RecyclerView源码分析过程记录
RecyclerView源码分析过程记录
一.疑问
- 是如何完成初始化的
- 数据刷新机制
- 视图的缓存机制
- 关于
ItemDecoration - 关于
LinearLayoutManager
二.初次分析
分析过程将会忽略动画以及比较细节的部分,同时挑选最常用的垂直列表布局LinearLayoutManager来分析,此节会分成测量、布局、绘制三大部分来分析。
分析基于
androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.0.0的源码版本
测量:onMeasure()
先看下RecyclerView测量的代码:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthSpec, int heightSpec) {
if (mLayout == null) {
defaultOnMeasure(widthSpec, heightSpec);
return;
}
if (mLayout.isAutoMeasureEnabled()) {
...
} else {
...
}
}
显然,测量是委托给mLayout来做的。那就挑选:
@Override
public boolean isAutoMeasureEnabled() {
return true;
}
对于LinearLayoutManager默认实现返回true,那就看if代码块中的部分代码:
if (mLayout.isAutoMeasureEnabled()) {
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightSpec);
// 就如注释所说,这里本来可以用defautOnMesure方法替代
/**
* This specific call should be considered deprecated and replaced with
* {@link #defaultOnMeasure(int, int)}. It can't actually be replaced as it could
* break existing third party code but all documentation directs developers to not
* override {@link LayoutManager#onMeasure(int, int)} when
* {@link LayoutManager#isAutoMeasureEnabled()} returns true.
*/
mLayout.onMeasure(mRecycler, mState, widthSpec, heightSpec);
final boolean measureSpecModeIsExactly =
widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
// 如果指定了确定的宽高(不需要由item决定),就无需继续其它测量逻辑,直接返回;
// 或者未指定mAdapter,也直接返回,可知未指定大小时,测量需要mAdapter提供支持
if (measureSpecModeIsExactly || mAdapter == null) {
return;
}
// mState作为成员,mLayoutStep属性默认值就是State.STEP_START
if (mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START) {
dispatchLayoutStep1();
}
...
}
经常使用的场景是确定了宽高,由子项item来决定宽高的场景稍后再分析(跳转)。
布局:onLayout()
直接看布局代码:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
TraceCompat.beginSection(TRACE_ON_LAYOUT_TAG);
dispatchLayout();
TraceCompat.endSection();
mFirstLayoutComplete = true;
}
核心逻辑交给了dispatchLayout():
void dispatchLayout() {
if (mAdapter == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "No adapter attached; skipping layout");
// leave the state in START
return;
}
if (mLayout == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "No layout manager attached; skipping layout");
// leave the state in START
return;
}
mState.mIsMeasuring = false;
if (mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START) {
dispatchLayoutStep1();
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
dispatchLayoutStep2();
} else if (mAdapterHelper.hasUpdates() || mLayout.getWidth() != getWidth()
|| mLayout.getHeight() != getHeight()) {
// First 2 steps are done in onMeasure but looks like we have to run again due to
// changed size.
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
dispatchLayoutStep2();
} else {
// always make sure we sync them (to ensure mode is exact)
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
}
dispatchLayoutStep3();
}
可见dispatchLayout()又分成了Step1、Step2、Step3个步骤,先看第一种情况,即mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START满足,先执行dispatchLayoutStep1():
dispatchLayoutStep1()
/**
* The first step of a layout where we;
* - process adapter updates
* - decide which animation should run
* - save information about current views
* - If necessary, run predictive layout and save its information
*/
private void dispatchLayoutStep1() {
...
}
从注释可以看到该方法主要与动画相关,先跳过;接着通过mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);把RecyclerView的宽高设置给 LayoutManager,然后是dispatchLayoutStep2():
dispatchLayoutStep2()
/**
* The second layout step where we do the actual layout of the views for the final state.
* This step might be run multiple times if necessary (e.g. measure).
*/
private void dispatchLayoutStep2() {
startInterceptRequestLayout();
onEnterLayoutOrScroll();
mState.assertLayoutStep(State.STEP_LAYOUT | State.STEP_ANIMATIONS);
mAdapterHelper.consumeUpdatesInOnePass();
mState.mItemCount = mAdapter.getItemCount();
mState.mDeletedInvisibleItemCountSincePreviousLayout = 0;
// Step 2: Run layout
mState.mInPreLayout = false;
mLayout.onLayoutChildren(mRecycler, mState);
mState.mStructureChanged = false;
mPendingSavedState = null;
// onLayoutChildren may have caused client code to disable item animations; re-check
mState.mRunSimpleAnimations = mState.mRunSimpleAnimations && mItemAnimator != null;
mState.mLayoutStep = State.STEP_ANIMATIONS;
onExitLayoutOrScroll();
stopInterceptRequestLayout(false);
}
如该方法注释所写,真正完成布局的是在该方法中;显然,布局其实委托给了mLayout.onLayoutChildren(mRecycler, State)来执行,那接下来关注LinearLayoutManager的方法:
@Override
public void onLayoutChildren(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
// layout algorithm:
// 1) by checking children and other variables, find an anchor coordinate and an anchor
// item position.
// 2) fill towards start, stacking from bottom
// 3) fill towards end, stacking from top
// 4) scroll to fulfill requirements like stack from bottom.
// create layout state
...
ensureLayoutState(); // 如果还没创建LayoutState对象的话就创建
mLayoutState.mRecycle = false;
// resolve layout direction
resolveShouldLayoutReverse();
// 确认锚点信息,大部分场景下,是根据方向取首个可见
final View focused = getFocusedChild();
if (!mAnchorInfo.mValid || mPendingScrollPosition != RecyclerView.NO_POSITION
|| mPendingSavedState != null) {
mAnchorInfo.reset();
mAnchorInfo.mLayoutFromEnd = mShouldReverseLayout ^ mStackFromEnd;
// calculate anchor position and coordinate
updateAnchorInfoForLayout(recycler, state, mAnchorInfo);
mAnchorInfo.mValid = true;
} else if (focused != null && (mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedStart(focused)
>= mOrientationHelper.getEndAfterPadding()
|| mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedEnd(focused)
<= mOrientationHelper.getStartAfterPadding())) {
// This case relates to when the anchor child is the focused view and due to layout
// shrinking the focused view fell outside the viewport, e.g. when soft keyboard shows
// up after tapping an EditText which shrinks RV causing the focused view (The tapped
// EditText which is the anchor child) to get kicked out of the screen. Will update the
// anchor coordinate in order to make sure that the focused view is laid out. Otherwise,
// the available space in layoutState will be calculated as negative preventing the
// focused view from being laid out in fill.
// Note that we won't update the anchor position between layout passes (refer to
// TestResizingRelayoutWithAutoMeasure), which happens if we were to call
// updateAnchorInfoForLayout for an anchor that's not the focused view (e.g. a reference
// child which can change between layout passes).
mAnchorInfo.assignFromViewAndKeepVisibleRect(focused, getPosition(focused));
}
...
// LLM may decide to layout items for "extra" pixels to account for scrolling target,
// caching or predictive animations.
int extraForStart;
int extraForEnd; // 可布局的额外空间,由下文可知,包含了padding
final int extra = getExtraLayoutSpace(state);
// If the previous scroll delta was less than zero, the extra space should be laid out
// at the start. Otherwise, it should be at the end.
if (mLayoutState.mLastScrollDelta >= 0) {
extraForEnd = extra;
extraForStart = 0;
} else {
extraForStart = extra;
extraForEnd = 0;
}
extraForStart += mOrientationHelper.getStartAfterPadding();
extraForEnd += mOrientationHelper.getEndPadding();
...
int startOffset;
int endOffset;
// 确定布局的朝向
final int firstLayoutDirection;
if (mAnchorInfo.mLayoutFromEnd) {
firstLayoutDirection = mShouldReverseLayout ? LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_TAIL
: LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_HEAD;
} else {
firstLayoutDirection = mShouldReverseLayout ? LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_HEAD
: LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_TAIL;
}
onAnchorReady(recycler, state, mAnchorInfo, firstLayoutDirection);
detachAndScrapAttachedViews(recycler);
mLayoutState.mInfinite = resolveIsInfinite();
mLayoutState.mIsPreLayout = state.isPreLayout();
if (mAnchorInfo.mLayoutFromEnd) {
...
} else {
// 布局的重点在这!
// fill towards end
updateLayoutStateToFillEnd(mAnchorInfo); // 更新布局参数
mLayoutState.mExtra = extraForEnd;
fill(recycler, mLayoutState, state, false); // 根据锚点位置向后布局
endOffset = mLayoutState.mOffset;
final int lastElement = mLayoutState.mCurrentPosition;
if (mLayoutState.mAvailable > 0) {
extraForStart += mLayoutState.mAvailable;
}
// fill towards start
updateLayoutStateToFillStart(mAnchorInfo); // 更新参数
mLayoutState.mExtra = extraForStart;
mLayoutState.mCurrentPosition += mLayoutState.mItemDirection;
fill(recycler, mLayoutState, state, false); // 根据锚点位置向前布局
startOffset = mLayoutState.mOffset;
if (mLayoutState.mAvailable > 0) {
extraForEnd = mLayoutState.mAvailable;
// start could not consume all it should. add more items towards end
updateLayoutStateToFillEnd(lastElement, endOffset);
mLayoutState.mExtra = extraForEnd;
fill(recycler, mLayoutState, state, false);
endOffset = mLayoutState.mOffset;
}
}
...
}
从这段删减过的代码中可以提炼出布局的流程:
- 首先确定布局参照的锚点
- 确定布局的朝向
- 根据布局的朝向更新
LayoutState参数(updateLayoutStateToFillEnd和updateLayoutStateToFillStart) - 然后根据确定的朝向,从锚点位置(锚点View顶端或左边坐标)的两侧先后执行
fill()函数完成布局
锚点大部分情况下在首个(取决于方向),先跳过具体分析(后续需要锚点信息的可以先假定锚点在首个item的情况),直接到updateLayoutStateToFillEnd():
private void updateLayoutStateToFillEnd(AnchorInfo anchorInfo) {
updateLayoutStateToFillEnd(anchorInfo.mPosition, anchorInfo.mCoordinate);
}
private void updateLayoutStateToFillEnd(int itemPosition, int offset) {
// 布局可用空间:RV高度-paddingBottom-锚点的起始坐标
mLayoutState.mAvailable = mOrientationHelper.getEndAfterPadding() - offset;
// item索引计算方向,值为-1和1,这么设计方便计算时不需要考虑正负值,后续分析可以验证
mLayoutState.mItemDirection = mShouldReverseLayout ? LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_HEAD :
LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_TAIL;
// 锚点的position
mLayoutState.mCurrentPosition = itemPosition;
// 布局方向,值为1,也是方便计算,后续分析可以验证
mLayoutState.mLayoutDirection = LayoutState.LAYOUT_END;
// 当前偏移设置为锚点的起始坐标
mLayoutState.mOffset = offset;
// 滑动相关,先忽略
mLayoutState.mScrollingOffset = LayoutState.SCROLLING_OFFSET_NaN;
}
public abstract class OrientationHelper {
...
/**
* Creates a vertical OrientationHelper for the given LayoutManager.
*
* @param layoutManager The LayoutManager to attach to.
* @return A new OrientationHelper
*/
public static OrientationHelper createVerticalHelper(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager) {
return new OrientationHelper(layoutManager) {
@Override
public int getEndAfterPadding() {
// 获取当前高度值-paddingBottom值
return mLayoutManager.getHeight() - mLayoutManager.getPaddingBottom();
}
...
}
}
...
}
参数设置分析完,接着进入fill()方法:
/**
* The magic functions :). Fills the given layout, defined by the layoutState. This is fairly
* independent from the rest of the {@link LinearLayoutManager}
* and with little change, can be made publicly available as a helper class.
*
* @param recycler Current recycler that is attached to RecyclerView
* @param layoutState Configuration on how we should fill out the available space.
* @param state Context passed by the RecyclerView to control scroll steps.
* @param stopOnFocusable If true, filling stops in the first focusable new child
* @return Number of pixels that it added. Useful for scroll functions.
*/
int fill(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, LayoutState layoutState,
RecyclerView.State state, boolean stopOnFocusable) {
// max offset we should set is mFastScroll + available
final int start = layoutState.mAvailable;
if (layoutState.mScrollingOffset != LayoutState.SCROLLING_OFFSET_NaN) {
// TODO ugly bug fix. should not happen
if (layoutState.mAvailable < 0) {
layoutState.mScrollingOffset += layoutState.mAvailable;
}
recycleByLayoutState(recycler, layoutState);
}
// 初始剩余空间=布局参数设置的可用空间+额外空间,前面如果有去分析mExtra的赋值
// 可以发现paddingBottom会被加到mExtra的值中
int remainingSpace = layoutState.mAvailable + layoutState.mExtra;
LayoutChunkResult layoutChunkResult = mLayoutChunkResult;
// 重点来了:当条件满足时,会循环调用
while ((layoutState.mInfinite || remainingSpace > 0) && layoutState.hasMore(state)) {
// 重置块布局结果参数
layoutChunkResult.resetInternal();
// 如方法名所表达的含义,布局块,即item
layoutChunk(recycler, state, layoutState, layoutChunkResult);
if (layoutChunkResult.mFinished) {
break;
}
// item所消费的空间*方向,刚才分析到了,该值为LayoutState.LAYOUT_END=1或LayoutState.LAYOUT_START=-1
layoutState.mOffset += layoutChunkResult.mConsumed * layoutState.mLayoutDirection;
/**
* Consume the available space if:
* * layoutChunk did not request to be ignored
* * OR we are laying out scrap children
* * OR we are not doing pre-layout
*/
if (!layoutChunkResult.mIgnoreConsumed || mLayoutState.mScrapList != null
|| !state.isPreLayout()) {
layoutState.mAvailable -= layoutChunkResult.mConsumed;
// we keep a separate remaining space because mAvailable is important for recycling
remainingSpace -= layoutChunkResult.mConsumed;
}
...
}
if (DEBUG) {
validateChildOrder();
}
return start - layoutState.mAvailable;
}
注意方法中循环成立的条件while ((layoutState.mInfinite || remainingSpace > 0) && layoutState.hasMore(state)),mInfinite默认为false,先忽略,即条件要满足的情况为有剩余可用空间并且有足够的数据可用;循环体中核心为执行layoutChunk()后得到布局当前item的结果layoutChunkResult,根据结果更新布局参数layoutState.mAvailable和当前剩余空间remainingSpace。
接下来分析layoutChunk():
void layoutChunk(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state,
LayoutState layoutState, LayoutChunkResult result) {
// 获得view
View view = layoutState.next(recycler);
...
// 根据方向来决定添加View到容器的顺序
RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
if (layoutState.mScrapList == null) {
if (mShouldReverseLayout == (layoutState.mLayoutDirection
== LayoutState.LAYOUT_START)) {
addView(view);
} else {
addView(view, 0);
}
} else {
if (mShouldReverseLayout == (layoutState.mLayoutDirection
== LayoutState.LAYOUT_START)) {
addDisappearingView(view);
} else {
addDisappearingView(view, 0);
}
}
// 如果有必要,测量child
measureChildWithMargins(view, 0, 0);
// 赋值当前child消费的高度/宽度
result.mConsumed = mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedMeasurement(view);
int left, top, right, bottom;
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
// 确定左右位置
if (isLayoutRTL()) {
right = getWidth() - getPaddingRight();
left = right - mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedMeasurementInOther(view);
} else {
left = getPaddingLeft();
right = left + mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedMeasurementInOther(view);
}
// 确定上下位置
if (layoutState.mLayoutDirection == LayoutState.LAYOUT_START) {
bottom = layoutState.mOffset;
top = layoutState.mOffset - result.mConsumed;
} else {
top = layoutState.mOffset;
bottom = layoutState.mOffset + result.mConsumed;
}
} else {
...
}
// 布局child
// We calculate everything with View's bounding box (which includes decor and margins)
// To calculate correct layout position, we subtract margins.
layoutDecoratedWithMargins(view, left, top, right, bottom);
...
}
可知该方法主要做了几件事:
- 获取
View - 根据方向决定添加
child到容器的顺序 - 如果有必要,测量
child的宽高 - 赋值当前
child消费的高度/宽度给result.mConsumed - 确定
child的上下左右位置,并根据该位置放置child
继续关注该方法第25行调用的measureChildWithMargins(view, 0, 0);方法,该方法定义在Recycler.LayoutManager中:
/**
* Measure a child view using standard measurement policy, taking the padding
* of the parent RecyclerView, any added item decorations and the child margins
* into account.
*
* If the RecyclerView can be scrolled in either dimension the caller may
* pass 0 as the widthUsed or heightUsed parameters as they will be irrelevant.
*
* @param child Child view to measure
* @param widthUsed Width in pixels currently consumed by other views, if relevant
* @param heightUsed Height in pixels currently consumed by other views, if relevant
*/
public void measureChildWithMargins(@NonNull View child, int widthUsed, int heightUsed) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final Rect insets = mRecyclerView.getItemDecorInsetsForChild(child);
widthUsed += insets.left + insets.right;
heightUsed += insets.top + insets.bottom;
final int widthSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(getWidth(), getWidthMode(),
getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight()
+ lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + widthUsed, lp.width,
canScrollHorizontally());
final int heightSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(getHeight(), getHeightMode(),
getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom()
+ lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + heightUsed, lp.height,
canScrollVertically());
if (shouldMeasureChild(child, widthSpec, heightSpec, lp)) {
child.measure(widthSpec, heightSpec);
}
}
接着看mRecyclerView.getItemDecorInsetsForChild(child):
Rect getItemDecorInsetsForChild(View child) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (!lp.mInsetsDirty) {
return lp.mDecorInsets;
}
if (mState.isPreLayout() && (lp.isItemChanged() || lp.isViewInvalid())) {
// changed/invalid items should not be updated until they are rebound.
return lp.mDecorInsets;
}
final Rect insets = lp.mDecorInsets;
insets.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
final int decorCount = mItemDecorations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < decorCount; i++) {
mTempRect.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
mItemDecorations.get(i).getItemOffsets(mTempRect, child, this, mState);
insets.left += mTempRect.left;
insets.top += mTempRect.top;
insets.right += mTempRect.right;
insets.bottom += mTempRect.bottom;
}
lp.mInsetsDirty = false;
return insets;
}
可知,会获取当前child对应的所有ItemDecoration所占用的区域,并计算到宽高中,并参与测量。
紧接着回到layoutChunk()的第27行result.mConsumed = mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedMeasurement(view);,当前分析例子为竖直布局,所以关注通过OrientationHelper.createVerticalHelper()创建的OrientationHelper实例对应的方法:
@Override
public int getDecoratedMeasurement(View view) {
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams)
view.getLayoutParams();
return mLayoutManager.getDecoratedMeasuredHeight(view) + params.topMargin
+ params.bottomMargin;
}
可知刚才insets的top和bottom以及child的上下margin都计算在返回值中,该值即为整个item所消费的高度;
再回到layoutChunk()的第53行layoutDecoratedWithMargins(view, left, top, right, bottom);:
public void layoutDecoratedWithMargins(@NonNull View child, int left, int top, int right,
int bottom) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final Rect insets = lp.mDecorInsets;
child.layout(left + insets.left + lp.leftMargin, top + insets.top + lp.topMargin,
right - insets.right - lp.rightMargin,
bottom - insets.bottom - lp.bottomMargin);
}
可知child的位置与insets和margin之间的关系。
dispatchLayoutStep3()
该函数也是主要和动画相关,忽略。
绘制:onDraw()
关于绘制比较简单,RecyclerView重写了与draw相关的方法主要有两个:draw()和onDraw()。
重写的draw()
@Override
public void draw(Canvas c) {
super.draw(c);
final int count = mItemDecorations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mItemDecorations.get(i).onDrawOver(c, this, mState);
}
// TODO If padding is not 0 and clipChildrenToPadding is false, to draw glows properly, we
// need find children closest to edges. Not sure if it is worth the effort.
boolean needsInvalidate = false;
if (mLeftGlow != null && !mLeftGlow.isFinished()) {
final int restore = c.save();
final int padding = mClipToPadding ? getPaddingBottom() : 0;
c.rotate(270);
c.translate(-getHeight() + padding, 0);
needsInvalidate = mLeftGlow != null && mLeftGlow.draw(c);
c.restoreToCount(restore);
}
if (mTopGlow != null && !mTopGlow.isFinished()) {
final int restore = c.save();
if (mClipToPadding) {
c.translate(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop());
}
needsInvalidate |= mTopGlow != null && mTopGlow.draw(c);
c.restoreToCount(restore);
}
if (mRightGlow != null && !mRightGlow.isFinished()) {
final int restore = c.save();
final int width = getWidth();
final int padding = mClipToPadding ? getPaddingTop() : 0;
c.rotate(90);
c.translate(-padding, -width);
needsInvalidate |= mRightGlow != null && mRightGlow.draw(c);
c.restoreToCount(restore);
}
if (mBottomGlow != null && !mBottomGlow.isFinished()) {
final int restore = c.save();
c.rotate(180);
if (mClipToPadding) {
c.translate(-getWidth() + getPaddingRight(), -getHeight() + getPaddingBottom());
} else {
c.translate(-getWidth(), -getHeight());
}
needsInvalidate |= mBottomGlow != null && mBottomGlow.draw(c);
c.restoreToCount(restore);
}
// If some views are animating, ItemDecorators are likely to move/change with them.
// Invalidate RecyclerView to re-draw decorators. This is still efficient because children's
// display lists are not invalidated.
if (!needsInvalidate && mItemAnimator != null && mItemDecorations.size() > 0
&& mItemAnimator.isRunning()) {
needsInvalidate = true;
}
if (needsInvalidate) {
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
知道View的绘制流程的都知道,该方法执行会绘制该View以及所有子View,第5行开始,会遍历所有的ItemDecoration,并回调onDrawOver()方法。由此可知,onDrawOver()实现的绘制,如果与child有重叠部分,那这些内容会绘制到child上方。
重写的onDraw()
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c) {
super.onDraw(c);
final int count = mItemDecorations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mItemDecorations.get(i).onDraw(c, this, mState);
}
}
逻辑比较简单,遍历所有的ItemDecoration,并回调onDraw()方法。可知,如果与child有重叠部分,那这部分内容会绘制到child下方。
LinearLayoutManager的WRAP_CONTENT场景
我们知道,LinearLayoutManager支持wrap_content自动测量,下面就来分析下是如何完成的。再次查看onMeasure方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthSpec, int heightSpec) {
...
if (mLayout.isAutoMeasureEnabled()) {
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightSpec);
/**
* This specific call should be considered deprecated and replaced with
* {@link #defaultOnMeasure(int, int)}. It can't actually be replaced as it could
* break existing third party code but all documentation directs developers to not
* override {@link LayoutManager#onMeasure(int, int)} when
* {@link LayoutManager#isAutoMeasureEnabled()} returns true.
*/
mLayout.onMeasure(mRecycler, mState, widthSpec, heightSpec);
final boolean measureSpecModeIsExactly =
widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
if (measureSpecModeIsExactly || mAdapter == null) {
return;
}
if (mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START) {
dispatchLayoutStep1();
}
// set dimensions in 2nd step. Pre-layout should happen with old dimensions for
// consistency
mLayout.setMeasureSpecs(widthSpec, heightSpec);
mState.mIsMeasuring = true;
dispatchLayoutStep2();
// now we can get the width and height from the children.
mLayout.setMeasuredDimensionFromChildren(widthSpec, heightSpec);
// if RecyclerView has non-exact width and height and if there is at least one child
// which also has non-exact width & height, we have to re-measure.
if (mLayout.shouldMeasureTwice()) {
mLayout.setMeasureSpecs(
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredWidth(), MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredHeight(), MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
mState.mIsMeasuring = true;
dispatchLayoutStep2();
// now we can get the width and height from the children.
mLayout.setMeasuredDimensionFromChildren(widthSpec, heightSpec);
}
} else {
...
}
}
因为heightMode为AT_MOST,所以19行的条件不满足,直接关注第28行mLayout.setMeasureSpecs(widthSpec, heightSpec),该方法定义在RecyclerView.LayoutManager中:
void setMeasureSpecs(int wSpec, int hSpec) {
mWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(wSpec);
mWidthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(wSpec);
if (mWidthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED && !ALLOW_SIZE_IN_UNSPECIFIED_SPEC) {
mWidth = 0;
}
mHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(hSpec);
mHeightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(hSpec);
if (mHeightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED && !ALLOW_SIZE_IN_UNSPECIFIED_SPEC) {
mHeight = 0;
}
}
会保存当前的测量规格,因为是高度设为wrap_content,所以mHeightMode=MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,mHeight取决于RecyclerView父布局留下多少空间给自己。
紧接着回到onMeasure()的第30行,又是dispatchLayoutStep2(),此条件下的分析与上文差异不大,在于当前给定的RecyclerView的高度为最大可用高度以及因为item个数的问题,LinearLayoutManager.fill()函数中循环的结束的条件可能是item个数过少。
接着看第33行mLayout.setMeasuredDimensionFromChildren(widthSpec, heightSpec),该方法定义也定义在RecyclerView.LayoutManager中:
/**
* Called after a layout is calculated during a measure pass when using auto-measure.
*
* It simply traverses all children to calculate a bounding box then calls
* {@link #setMeasuredDimension(Rect, int, int)}. LayoutManagers can override that method
* if they need to handle the bounding box differently.
*
* For example, GridLayoutManager override that method to ensure that even if a column is
* empty, the GridLayoutManager still measures wide enough to include it.
*
* @param widthSpec The widthSpec that was passing into RecyclerView's onMeasure
* @param heightSpec The heightSpec that was passing into RecyclerView's onMeasure
*/
void setMeasuredDimensionFromChildren(int widthSpec, int heightSpec) {
final int count = getChildCount();
if (count == 0) {
mRecyclerView.defaultOnMeasure(widthSpec, heightSpec);
return;
}
int minX = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxX = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int maxY = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
final Rect bounds = mRecyclerView.mTempRect;
getDecoratedBoundsWithMargins(child, bounds);
if (bounds.left < minX) {
minX = bounds.left;
}
if (bounds.right > maxX) {
maxX = bounds.right;
}
if (bounds.top < minY) {
minY = bounds.top;
}
if (bounds.bottom > maxY) {
maxY = bounds.bottom;
}
}
mRecyclerView.mTempRect.set(minX, minY, maxX, maxY);
setMeasuredDimension(mRecyclerView.mTempRect, widthSpec, heightSpec);
}
函数逻辑比较少,遍历当前所有的child,获取item的bounds(注意是item,代表了包含了child的margin和ItemDecoration所占用大小),并最终获取其中四边的最值,设置到mRecyclerView.mTempRect中,并调用setMeasuredDimension(mRecyclerView.mTempRect, widthSpec, heightSpec):
/**
* Sets the measured dimensions from the given bounding box of the children and the
* measurement specs that were passed into {@link RecyclerView#onMeasure(int, int)}. It is
* only called if a LayoutManager returns true from
* {@link #isAutoMeasureEnabled()} and it is called after the RecyclerView calls
* {@link LayoutManager#onLayoutChildren(Recycler, State)} in the execution of
* {@link RecyclerView#onMeasure(int, int)}.
*
* This method must call {@link #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)}.
*
* The default implementation adds the RecyclerView's padding to the given bounding box
* then caps the value to be within the given measurement specs.
*
* @param childrenBounds The bounding box of all children
* @param wSpec The widthMeasureSpec that was passed into the RecyclerView.
* @param hSpec The heightMeasureSpec that was passed into the RecyclerView.
*
* @see #isAutoMeasureEnabled()
* @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)
*/
public void setMeasuredDimension(Rect childrenBounds, int wSpec, int hSpec) {
int usedWidth = childrenBounds.width() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
int usedHeight = childrenBounds.height() + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
int width = chooseSize(wSpec, usedWidth, getMinimumWidth());
int height = chooseSize(hSpec, usedHeight, getMinimumHeight());
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
...
/**
* Chooses a size from the given specs and parameters that is closest to the desired size
* and also complies with the spec.
*
* @param spec The measureSpec
* @param desired The preferred measurement
* @param min The minimum value
*
* @return A size that fits to the given specs
*/
public static int chooseSize(int spec, int desired, int min) {
final int mode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
final int size = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
switch (mode) {
case View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
// match_parent或固定尺寸,直接返回
return size;
case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
// wrap_content模式,取可用大小size和需要用到的最小值
return Math.min(size, Math.max(desired, min));
case View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
// 当前需要用到的大小
default:
return Math.max(desired, min);
}
}
...
/**
* {@link View#setMeasuredDimension(int, int) Set the measured dimensions} of the
* host RecyclerView.
*
* @param widthSize Measured width
* @param heightSize Measured height
*/
public void setMeasuredDimension(int widthSize, int heightSize) {
mRecyclerView.setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}
先根据刚才得到的bounds计算出usedHeight,然后调用chooseSize,走case View.MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:分支条件,获取合适的高度height,最终调用setMeasuredDimension(width, height)给RecyclerView设置宽高。
接下来看onLayout()->dispatchLayout()方法:
void dispatchLayout() {
if (mAdapter == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "No adapter attached; skipping layout");
// leave the state in START
return;
}
if (mLayout == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "No layout manager attached; skipping layout");
// leave the state in START
return;
}
mState.mIsMeasuring = false;
if (mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START) {
dispatchLayoutStep1();
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
dispatchLayoutStep2();
} else if (mAdapterHelper.hasUpdates() || mLayout.getWidth() != getWidth()
|| mLayout.getHeight() != getHeight()) {
// First 2 steps are done in onMeasure but looks like we have to run again due to
// changed size.
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
dispatchLayoutStep2();
} else {
// always make sure we sync them (to ensure mode is exact)
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
}
dispatchLayoutStep3();
}
因为在onMeasure()已经执行过dispatchLayoutStep2(),所以mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START条件不成立,此时关注mLayout.getHeight() != getHeight()这个条件,因为mLayout.getHeight()获取的高度为在onMeasure()中设置的可用高度,而getHeight()此时返回的是真实高度,这两个值部分情况下都不相等,所以,第21行mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this)会把RecyclerView的最终高度设置给mLayout,再进行一次dispatchLayoutStep2(),最终执行dispatchLayoutStep3()完成所有步骤。
初步分析小结
初步分析结束后,我们弄懂了ItemDecoration、LinearLayoutManager是如何工作的,以及wrap_content模式下是如何测量和布局的。
三.深入分析
此节会更深入分析,了解缓存机制。想了解缓存,首先需要了解RecyclerView的滑动。
滑动:scrollStep()
注意:
RecyclerView的dy > 0表示手指上滑。
很容易发现,普通滑动、fling最终都会走到scrollStep():
/**
* Scrolls the RV by 'dx' and 'dy' via calls to
* {@link LayoutManager#scrollHorizontallyBy(int, Recycler, State)} and
* {@link LayoutManager#scrollVerticallyBy(int, Recycler, State)}.
*
* Also sets how much of the scroll was actually consumed in 'consumed' parameter (indexes 0 and
* 1 for the x axis and y axis, respectively).
*
* This method should only be called in the context of an existing scroll operation such that
* any other necessary operations (such as a call to {@link #consumePendingUpdateOperations()})
* is already handled.
*/
void scrollStep(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed) {
startInterceptRequestLayout();
onEnterLayoutOrScroll();
TraceCompat.beginSection(TRACE_SCROLL_TAG);
fillRemainingScrollValues(mState);
int consumedX = 0;
int consumedY = 0;
if (dx != 0) {
consumedX = mLayout.scrollHorizontallyBy(dx, mRecycler, mState);
}
if (dy != 0) {
consumedY = mLayout.scrollVerticallyBy(dy, mRecycler, mState);
}
TraceCompat.endSection();
repositionShadowingViews();
onExitLayoutOrScroll();
stopInterceptRequestLayout(false);
if (consumed != null) {
consumed[0] = consumedX;
consumed[1] = consumedY;
}
}
滚动会交给mLayout处理,那看LineraLayoutManager的scrollVerticallyBy():
@Override
public int scrollVerticallyBy(int dy, RecyclerView.Recycler recycler,
RecyclerView.State state) {
if (mOrientation == HORIZONTAL) {
return 0;
}
return scrollBy(dy, recycler, state);
}
int scrollBy(int dy, RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
if (getChildCount() == 0 || dy == 0) {
return 0;
}
mLayoutState.mRecycle = true;
ensureLayoutState();
final int layoutDirection = dy > 0 ? LayoutState.LAYOUT_END : LayoutState.LAYOUT_START;
final int absDy = Math.abs(dy);
updateLayoutState(layoutDirection, absDy, true, state);
final int consumed = mLayoutState.mScrollingOffset
+ fill(recycler, mLayoutState, state, false);
if (consumed < 0) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Don't have any more elements to scroll");
}
return 0;
}
final int scrolled = absDy > consumed ? layoutDirection * consumed : dy;
mOrientationHelper.offsetChildren(-scrolled);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "scroll req: " + dy + " scrolled: " + scrolled);
}
mLayoutState.mLastScrollDelta = scrolled;
return scrolled;
}
首先第16行根据dy的正负来给layoutDirection设置方向,手指往上滑动,即dy>0,此时layoutDirection = LayoutState.LAYOUT_END,手指往下滑动,反之;
然后第17行final int absDy = Math.abs(dy)获取滑动的绝对距离absDy;
第18行updateLayoutState(layoutDirection, absDy, true, state)根据函数名可大概知道是更新布局状态LayoutState;第19、20行执行fill()来进行真正的布局(如果需要的话);
接下来进入updateLayoutState()探究布局状态是如何更新的:
private void updateLayoutState(int layoutDirection, int requiredSpace,
boolean canUseExistingSpace, RecyclerView.State state) {
// If parent provides a hint, don't measure unlimited.
mLayoutState.mInfinite = resolveIsInfinite();
mLayoutState.mExtra = getExtraLayoutSpace(state);
// 设置布局方向
mLayoutState.mLayoutDirection = layoutDirection;
int scrollingOffset;
if (layoutDirection == LayoutState.LAYOUT_END) {
mLayoutState.mExtra += mOrientationHelper.getEndPadding();
// get the first child in the direction we are going
final View child = getChildClosestToEnd(); // 根据方向,获取最后一个child
// the direction in which we are traversing children
mLayoutState.mItemDirection = mShouldReverseLayout ? LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_HEAD
: LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_TAIL;
// 更新当前position为下一个即将需要出现的item索引
mLayoutState.mCurrentPosition = getPosition(child) + mLayoutState.mItemDirection;
// 设置为最后一个item的边界值,例如bottom
mLayoutState.mOffset = mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedEnd(child);
// 计算在不增加新item的情况下,有多少空间可偏移,即最后一个item超出rv的部分
// calculate how much we can scroll without adding new children (independent of layout)
scrollingOffset = mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedEnd(child)
- mOrientationHelper.getEndAfterPadding();
} else {
final View child = getChildClosestToStart();
mLayoutState.mExtra += mOrientationHelper.getStartAfterPadding();
mLayoutState.mItemDirection = mShouldReverseLayout ? LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_TAIL
: LayoutState.ITEM_DIRECTION_HEAD;
mLayoutState.mCurrentPosition = getPosition(child) + mLayoutState.mItemDirection;
mLayoutState.mOffset = mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedStart(child);
scrollingOffset = -mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedStart(child)
+ mOrientationHelper.getStartAfterPadding();
}
mLayoutState.mAvailable = requiredSpace;
if (canUseExistingSpace) {
// 当前滑动绝对距离减掉scrollingOffset,结合fill函数可知大于0表示当前滑动需要新增item
// mAvailable含义:可理解为表示的是滑动后当前最后一个item距离边界的大小,
// 正值表示需要新item来填补的空间,负值表示最后一个item超出边界的大小
mLayoutState.mAvailable -= scrollingOffset;
}
// 赋值
mLayoutState.mScrollingOffset = scrollingOffset;
}
注意第38行mLayoutState.mAvailable -= scrollingOffset,如果滑动距离小于等于scollingOffset,此时经过计算后mAvailable值为负值,大小为超出边界的大小;只有滑动距离大于scrollingOffset的情况下mAvailable会大于0,也就是此次滑动需要加入item;如果对fill()函数还有印象的话,只有足够的剩余空间才会执行循环layoutChunk()的代码;把fill()再次分析下:
int fill(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, LayoutState layoutState,
RecyclerView.State state, boolean stopOnFocusable) {
// max offset we should set is mFastScroll + available
final int start = layoutState.mAvailable;
// 滑动进入,此时条件满足
if (layoutState.mScrollingOffset != LayoutState.SCROLLING_OFFSET_NaN) {
// 如果可用布局空间小于0,即更新mScrollingOffset值,联系updateLayoutState函数可知,
// 计算出的值为实际滑动的距离
// TODO ugly bug fix. should not happen
if (layoutState.mAvailable < 0) {
layoutState.mScrollingOffset += layoutState.mAvailable;
}
// 回收滑动后会超出RV边界的children
recycleByLayoutState(recycler, layoutState);
}
int remainingSpace = layoutState.mAvailable + layoutState.mExtra;
LayoutChunkResult layoutChunkResult = mLayoutChunkResult;
while ((layoutState.mInfinite || remainingSpace > 0) && layoutState.hasMore(state)) {
layoutChunkResult.resetInternal();
...
layoutChunk(recycler, state, layoutState, layoutChunkResult);
...
if (layoutChunkResult.mFinished) {
break;
}
layoutState.mOffset += layoutChunkResult.mConsumed * layoutState.mLayoutDirection;
/**
* Consume the available space if:
* * layoutChunk did not request to be ignored
* * OR we are laying out scrap children
* * OR we are not doing pre-layout
*/
if (!layoutChunkResult.mIgnoreConsumed || mLayoutState.mScrapList != null
|| !state.isPreLayout()) {
// 更新可用空间
layoutState.mAvailable -= layoutChunkResult.mConsumed;
// we keep a separate remaining space because mAvailable is important for recycling
remainingSpace -= layoutChunkResult.mConsumed;
}
// 滑动进入,此时条件满足
if (layoutState.mScrollingOffset != LayoutState.SCROLLING_OFFSET_NaN) {
// 先更新滑动偏移
layoutState.mScrollingOffset += layoutChunkResult.mConsumed;
if (layoutState.mAvailable < 0) {
// 如果mAvailable<0,此时mAvaiable值为最后一个填充item超出边界部分(负数),计算得出实际的滑动距离
layoutState.mScrollingOffset += layoutState.mAvailable;
}
// 回收滑动后会超出RV边界的children
recycleByLayoutState(recycler, layoutState);
}
if (stopOnFocusable && layoutChunkResult.mFocusable) {
break;
}
}
...
// 如果未进行layoutChunk,即start=mAvailable,此时返回0,即未消耗任何可用空间;
// 如果进行了layoutChunk,start为初始可填充空间,当mAvailable值为负值,则大小为最后一个填充的item超出边界部分;
// 当mAvailable为正值,则大小为剩余未被填充的空间;表达式计算的结果表示填充最终用到的空间
return start - layoutState.mAvailable;
}
以下分两种情况分析:remainingSpace大于0和小于等于0(假设layoutState.mExtra=0,即remainingSpace=layoutState.mAvailable);
remainingSpace>0时:表示循环条件满足,执行layoutChunk,关注第36行layoutState.mAvailable -= layoutChunkResult.mConsumed会扣除已经消耗的距离,如果此值变为负数(此时remainingSpace也为该值),则表示即将退出循环,第44行layoutState.mScrollingOffset += layoutChunkResult.mConsumed到第47行会经过计算得出实际滑动的距离,然后第50行recycleByLayoutState(recycler, layoutState)中会根据滑动距离来判断回收超出边界的children,该函数稍后再具体分析;最终返回start - layoutState.mAvailable;remainingSpace<=0时:第10行layoutState.mAvailable < 0条件满足,第11行经过计算更新layoutState.mScrollingOffset值为滑动的距离,第14行recycleByLayoutState(recycler, layoutState)回收不需要的children;最终返回start - layoutState.mAvailable,此情况下会返回0;
再次回到scrollBy():
int scrollBy(int dy, RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
if (getChildCount() == 0 || dy == 0) {
return 0;
}
mLayoutState.mRecycle = true;
ensureLayoutState();
final int layoutDirection = dy > 0 ? LayoutState.LAYOUT_END : LayoutState.LAYOUT_START;
final int absDy = Math.abs(dy);
updateLayoutState(layoutDirection, absDy, true, state);
final int consumed = mLayoutState.mScrollingOffset
+ fill(recycler, mLayoutState, state, false);
if (consumed < 0) {
...
return 0;
}
final int scrolled = absDy > consumed ? layoutDirection * consumed : dy;
mOrientationHelper.offsetChildren(-scrolled);
...
mLayoutState.mLastScrollDelta = scrolled;
return scrolled;
}
因为mAvailable = absDy - mScrollingOffset:
当mAvailable <= 0时,表示不需要新的item加入,此时fill()返回0表示未填充任何空间,consumed = mLayoutState.mScrollingOffset = 滑动开始时最后一个item超出边界部分,得出absDy > consumed条件不成立,scrolled = dy;
当mAvailable > 0时(即absDy > mLayoutState.mScrollingOffset,表示该值肯定都会被滑动所覆盖),表示需要新的item加入,此时fill()返回填充最终用到的大小;如果该填充大小小于初始可用空间,则表示还有剩余空间未被填充,此时consumed = 滑动开始时最后一个item超出边界部分 + 填充大小,此时absDy > consumed条件满足,scrolled = layoutDirection * consumed,表示滑动距离超出了最终填充的区域,所以要修正scrolled的值;如果fill()返回值大于初始可用空间,表示填充大小超出了可用空间,consumed = 滑动开始时最后一个item超出边界部分 + 填充大小,此时absDy > consumed条件不满足,scrolled = dy;
scrolled确定后,在第17行mOrientationHelper.offsetChildren(-scrolled)经过转发最终会调用到RecyclerView.offsetChildrenVertical()来更新所有child的top、bottom参数来达到滑动的效果。
至此,RecyclerView的滑动已分析完成,核心还是通过updateLayoutState()函数更新滑动后达到的状态,并通过fill()函数来增加和移除回收item。
补充:
RecyclerView重写了scrollTo()和scrollBy(),但只有scrollBy有实现功能,不能通过getScrollX()和getScrollY()来获取滑动位置。
缓存:Recycler
通过上面的分析知道View的获得是通过layoutChunk()中的View view = layoutState.next(recycler)调用来获取的,接下来就先看LinearLayoutManager.LayoutState.next(recycler):
/**
* Gets the view for the next element that we should layout.
* Also updates current item index to the next item, based on {@link #mItemDirection}
*
* @return The next element that we should layout.
*/
View next(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler) {
if (mScrapList != null) {
return nextViewFromScrapList();
}
final View view = recycler.getViewForPosition(mCurrentPosition);
mCurrentPosition += mItemDirection;
return view;
}
就如注释所写,刚方法获取下一个需要布局的元素,同时更新mCurrentPosition的值为下一个即将布局的元素索引,该值计算取决于布局方向mItemDerection;
因为mScrapList默认为null并且只有在LinearLayoutManager.layoutForPredictiveAnimations()被赋值,所以可以直接关注recycler.getViewForPosition(mCurrentPosition),该函数内部会调用到Recycler.tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline():
tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline()
/**
* Attempts to get the ViewHolder for the given position, either from the Recycler scrap,
* cache, the RecycledViewPool, or creating it directly.
*
* If a deadlineNs other than {@link #FOREVER_NS} is passed, this method early return
* rather than constructing or binding a ViewHolder if it doesn't think it has time.
* If a ViewHolder must be constructed and not enough time remains, null is returned. If a
* ViewHolder is aquired and must be bound but not enough time remains, an unbound holder is
* returned. Use {@link ViewHolder#isBound()} on the returned object to check for this.
*
* @param position Position of ViewHolder to be returned.
* @param dryRun True if the ViewHolder should not be removed from scrap/cache/
* @param deadlineNs Time, relative to getNanoTime(), by which bind/create work should
* complete. If FOREVER_NS is passed, this method will not fail to
* create/bind the holder if needed.
*
* @return ViewHolder for requested position
*/
@Nullable
ViewHolder tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline(int position,
boolean dryRun, long deadlineNs) {
...
boolean fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache = false;
ViewHolder holder = null;
// 0) If there is a changed scrap, try to find from there
if (mState.isPreLayout()) {
holder = getChangedScrapViewForPosition(position);
fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache = holder != null;
}
// 1) Find by position from scrap/hidden list/cache
if (holder == null) {
// 先从scrap/hidden/cache列表中尝试获取holder
holder = getScrapOrHiddenOrCachedHolderForPosition(position, dryRun);
if (holder != null) {
if (!validateViewHolderForOffsetPosition(holder)) {
// recycle holder (and unscrap if relevant) since it can't be used
if (!dryRun) {
// we would like to recycle this but need to make sure it is not used by
// animation logic etc.
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID);
if (holder.isScrap()) {
removeDetachedView(holder.itemView, false);
holder.unScrap();
} else if (holder.wasReturnedFromScrap()) {
holder.clearReturnedFromScrapFlag();
}
recycleViewHolderInternal(holder);
}
holder = null;
} else {
fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache = true;
}
}
}
if (holder == null) {
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
...
// 获取类型
final int type = mAdapter.getItemViewType(offsetPosition);
// 2) Find from scrap/cache via stable ids, if exists
if (mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
holder = getScrapOrCachedViewForId(mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition),
type, dryRun);
if (holder != null) {
// update position
holder.mPosition = offsetPosition;
fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache = true;
}
}
// 如果有设置拓展缓存mViewCacheExtension,尝试从拓展缓存获取
if (holder == null && mViewCacheExtension != null) {
// We are NOT sending the offsetPosition because LayoutManager does not
// know it.
final View view = mViewCacheExtension
.getViewForPositionAndType(this, position, type);
if (view != null) {
holder = getChildViewHolder(view);
...
}
}
if (holder == null) { // fallback to pool
...
// 尝试从缓存池RecycledViewPool获取
holder = getRecycledViewPool().getRecycledView(type);
if (holder != null) {
holder.resetInternal();
if (FORCE_INVALIDATE_DISPLAY_LIST) {
invalidateDisplayListInt(holder);
}
}
}
if (holder == null) {
long start = getNanoTime();
...
// 从adapter创建
holder = mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type);
if (ALLOW_THREAD_GAP_WORK) {
// only bother finding nested RV if prefetching
RecyclerView innerView = findNestedRecyclerView(holder.itemView);
if (innerView != null) {
holder.mNestedRecyclerView = new WeakReference<>(innerView);
}
}
long end = getNanoTime();
mRecyclerPool.factorInCreateTime(type, end - start);
...
}
}
// This is very ugly but the only place we can grab this information
// before the View is rebound and returned to the LayoutManager for post layout ops.
// We don't need this in pre-layout since the VH is not updated by the LM.
if (fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache && !mState.isPreLayout() && holder
.hasAnyOfTheFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUNCED_FROM_HIDDEN_LIST)) {
holder.setFlags(0, ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUNCED_FROM_HIDDEN_LIST);
if (mState.mRunSimpleAnimations) {
int changeFlags = ItemAnimator
.buildAdapterChangeFlagsForAnimations(holder);
changeFlags |= ItemAnimator.FLAG_APPEARED_IN_PRE_LAYOUT;
final ItemHolderInfo info = mItemAnimator.recordPreLayoutInformation(mState,
holder, changeFlags, holder.getUnmodifiedPayloads());
recordAnimationInfoIfBouncedHiddenView(holder, info);
}
}
boolean bound = false;
if (mState.isPreLayout() && holder.isBound()) {
// do not update unless we absolutely have to.
holder.mPreLayoutPosition = position;
} else if (!holder.isBound() || holder.needsUpdate() || holder.isInvalid()) {
...
// 如果未绑定/需要更新/数据无效,holder都需要重新绑定数据
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
bound = tryBindViewHolderByDeadline(holder, offsetPosition, position, deadlineNs);
}
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = holder.itemView.getLayoutParams();
final LayoutParams rvLayoutParams;
if (lp == null) {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) generateDefaultLayoutParams();
holder.itemView.setLayoutParams(rvLayoutParams);
} else if (!checkLayoutParams(lp)) {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) generateLayoutParams(lp);
holder.itemView.setLayoutParams(rvLayoutParams);
} else {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) lp;
}
rvLayoutParams.mViewHolder = holder;
rvLayoutParams.mPendingInvalidate = fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache && bound;
return holder;
}
该函数内容比较多,但总结起来就是:
- 先尝试从一级缓存
mCachedViews(默认大小2,不区分type)中获取,从该缓存获取的holder直接可用,无需重新bind - 如果存在拓展缓存
mViewCacheExtension,尝试从拓展缓存中获取 - 再尝试从缓存池
RecycledViewPool(默认大小5,区分type)中获取,从该缓存获取的holder需要重新bind - 如果缓存中都没找到,就调用
mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type)创建 - 根据
holder的状态判断是否需要调用绑定数据函数tryBindViewHolderByDeadline() - 确保
itemView设置了布局参数 - 最终返回
holder
顺便看下绑定数据函数tryBindViewHolderByDeadline(),该函数内部会执行mAdapter.bindViewHolder(holder, offsetPosition):
public final void bindViewHolder(@NonNull VH holder, int position) {
holder.mPosition = position;
if (hasStableIds()) {
holder.mItemId = getItemId(position);
}
holder.setFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUND,
ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUND | ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE | ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID
| ViewHolder.FLAG_ADAPTER_POSITION_UNKNOWN);
TraceCompat.beginSection(TRACE_BIND_VIEW_TAG);
onBindViewHolder(holder, position, holder.getUnmodifiedPayloads());
holder.clearPayload();
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = holder.itemView.getLayoutParams();
if (layoutParams instanceof RecyclerView.LayoutParams) {
((LayoutParams) layoutParams).mInsetsDirty = true;
}
TraceCompat.endSection();
}
可以看到熟悉的函数onBindViewHolder(holder, position, holder.getUnmodifiedPayloads())被调用。
接下来关注下是如何进行回收的。
recycleViewHolderInternal()
从滑动小结中的LinearLayoutManager.fill()函数分析可知,会执行recycleByLayoutState()来移除并回收超出区域的视图,跟到函数内部,最终会调用到Recycler.recycleViewHolderInternal()函数:
/**
* internal implementation checks if view is scrapped or attached and throws an exception
* if so.
* Public version un-scraps before calling recycle.
*/
void recycleViewHolderInternal(ViewHolder holder) {
...
//noinspection unchecked
final boolean transientStatePreventsRecycling = holder
.doesTransientStatePreventRecycling();
final boolean forceRecycle = mAdapter != null
&& transientStatePreventsRecycling
&& mAdapter.onFailedToRecycleView(holder);
boolean cached = false;
boolean recycled = false;
...
if (forceRecycle || holder.isRecyclable()) {
if (mViewCacheMax > 0
&& !holder.hasAnyOfTheFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID
| ViewHolder.FLAG_REMOVED
| ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE
| ViewHolder.FLAG_ADAPTER_POSITION_UNKNOWN)) {
// “退休”最旧的cached,即将cached的最旧缓存移除,放置到RecycledViewPool中
// Retire oldest cached view
int cachedViewSize = mCachedViews.size();
if (cachedViewSize >= mViewCacheMax && cachedViewSize > 0) {
recycleCachedViewAt(0);
cachedViewSize--;
}
int targetCacheIndex = cachedViewSize;
if (ALLOW_THREAD_GAP_WORK
&& cachedViewSize > 0
&& !mPrefetchRegistry.lastPrefetchIncludedPosition(holder.mPosition)) {
// when adding the view, skip past most recently prefetched views
int cacheIndex = cachedViewSize - 1;
while (cacheIndex >= 0) {
int cachedPos = mCachedViews.get(cacheIndex).mPosition;
if (!mPrefetchRegistry.lastPrefetchIncludedPosition(cachedPos)) {
break;
}
cacheIndex--;
}
targetCacheIndex = cacheIndex + 1;
}
// 将新回收的holder放置到mCacheViews的末尾
mCachedViews.add(targetCacheIndex, holder);
cached = true;
}
if (!cached) {
addViewHolderToRecycledViewPool(holder, true);
recycled = true;
}
} else {
// NOTE: A view can fail to be recycled when it is scrolled off while an animation
// runs. In this case, the item is eventually recycled by
// ItemAnimatorRestoreListener#onAnimationFinished.
// TODO: consider cancelling an animation when an item is removed scrollBy,
// to return it to the pool faster
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "trying to recycle a non-recycleable holder. Hopefully, it will "
+ "re-visit here. We are still removing it from animation lists"
+ exceptionLabel());
}
}
// even if the holder is not removed, we still call this method so that it is removed
// from view holder lists.
mViewInfoStore.removeViewHolder(holder);
if (!cached && !recycled && transientStatePreventsRecycling) {
holder.mOwnerRecyclerView = null;
}
}
可以知道,holder被回收时,会优先判断mCachedViews是否还能放置,如果不能,将移除mCachedViews中最旧的holder(即最早进入该缓存列表的数据),并放置到mRecyclerPool中(前提是mRecyclerPool还未放满),最终将刚被回收的holder加到mCachedViews列表的末尾。
补充
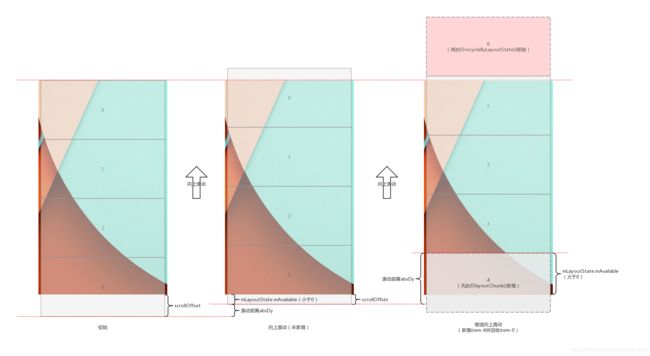
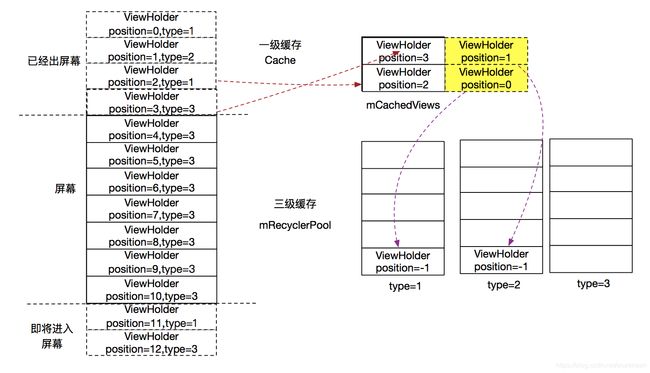
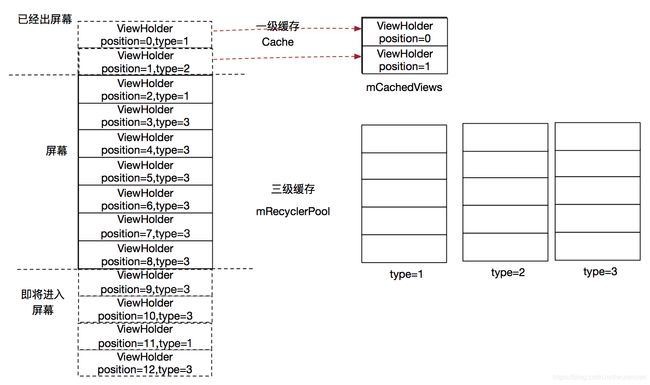
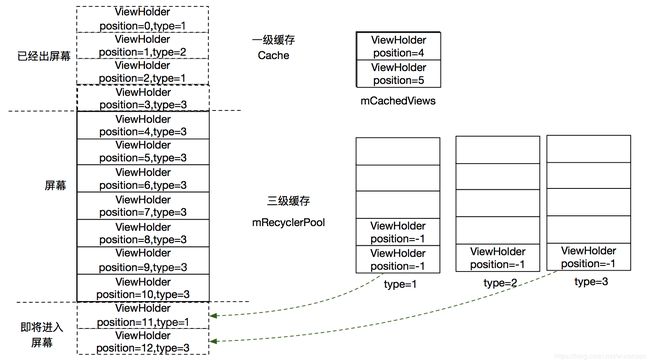
结合以下几张从网上找的图片,可以更好的理解缓存。(出处:RecyclerView缓存原理,有图有真相)
- 出屏幕时候的情况-mCacheViews未满:
- 出屏幕时候的情况-mCacheViews已经满:
- 屏幕往下拉ViewHolder(position=1)进入屏幕的情况:
- 进屏幕时候的情况:
数据刷新
接下来看下数据刷新是怎么实现的。
Adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()
最常见的刷新是全部刷新,看下代码:
public final void notifyDataSetChanged() {
mObservable.notifyChanged();
}
跟进去会走到:
private class RecyclerViewDataObserver extends AdapterDataObserver {
...
@Override
public void onChanged() {
assertNotInLayoutOrScroll(null);
mState.mStructureChanged = true;
processDataSetCompletelyChanged(true);
if (!mAdapterHelper.hasPendingUpdates()) {
requestLayout();
}
}
...
}
该类定义在RecyclerView中,紧接着是processDataSetCompletelyChanged(true):
/**
* Processes the fact that, as far as we can tell, the data set has completely changed.
*
*
* - Once layout occurs, all attached items should be discarded or animated.
*
- Attached items are labeled as invalid.
*
- Because items may still be prefetched between a "data set completely changed"
* event and a layout event, all cached items are discarded.
*
*
* @param dispatchItemsChanged Whether to call
* {@link LayoutManager#onItemsChanged(RecyclerView)} during measure/layout.
*/
void processDataSetCompletelyChanged(boolean dispatchItemsChanged) {
mDispatchItemsChangedEvent |= dispatchItemsChanged;
mDataSetHasChangedAfterLayout = true;
markKnownViewsInvalid();
}
/**
* Mark all known views as invalid. Used in response to a, "the whole world might have changed"
* data change event.
*/
void markKnownViewsInvalid() {
final int childCount = mChildHelper.getUnfilteredChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = getChildViewHolderInt(mChildHelper.getUnfilteredChildAt(i));
if (holder != null && !holder.shouldIgnore()) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE | ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID);
}
}
markItemDecorInsetsDirty();
mRecycler.markKnownViewsInvalid();
}
在markKnownViewsInvalid()中,会遍历更新当前所有child的holder的标记为ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE | ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID,同时会调用mRecycler.markKnownViewsInvalid()来更新Recycler缓存:
void markKnownViewsInvalid() {
final int cachedCount = mCachedViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cachedCount; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mCachedViews.get(i);
if (holder != null) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE | ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID);
holder.addChangePayload(null);
}
}
if (mAdapter == null || !mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
// we cannot re-use cached views in this case. Recycle them all
recycleAndClearCachedViews();
}
}
会先更新缓存holder的标记状态,如果!mAdapter.hasStableIds()条件成立,会回收mCachedViews的缓存到RecycledViewPool中。
以上仅仅是更新了holder的标记状态,继续回到RecyclerViewDataObserver.onChanged()方法中可知,会调用requestLayout()来请求刷新,最终就会重新执行布局。根据上一节“缓存:Recycler-tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline()”分析提到的,视图会重新绑定数据来达到刷新。
Adapter.notifyItemChanged()
该函数有重载方法,但都会执行AdapterDataObservable.notifyItemRangeChanged()方法,并走到RecyclerViewDataObserver.onItemRangeChanged():
@Override
public void onItemRangeChanged(int positionStart, int itemCount, Object payload) {
assertNotInLayoutOrScroll(null);
if (mAdapterHelper.onItemRangeChanged(positionStart, itemCount, payload)) {
triggerUpdateProcessor();
}
}
继续跟进AdatperHelper.onItemRangeChanged方法:
/**
* @return True if updates should be processed.
*/
boolean onItemRangeChanged(int positionStart, int itemCount, Object payload) {
if (itemCount < 1) {
return false;
}
mPendingUpdates.add(obtainUpdateOp(UpdateOp.UPDATE, positionStart, itemCount, payload));
mExistingUpdateTypes |= UpdateOp.UPDATE;
return mPendingUpdates.size() == 1;
}
@Override
public UpdateOp obtainUpdateOp(int cmd, int positionStart, int itemCount, Object payload) {
UpdateOp op = mUpdateOpPool.acquire();
if (op == null) {
op = new UpdateOp(cmd, positionStart, itemCount, payload);
} else {
op.cmd = cmd;
op.positionStart = positionStart;
op.itemCount = itemCount;
op.payload = payload;
}
return op;
}
核心就是把“更新操作-UpdateOp.UPDATE“添加到延期更新列表mPendingUpdates,obtainUpdateOp()函数从对象池获取对象。
回到RecyclerViewDataObserver.onItemRangeChanged()的triggerUpdateProcessor()函数:
void triggerUpdateProcessor() {
if (POST_UPDATES_ON_ANIMATION && mHasFixedSize && mIsAttached) {
ViewCompat.postOnAnimation(RecyclerView.this, mUpdateChildViewsRunnable);
} else {
mAdapterUpdateDuringMeasure = true;
requestLayout();
}
}
最终还是会回到布局流程。那可以知道,更新操作需要有地方去处理更新操作列表mPendingUpdates,跟进布局流程,在dispatchLayoutStep2()中执行了函数mAdapterHelper.consumeUpdatesInOnePass();:
/**
* Skips pre-processing and applies all updates in one pass.
*/
void consumeUpdatesInOnePass() {
// we still consume postponed updates (if there is) in case there was a pre-process call
// w/o a matching consumePostponedUpdates.
consumePostponedUpdates();
final int count = mPendingUpdates.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
UpdateOp op = mPendingUpdates.get(i);
switch (op.cmd) {
case UpdateOp.ADD:
mCallback.onDispatchSecondPass(op);
mCallback.offsetPositionsForAdd(op.positionStart, op.itemCount);
break;
case UpdateOp.REMOVE:
mCallback.onDispatchSecondPass(op);
mCallback.offsetPositionsForRemovingInvisible(op.positionStart, op.itemCount);
break;
case UpdateOp.UPDATE:
mCallback.onDispatchSecondPass(op);
mCallback.markViewHoldersUpdated(op.positionStart, op.itemCount, op.payload);
break;
case UpdateOp.MOVE:
mCallback.onDispatchSecondPass(op);
mCallback.offsetPositionsForMove(op.positionStart, op.itemCount);
break;
}
if (mOnItemProcessedCallback != null) {
mOnItemProcessedCallback.run();
}
}
recycleUpdateOpsAndClearList(mPendingUpdates);
mExistingUpdateTypes = 0;
}
当前为UpdateOp.UPDATE类型,会先执行mCallback.onDispatchSecondPass(op):
@Override
public void onDispatchSecondPass(AdapterHelper.UpdateOp op) {
dispatchUpdate(op);
}
void dispatchUpdate(AdapterHelper.UpdateOp op) {
switch (op.cmd) {
case AdapterHelper.UpdateOp.ADD:
mLayout.onItemsAdded(RecyclerView.this, op.positionStart, op.itemCount);
break;
case AdapterHelper.UpdateOp.REMOVE:
mLayout.onItemsRemoved(RecyclerView.this, op.positionStart, op.itemCount);
break;
case AdapterHelper.UpdateOp.UPDATE:
mLayout.onItemsUpdated(RecyclerView.this, op.positionStart, op.itemCount,
op.payload);
break;
case AdapterHelper.UpdateOp.MOVE:
mLayout.onItemsMoved(RecyclerView.this, op.positionStart, op.itemCount, 1);
break;
}
}
最终会执行LayoutManager中对应的函数,因为LinearLayoutManager并没有重写这几个方法,所以不做分析;
回到consumeUpdatesInOnePass()中,紧接着执行mCallback.markViewHoldersUpdated(op.positionStart, op.itemCount, op.payload):
@Override
public void markViewHoldersUpdated(int positionStart, int itemCount, Object payload) {
viewRangeUpdate(positionStart, itemCount, payload);
mItemsChanged = true;
}
执行到RecyclerView.viewRangeUpdate():
* Rebind existing views for the given range, or create as needed.
*
* @param positionStart Adapter position to start at
* @param itemCount Number of views that must explicitly be rebound
*/
void viewRangeUpdate(int positionStart, int itemCount, Object payload) {
final int childCount = mChildHelper.getUnfilteredChildCount();
final int positionEnd = positionStart + itemCount;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = mChildHelper.getUnfilteredChildAt(i);
final ViewHolder holder = getChildViewHolderInt(child);
if (holder == null || holder.shouldIgnore()) {
continue;
}
if (holder.mPosition >= positionStart && holder.mPosition < positionEnd) {
// We re-bind these view holders after pre-processing is complete so that
// ViewHolders have their final positions assigned.
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE);
holder.addChangePayload(payload);
// lp cannot be null since we get ViewHolder from it.
((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).mInsetsDirty = true;
}
}
mRecycler.viewRangeUpdate(positionStart, itemCount);
}
会根据传入的位置等参数更新指定位置视图对应的holder的标记为ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE,以及记录payload,并更新Recycler中满足条件的缓存。
可见,视图的数据更新的核心就是先更新holder标记参数,再刷新布局回到布局过程中的绑定数据调用达到更新的目的。
局部刷新的核心
payloads参数,就是让开发者自己定义标记,再根据标记自己定义刷新的视图范围。
其它刷新方式
Adapter还提供了其它更新接口,比如插入、移除、移动等等操作,分析方式都差不多,可从mAdapterHelper.consumeUpdatesInOnePass()中的其它操作类型去一一分析。