从源码角度看LinkedList一些基本操作(jdk1.7)
介绍
LinkedList是一个双向链表,就像下图展示那样,每个节点有个指向上个元素和一个指向下个元素的指针。
接下来我会对我们经常使用的方法进行介绍,代码如下
@Test
public void testLinkedList(){
//1.实例化LinkedList
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//2.添加元素
for (Character i = 'A'; i <= 'Z'; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
//3.添加null值和其他元素
list.add(null);
list.add('G');
//4.移除元素
list.remove(new Character('V'));
list.remove(new Character('G'));
//5.获取元素...
}
现在我们先来看看实例化LinkedList调用的构造函数。
构造函数
LinkedList的构造函数有两个,如下
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
一个是无参的构造函数,无参的构造函数没什么可以讲的,另外一个是传入一个Collection集合的构造函数。我们先来看看LinkedList的成员变量。
成员变量
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node last;
从源码中可以看到有三个成员变量
第一个是size,表示LinkedList的长度;
第二个是first,表示LinkedList的第一个节点;
第三个是last,表示LinkedList的最后一个节点;
第二个成员变量first和第三个成员变量last让LinkedList可以从第一个节点添加也可以从第二各节点添加,也就是说可以作为先进先出(FIFO)的队列,也可以作为LIFO(后进先出)的栈。
成员变量介绍完了,现在来看看有参的构造函数
LinkedList(Collection c)
构造函数里面只是调用两个函数,一个是无参的构造函数,一个是addAll方法。接下来就看看addAll方法吧。
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
addAll(Collection c)
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
这边又调用了重载方法,传入当前的长度和集合,让我么继续查看这个重载的方法。
addAll(int index, Collection c)
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
//1.检查传入的index是否大于等于0且小于等于LinkedList的长度(index >= 0 && index <= size)
checkPositionIndex(index);
//2.将集合元素转换成数组对象,获取数组对象的长度,如果长度为0,则直接返回false
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
//3.定义两个节点pred、succ,判断传入的index是否等于当前LinkedList的长度
//-->是,succ节点赋值为null,pred节点赋值为LinkedList的最后一个元素
//-->否,succ节点赋值为位置为index的值,pred节点赋值为succ节点之前的值
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
//4.循环数组对象,创建新节点newNode
//判断pred节点是否为null
//-->是,首节点first赋值为新节点newNode
//-->否,pred节点的next指向newNode节点
//pred节点重新赋值为newNode节点
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
//5.succ节点是否为null
//-->是,最后一个节点last赋值为pred节点
//-->否,pred节点的next指向succ节点,将原先的节点加到插入新数据之后。succ节点的prev指向pred。
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
//6.当前元素大小加上新插入的数组大小
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
这边也就第三点会有些疑问了,其实最主要的就是succ节点的赋值,如果index是链表的最后就赋值为null,如果不是就赋值index所在的值(要在位置为index的地方插入新的元素,之后的元素加载新插入元素之后)
添加节点
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
add方法调用linkLast方法(添加到链表的尾部),那么就来看看linkLast方法。
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
代码比较简单,总体步骤就是创建一个新节点,将当前的尾节点的next指向新节点,然后新节点变成尾节点,元素长度size加1,修改统计modCount加1。linkFirst方法也类似,如下
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
空值的添加也是一样
删除节点
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
删除元素的代码如上,删除时先判断传入的元素是否为null,null之的用==来比较,其他则用equals方法比较。找到匹配的节点是调用unlink方法,传入要删除的节点。
E unlink(Node x) {
//1.获得当前节点、当前节点的前一个节点和后一个节点
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
//2.判断当前节点的前一个节点是否为null
//-->是,则当前节点的后一个节点则变成头节点
//-->否,当前节点的前一个节点的next指向当前节点的后一个节点,当前节点的prev赋值为null
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
//3.判断当前节点的后一个节点是否为null
//-->是,当前节点的前一个节点变成尾节点
//-->否,当前节点的后一个节点的prev指向当前元素的前一个节点,当前节点的next赋值为null
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
//4.当前节点的内容item赋值为null,
//长度size减1
//修改次数modCount+1
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
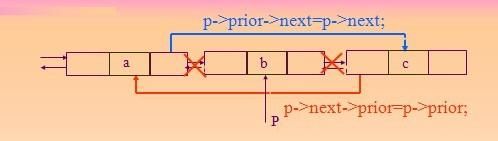
原理就类似下图,a节点的next原本指向b,c节点的prev原本指向b,因为要删除b节点,所以a节点的next重新指向c,c节点的prev则重新指向a,至此,节点的删除就完成了。
获取节点
LinkedList获取节点的方式有很多种,可以通过如下
- Iterator
- 根据索引值获取
- foreach循环获取
- pollFirst方法获取,会删除头结点(null值不会报错,只会返回null)
- pollLast方法获取,会删除尾节点(null值不会报错,只会返回null)
- removeFirst方法获取,会删除头结点(null值会报NoSuchElementException异常)
- removeLast方法获取,会删除尾结点(null值会报NoSuchElementException异常)
作者: 云枭zd
Github: Github地址
出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/fixzd/
版权声明:本文欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则视为侵权。