8.☆SpringMVC源码剖析其运行过程☆
文章目录
- 探索SpringMVC的秘密
- `doDispatch()`方法
- 确定当前请求的处理程序getHandler
- 确定当前请求的处理程序适配器getHandlerAdapter
- 实际调用处理程序
- 小结
- 附:
- `DispatcherServlet.properties`
- 定义的Controller
探索SpringMVC的秘密
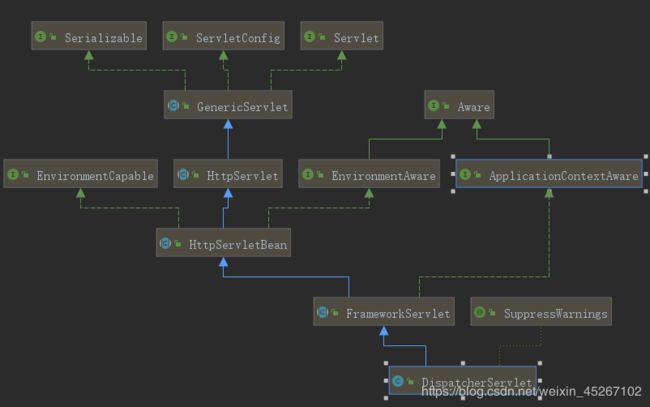
我们都知道在Springmvc中前端控制器,是执行的核心控制器,从继承关系上看其实DispatcherServlet就是一个servlet。这时候我们回顾一下DispatcherServlet是怎么配置的?是不是在
里面配置的,我们刚学习servlet的时候是不是自定义servlet也是在web.xml中通过配置的呢?答案都是yes,下面的图了解一下,就继续看下面的内容…
我们学过javaweb部分都知道servlet的生命周期中有一个service方法是提供服务的方法,每次访问servlet的时候,service方法就会被调用一次。
在FrameworkServlet中有service方法,源码如下:
重点关注:
processRequest(request, response);
super.service(request, response);
/**
* Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH
* requests.
* 重写父类实现以拦截PATCH请求。
*/
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = request.getMethod();
if (method.equalsIgnoreCase(RequestMethod.PATCH.name())) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
//
super.service(request, response);
}
}
这里做了 一下请求方式的判断如果请求的方式是下面这几种的话调用processRequest()方法,否则调用父类的service方法,即HttpServlet的service方法。
public enum RequestMethod {
GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE
}
这里我们进入processRequest()方法,源码如下:
处理此请求,发布事件,无论结果如何。
实际的事件处理由抽象的
doService模板方法执行,所以我们只需要关注其中调用的doService()方法,其他代码一笑而过...
/**
* Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome.
* The actual event handling is performed by the abstract
* {@link #doService} template method.
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
点击doService()方法之后,我们发现它在 FrameworkServlet中是一个抽象的方法,所以它的子类一定会实现它,我们回到DispatcherServlet中寻找doService()方法,其源代码如下:
公开特定于DispatcherServlet的请求属性,并将其委托给
doDispatch()进行实际的调度,同上我们只需要找到doDispatch()方法,其他代码一笑而过....
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link *#doDispatch} for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + requestUri + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
logger.debug("Taking snapshot of request attributes before include");
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
doDispatch()方法
当我们进入doDispatch()方法,下面好戏就开始了…
下面的内容是翻译自
doDispatch()方法的注释:
- 将实际的分派处理程序处理。
- 该处理程序将通过依次应用servlet的处理程序映射来获得。
HandlerAdapter将通过查询servlet已安装的HandlerAdapter来找到第一个支持handler类的HandlerAdapter。所有HTTP方法都由此方法处理。- 由处理器适配器或处理器本身来决定哪些方法是可接受的。
特别是第3点,是促使我探究源码的原因,因为这里使用了设计模式中适配器模式的思想实现的。
下面将对这个方法进行详细的解释:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 确定当前请求的处理程序。
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + requestUri + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
try {
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 实际调用处理程序。
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
}
applyDefaultViewName(request, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Error err) {
triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
确定当前请求的处理程序getHandler
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);我们进入到
DispatcherServlet的getHandler()方法,源码如下:
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
返回结果为:处理程序执行链HandlerExecutionChain。
确定当前请求的处理程序适配器getHandlerAdapter
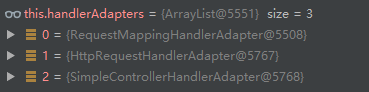
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());返回此处理程序对象的HandlerAdapter。根据不同的handler获取不同的handlerAdapter。
结果返回的是:
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
/**
* Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object.
* @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for
* @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error.
*/
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
通过拿到的RequestMappingHandlerAdapter去执行handler,即去执行控制器也就是我配置的HelloWorldController
实际调用处理程序
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());到了这一步我们就得到了ModelAndView对象,然后根据ModelAndView对象去找对应的视图解析器去解析视图,返回逻辑视图,然后渲染视图返回就可以了。
小结
如果你跟着上面的思路,并熟悉配置Controller,ModelAndView,视图解析器,设计模式-适配器模式的话再结合着下面这张图,我相信你会非常通透。
附:
DispatcherServlet.properties
两种HandlerMapping
BeanNameUrlHandlerMappingDefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping三种HandlerAdapter
HttpRequestHandlerAdapterSimpleControllerHandlerAdapterAnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
定义的Controller
调试的过程中断点大多在都
doDispatch()方法中。
/**
* @Date 2020/6/16 17:22
* @Version 10.21
* @Author DuanChaojie
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/justweb" )
public String hello(){
System.out.println("使用注解配置的Controller,访问成功了...\n\r开始源码分析....");
return "success";
}
}