalize.css and some additional base styles.
*
* You can see the styles here:
* https://github.com/tailwindcss/tailwindcss/blob/master/css/preflight.css
*/
@import "tailwindcss/preflight";
/**
* This injects any component classes registered by plugins.
*
*/
@import 'tailwindcss/components';
/**
* Here we add custom component classes; stuff we want loaded
* *before* the utilities so that the utilities can still
* override them.
*
*/
@import './components/global.pcss';
@import './components/typography.pcss';
@import './components/webfonts.pcss';
/**
* This injects all of Tailwind's utility classes, generated based on your
* config file.
*
*/
@import 'tailwindcss/utilities';
/**
* Include styles for individual pages
*
*/
@import './pages/homepage.pcss';
/**
* Include vendor css.
*
*/
@import 'vendor.pcss';
显然,定制它以包含您用于自定义 CSS 的任何组件/页面。
POST-BUILD PROJECT TREE
这是我们的项目树在构建后的样子:
├── example.env
├── package.json
├── postcss.config.js
├── src
│ ├── css
│ │ ├── app.pcss
│ │ ├── components
│ │ │ ├── global.pcss
│ │ │ ├── typography.pcss
│ │ │ └── webfonts.pcss
│ │ ├── pages
│ │ │ └── homepage.pcss
│ │ └── vendor.pcss
│ ├── fonts
│ ├── img
│ │ └── favicon-src.png
│ ├── js
│ │ ├── app.js
│ │ └── workbox-catch-handler.js
│ └── vue
│ └── Confetti.vue
├── tailwind.config.js
├── templates
├── web
│ ├── dist
│ │ ├── criticalcss
│ │ │ └── index_critical.min.css
│ │ ├── css
│ │ │ ├── styles.d833997e3e3f91af64e7.css
│ │ │ └── styles.d833997e3e3f91af64e7.css.map
│ │ ├── img
│ │ │ └── favicons
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-144x144.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-192x192.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-256x256.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-36x36.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-384x384.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-48x48.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-512x512.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-72x72.png
│ │ │ ├── android-chrome-96x96.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-114x114.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-120x120.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-144x144.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-152x152.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-167x167.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-180x180.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-57x57.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-60x60.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-72x72.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-76x76.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-icon-precomposed.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-1182x2208.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-1242x2148.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-1496x2048.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-1536x2008.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-320x460.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-640x1096.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-640x920.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-748x1024.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-750x1294.png
│ │ │ ├── apple-touch-startup-image-768x1004.png
│ │ │ ├── browserconfig.xml
│ │ │ ├── coast-228x228.png
│ │ │ ├── favicon-16x16.png
│ │ │ ├── favicon-32x32.png
│ │ │ ├── favicon.ico
│ │ │ ├── firefox_app_128x128.png
│ │ │ ├── firefox_app_512x512.png
│ │ │ ├── firefox_app_60x60.png
│ │ │ ├── manifest.json
│ │ │ ├── manifest.webapp
│ │ │ ├── mstile-144x144.png
│ │ │ ├── mstile-150x150.png
│ │ │ ├── mstile-310x150.png
│ │ │ ├── mstile-310x310.png
│ │ │ ├── mstile-70x70.png
│ │ │ ├── yandex-browser-50x50.png
│ │ │ └── yandex-browser-manifest.json
│ │ ├── js
│ │ │ ├── analytics.45eff9ff7d6c7c1e3c3d4184fdbbed90.js
│ │ │ ├── app.30334b5124fa6e221464.js
│ │ │ ├── app.30334b5124fa6e221464.js.map
│ │ │ ├── app-legacy.560ef247e6649c0c24d0.js
│ │ │ ├── app-legacy.560ef247e6649c0c24d0.js.map
│ │ │ ├── confetti.1152197f8c58a1b40b34.js
│ │ │ ├── confetti.1152197f8c58a1b40b34.js.map
│ │ │ ├── confetti-legacy.8e9093b414ea8aed46e5.js
│ │ │ ├── confetti-legacy.8e9093b414ea8aed46e5.js.map
│ │ │ ├── precache-manifest.f774c437974257fc8026ca1bc693655c.js
│ │ │ ├── styles-legacy.d833997e3e3f91af64e7.js
│ │ │ ├── styles-legacy.d833997e3e3f91af64e7.js.map
│ │ │ ├── vendors~confetti~vue.03b9213ce186db5518ea.js
│ │ │ ├── vendors~confetti~vue.03b9213ce186db5518ea.js.map
│ │ │ ├── vendors~confetti~vue-legacy.e31223849ab7fea17bb8.js
│ │ │ ├── vendors~confetti~vue-legacy.e31223849ab7fea17bb8.js.map
│ │ │ └── workbox-catch-handler.js
│ │ ├── manifest.json
│ │ ├── manifest-legacy.json
│ │ ├── report-legacy.html
│ │ ├── report-modern.html
│ │ ├── webapp.html
│ │ └── workbox-catch-handler.js
│ ├── favicon.ico -> dist/img/favicons/favicon.ico
│ ├── index.php
│ ├── offline.html
│ ├── offline.svg
│ └── sw.js
├── webpack.common.js
├── webpack.dev.js
├── webpack.prod.js
├── webpack.settings.js
└── yarn.lock
INJECTING SCRIPT & CSS TAGS IN YOUR HTML
使用此处显示的 webpack 配置,