Spark-Sql源码解析之六 PrepareForExecution: spark plan -> executed Plan
在SparkPlan中插入Shuffle的操作,如果前后2个SparkPlan的outputPartitioning不一样的话,则中间需要插入Shuffle的动作,比分说聚合函数,先局部聚合,然后全局聚合,局部聚合和全局聚合的分区规则是不一样的,中间需要进行一次Shuffle。
比方说sql语句:selectSUM(id) from test group by dev_chnid
其从逻辑计划转换为的物理计划如下:
Aggregate false, [dev_chnid#0], [CombineSum(PartialSum#45L) AS c0#43L]
Aggregate true, [dev_chnid#0], [dev_chnid#0,SUM(id#17L) AS PartialSum#45L]
PhysicalRDD [dev_chnid#0,id#17L], MapPartitionsRDD[1]其中Aggregate的第一个构造函数指明了其ChildDistribution,即规定了该SparkPlan的分区规则
case class Aggregate(
partial: Boolean,
groupingExpressions: Seq[Expression],
aggregateExpressions: Seq[NamedExpression],
child: SparkPlan)
extends UnaryNode {
override def requiredChildDistribution: List[Distribution] = {
if (partial) {
UnspecifiedDistribution :: Nil //当为true时,则对于Child的分区规则无所谓
} else {
if (groupingExpressions == Nil) {
AllTuples :: Nil
} else {
ClusteredDistribution(groupingExpressions) :: Nil //当为false时,必须按照聚合字段进行分区,此时为dev_chnid
}
}
}
……
}因此如果按照以上SparkPlan执行的话,其流程图如下:
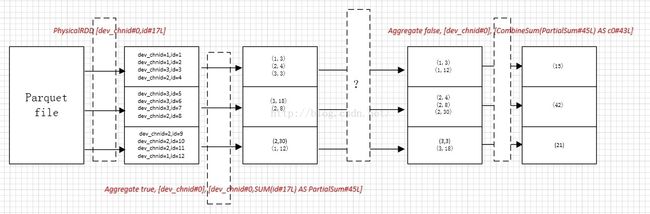
Aggregate true, [dev_chnid#0], [dev_chnid#0,SUM(id#17L)AS PartialSum#45L]的输出是没有规则的,Aggregate false, [dev_chnid#0],[CombineSum(PartialSum#45L) AS c0#43L]所要求的输入是必须按照group字段分区的,因此中间必然有个转变,将前一个Aggretae无规则的输出变为后一个Aggregate有规则的输入,这就是prepareForExecution所负责的事。
lazy val executedPlan: SparkPlan = prepareForExecution.execute(sparkPlan)
protected[sql] val prepareForExecution = new RuleExecutor[SparkPlan] {
val batches =
Batch("Add exchange", Once, EnsureRequirements(self)) :: Nil
}
private[sql] case class EnsureRequirements(sqlContext: SQLContext) extends Rule[SparkPlan] {
// TODO: Determine the number of partitions.
def numPartitions: Int = sqlContext.conf.numShufflePartitions
def apply(plan: SparkPlan): SparkPlan = plan.transformUp {//先遍历孩子节点,然后遍历自己
case operator: SparkPlan =>
// True iff every child's outputPartitioning satisfies the corresponding
// required data distribution.
//ClusteredDistribution(groupingExpressions) :: Nil zip
def meetsRequirements: Boolean =//判断该SparkPlan的child的outputPartitioning是否满足其本身的要求
operator.requiredChildDistribution.zip(operator.children).forall {
case (required, child) =>
val valid = child.outputPartitioning.satisfies(required)
logInfo(
s"${if (valid) "Valid" else "Invalid"} distribution," +
s"required: $required current: ${child.outputPartitioning}")
valid
}
// True iff any of the children are incorrectly sorted.
def needsAnySort: Boolean =//判断该SparkPlan的child的outputOrdering是否满足其本身的要求
operator.requiredChildOrdering.zip(operator.children).exists {
case (required, child) => required.nonEmpty && required != child.outputOrdering
}
// True iff outputPartitionings of children are compatible with each other.
// It is possible that every child satisfies its required data distribution
// but two children have incompatible outputPartitionings. For example,
// A dataset is range partitioned by "a.asc" (RangePartitioning) and another
// dataset is hash partitioned by "a" (HashPartitioning). Tuples in these two
// datasets are both clustered by "a", but these two outputPartitionings are not
// compatible.
// TODO: ASSUMES TRANSITIVITY?
def compatible: Boolean =//当SparkPlan有多个child的时候,需要判断各个child之间的兼容性
!operator.children
.map(_.outputPartitioning)
.sliding(2)
.map {
case Seq(a) => true
case Seq(a, b) => a.compatibleWith(b)
}.exists(!_)
// Adds Exchange or Sort operators as required
def addOperatorsIfNecessary(
partitioning: Partitioning,
rowOrdering: Seq[SortOrder],
child: SparkPlan): SparkPlan = {
val needSort = rowOrdering.nonEmpty && child.outputOrdering != rowOrdering
val needsShuffle = child.outputPartitioning != partitioning
val canSortWithShuffle = Exchange.canSortWithShuffle(partitioning, rowOrdering)
if (needSort && needsShuffle && canSortWithShuffle) {
Exchange(partitioning, rowOrdering, child)
} else {
val withShuffle = if (needsShuffle) {
Exchange(partitioning, Nil, child)
} else {
child
}
val withSort = if (needSort) {
if (sqlContext.conf.externalSortEnabled) {
ExternalSort(rowOrdering, global = false, withShuffle)
} else {
Sort(rowOrdering, global = false, withShuffle)
}
} else {
withShuffle
}
withSort
}
}
if (meetsRequirements && compatible && !needsAnySort) {//如果满足,则不做任何事情
operator
} else {
// At least one child does not satisfies its required data distribution or
// at least one child's outputPartitioning is not compatible with another child's
// outputPartitioning. In this case, we need to add Exchange operators.
val requirements =
(operator.requiredChildDistribution, operator.requiredChildOrdering, operator.children)
val fixedChildren = requirements.zipped.map {//根据不同的要求产生一个中间的过渡的SparkPlan
case (AllTuples, rowOrdering, child) =>
addOperatorsIfNecessary(SinglePartition, rowOrdering, child)
case (ClusteredDistribution(clustering), rowOrdering, child) =>//SUM分组求和的时候需要对分组字段进行hash分区
addOperatorsIfNecessary(HashPartitioning(clustering, numPartitions), rowOrdering, child)
case (OrderedDistribution(ordering), rowOrdering, child) =>
addOperatorsIfNecessary(RangePartitioning(ordering, numPartitions), rowOrdering, child)
case (UnspecifiedDistribution, Seq(), child) =>
child
case (UnspecifiedDistribution, rowOrdering, child) =>
if (sqlContext.conf.externalSortEnabled) {
ExternalSort(rowOrdering, global = false, child)
} else {
Sort(rowOrdering, global = false, child)
}
case (dist, ordering, _) =>
sys.error(s"Don't know how to ensure $dist with ordering $ordering")
}
operator.withNewChildren(fixedChildren)
}
}
}因此经过prepareForExecution处理之后其SparkPlan变成了如下的形式:
Aggregate false, [dev_chnid#0], [CombineSum(PartialSum#45L) AS c0#43L]
Exchange (HashPartitioning 200)
Aggregate true, [dev_chnid#0], [dev_chnid#0,SUM(id#17L) AS PartialSum#45L]
PhysicalRDD [dev_chnid#0,id#17L], MapPartitionsRDD[1]其流程图如下:

通过Exchange将原有2个数据集的实际输出和所要求的输入保持一致。