深度解析dubbo过滤器之ContextFilter
本文基于dubbo v2.6
文章目录
- 1.RpcContext
- 2. 使用RpcContext
- 2.1 公共接口
- 2.2 服务调用者端
- 2.3 服务提供者
- 2.4 测试
- 2.5 这个能干啥
- 3.原理解析
1.RpcContext
dubbo提供了一个调用上下文用来给服务提供者或者服务调用者传递一些信息,它只会在当前这个调用链上生效,比如说我服务调用者的某个方法中有两个rpc调用,然后分别调用同一个或者不同的服务提供者的某个方法,这个两个rpc调用就会有两个context,你可以往对应的context中塞东西,然后对应的服务提供者就能够根据context获取到,同理,服务提供者也可以给服务调用着带东西,对应的服务调用者也能够获得到。
我们先来看下这个RpcContext。
public class RpcContext {
/**
* use internal thread local to improve performance
* 这个是本地的context
*/
private static final InternalThreadLocal<RpcContext> LOCAL = new InternalThreadLocal<RpcContext>() {
@Override
protected RpcContext initialValue() {
return new RpcContext();
}
};
//远端的context,也就是服务提供者的context
private static final InternalThreadLocal<RpcContext> SERVER_LOCAL = new InternalThreadLocal<RpcContext>() {
@Override
protected RpcContext initialValue() {
return new RpcContext();
}
};
private final Map<String, String> attachments = new HashMap<String, String>();// 附加信息,kv形式
private final Map<String, Object> values = new HashMap<String, Object>();
private Future<?> future;// 异步调用的时候,将这个future设置到这里
private List<URL> urls;
private URL url;
private String methodName;// 调用方法名
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes;// 参数类型
private Object[] arguments;// 参数
private InetSocketAddress localAddress;// 本地地址
private InetSocketAddress remoteAddress;// 远端地址
@Deprecated
private List<Invoker<?>> invokers;// 这个一般服务调用者端用到,存储服务提供者invoker们
@Deprecated
private Invoker<?> invoker;// invoker
@Deprecated
private Invocation invocation;// 调用信息
// now we don't use the 'values' map to hold these objects
// we want these objects to be as generic as possible
private Object request;
private Object response;
protected RpcContext() {
}
/**
* get server side context.
*
* @return server context
*/
public static RpcContext getServerContext() {
return SERVER_LOCAL.get();
}
/**
* remove server side context.
*
* @see com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ContextFilter
*/
public static void removeServerContext() {
SERVER_LOCAL.remove();
}
/**
* get context.
*
* @return context
*/
public static RpcContext getContext() {
return LOCAL.get();
}
/**
* remove context.
*
* @see com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ContextFilter
*/
public static void removeContext() {
LOCAL.remove();
}
/**
* Get the request object of the underlying RPC protocol, e.g. HttpServletRequest
*
* @return null if the underlying protocol doesn't provide support for getting request
*/
public Object getRequest() {
return request;
}
/**
* Get the request object of the underlying RPC protocol, e.g. HttpServletRequest
*
* @return null if the underlying protocol doesn't provide support for getting request or the request is not of the specified type
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getRequest(Class<T> clazz) {
return (request != null && clazz.isAssignableFrom(request.getClass())) ? (T) request : null;
}
public void setRequest(Object request) {
this.request = request;
}
/**
* Get the response object of the underlying RPC protocol, e.g. HttpServletResponse
*
* @return null if the underlying protocol doesn't provide support for getting response
*/
public Object getResponse() {
return response;
}
/**
* Get the response object of the underlying RPC protocol, e.g. HttpServletResponse
*
* @return null if the underlying protocol doesn't provide support for getting response or the response is not of the specified type
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getResponse(Class<T> clazz) {
return (response != null && clazz.isAssignableFrom(response.getClass())) ? (T) response : null;
}
public void setResponse(Object response) {
this.response = response;
}
/**
* is provider side.
*
* @return provider side.
*/
public boolean isProviderSide() {
return !isConsumerSide();
}
/**
* is consumer side.
*
* @return consumer side.
*/
public boolean isConsumerSide() {
return getUrl().getParameter(Constants.SIDE_KEY, Constants.PROVIDER_SIDE).equals(Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE);
}
/**
* get future.
*
* @param
* @return future
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Future<T> getFuture() {
return (Future<T>) future;
}
/**
* set future.
*
* @param future
*/
public void setFuture(Future<?> future) {
this.future = future;
}
public List<URL> getUrls() {
return urls == null && url != null ? (List<URL>) Arrays.asList(url) : urls;
}
public void setUrls(List<URL> urls) {
this.urls = urls;
}
public URL getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(URL url) {
this.url = url;
}
/**
* get method name.
*
* @return method name.
*/
public String getMethodName() {
return methodName;
}
public void setMethodName(String methodName) {
this.methodName = methodName;
}
/**
* get parameter types.
*
* @serial
*/
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes;
}
public void setParameterTypes(Class<?>[] parameterTypes) {
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
}
/**
* get arguments.
*
* @return arguments.
*/
public Object[] getArguments() {
return arguments;
}
public void setArguments(Object[] arguments) {
this.arguments = arguments;
}
/**
* set local address.
*
* @param host
* @param port
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext setLocalAddress(String host, int port) {
if (port < 0) {
port = 0;
}
this.localAddress = InetSocketAddress.createUnresolved(host, port);
return this;
}
/**
* get local address.
*
* @return local address
*/
public InetSocketAddress getLocalAddress() {
return localAddress;
}
/**
* set local address.
*
* @param address
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext setLocalAddress(InetSocketAddress address) {
this.localAddress = address;
return this;
}
public String getLocalAddressString() {
return getLocalHost() + ":" + getLocalPort();
}
/**
* get local host name.
*
* @return local host name
*/
public String getLocalHostName() {
String host = localAddress == null ? null : localAddress.getHostName();
if (host == null || host.length() == 0) {
return getLocalHost();
}
return host;
}
/**
* set remote address.
*
* @param host
* @param port
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext setRemoteAddress(String host, int port) {
if (port < 0) {
port = 0;
}
this.remoteAddress = InetSocketAddress.createUnresolved(host, port);
return this;
}
/**
* get remote address.
*
* @return remote address
*/
public InetSocketAddress getRemoteAddress() {
return remoteAddress;
}
/**
* set remote address.
*
* @param address
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext setRemoteAddress(InetSocketAddress address) {
this.remoteAddress = address;
return this;
}
/**
* get remote address string.
*
* @return remote address string.
*/
public String getRemoteAddressString() {
return getRemoteHost() + ":" + getRemotePort();
}
/**
* get remote host name.
*
* @return remote host name
*/
public String getRemoteHostName() {
return remoteAddress == null ? null : remoteAddress.getHostName();
}
/**
* get local host.
*
* @return local host
*/
public String getLocalHost() {
String host = localAddress == null ? null :
localAddress.getAddress() == null ? localAddress.getHostName()
: NetUtils.filterLocalHost(localAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress());
if (host == null || host.length() == 0) {
return NetUtils.getLocalHost();
}
return host;
}
/**
* get local port.
*
* @return port
*/
public int getLocalPort() {
return localAddress == null ? 0 : localAddress.getPort();
}
/**
* get remote host.
*
* @return remote host
*/
public String getRemoteHost() {
return remoteAddress == null ? null :
remoteAddress.getAddress() == null ? remoteAddress.getHostName()
: NetUtils.filterLocalHost(remoteAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress());
}
/**
* get remote port.
*
* @return remote port
*/
public int getRemotePort() {
return remoteAddress == null ? 0 : remoteAddress.getPort();
}
/**
* get attachment.
*
* @param key
* @return attachment
*/
public String getAttachment(String key) {
return attachments.get(key);
}
/**
* set attachment.
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext setAttachment(String key, String value) {
if (value == null) {
attachments.remove(key);
} else {
attachments.put(key, value);
}
return this;
}
/**
* remove attachment.
*
* @param key
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext removeAttachment(String key) {
attachments.remove(key);
return this;
}
/**
* get attachments.
*
* @return attachments
*/
public Map<String, String> getAttachments() {
return attachments;
}
/**
* set attachments
*
* @param attachment
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext setAttachments(Map<String, String> attachment) {
this.attachments.clear();
if (attachment != null && attachment.size() > 0) {
this.attachments.putAll(attachment);
}
return this;
}
public void clearAttachments() {
this.attachments.clear();
}
/**
* get values.
*
* @return values
*/
public Map<String, Object> get() {
return values;
}
/**
* set value.
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return context
*/
public RpcContext set(String key, Object value) {
if (value == null) {
values.remove(key);
} else {
values.put(key, value);
}
return this;
}
/**
* remove value.
*
* @param key
* @return value
*/
public RpcContext remove(String key) {
values.remove(key);
return this;
}
/**
* get value.
*
* @param key
* @return value
*/
public Object get(String key) {
return values.get(key);
}
/**
* @deprecated Replace to isProviderSide()
*/
@Deprecated
public boolean isServerSide() {
return isProviderSide();
}
/**
* @deprecated Replace to isConsumerSide()
*/
@Deprecated
public boolean isClientSide() {
return isConsumerSide();
}
/**
* @deprecated Replace to getUrls()
*/
@Deprecated
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public List<Invoker<?>> getInvokers() {
return invokers == null && invoker != null ? (List) Arrays.asList(invoker) : invokers;
}
public RpcContext setInvokers(List<Invoker<?>> invokers) {
this.invokers = invokers;
if (invokers != null && !invokers.isEmpty()) {
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>(invokers.size());
for (Invoker<?> invoker : invokers) {
urls.add(invoker.getUrl());
}
setUrls(urls);
}
return this;
}
/**
* @deprecated Replace to getUrl()
*/
@Deprecated
public Invoker<?> getInvoker() {
return invoker;
}
public RpcContext setInvoker(Invoker<?> invoker) {
this.invoker = invoker;
if (invoker != null) {
setUrl(invoker.getUrl());
}
return this;
}
/**
* @deprecated Replace to getMethodName(), getParameterTypes(), getArguments()
*/
@Deprecated
public Invocation getInvocation() {
return invocation;
}
public RpcContext setInvocation(Invocation invocation) {
this.invocation = invocation;
if (invocation != null) {
setMethodName(invocation.getMethodName());
setParameterTypes(invocation.getParameterTypes());
setArguments(invocation.getArguments());
}
return this;
}
/**
* Async invocation. Timeout will be handled even if Future.get() is not called.
*
* @param callable
* @return get the return result from future.get()
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Future<T> asyncCall(Callable<T> callable) {
try {
try {
setAttachment(Constants.ASYNC_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
final T o = callable.call();
//local invoke will return directly
if (o != null) {
FutureTask<T> f = new FutureTask<T>(new Callable<T>() {
@Override
public T call() throws Exception {
return o;
}
});
f.run();
return f;
} else {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RpcException(e);
} finally {
removeAttachment(Constants.ASYNC_KEY);
}
} catch (final RpcException e) {
return new Future<T>() {
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isCancelled() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
return true;
}
@Override
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
throw new ExecutionException(e.getCause());
}
@Override
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException,
TimeoutException {
return get();
}
};
}
return ((Future<T>) getContext().getFuture());
}
/**
* one way async call, send request only, and result is not required
*
* @param runnable
*/
public void asyncCall(Runnable runnable) {
try {
setAttachment(Constants.RETURN_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString());
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable e) {
// FIXME should put exception in future?
throw new RpcException("oneway call error ." + e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
removeAttachment(Constants.RETURN_KEY);
}
}
}
这个篇幅有点长,我们主要就是看下它的成员,我们可以看到有两个ThreadLoacl的类成员,这样子rpc调用就不会乱套,因为一个线程绑定一个RpcContext对象,在看下面的一些成员变量,其实就是一些本次rpc调用的调用信息,其中attachments 就是我们带值的map,我们后面讲解源码的时候会看到,这个类自己看看就可以了,很简单。
2. 使用RpcContext
我们这里就使用一下这个RpcContext来帮我们干点事情。这里我们在调用者端使用RpcContext给服务提供者端带点东西,同时服务提供者端回带点东西给服务调用者端。演示如下:
2.1 公共接口
public interface IHelloProviderService {
String getName(Integer id);
}
2.2 服务调用者端
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Reference(check = false)
private IHelloProviderService iHelloProviderService;
@RequestMapping("/tests")
public String test(){
// 往context 添加点东西,带给服务调用者端
RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments().put("aaa","ok");
String name = iHelloProviderService.getName(1);
// 从服务调用者端context获取带过来的信息
String remoteData = RpcContext.getServerContext().getAttachments().get("bbb");
System.out.println("我从提供者端获得的数据:"+remoteData);
return null;
}
}
服务调用者端很简单,就是在调用前 获取context,塞了个kv进去,在调用后获取serverContext获取了一下服务提供者给带过来的信息。
2.3 服务提供者
我这里就是接口的实现类,我们从context中获取服务调用者带过来的信息,同时往serverContext中塞了kv带给服务调用者。
@org.springframework.stereotype.Service
@Service
public class IHelloProviderServiceImpl implements IHelloProviderService {
@Override
public String getName(Integer id) {
String remoteData = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments().get("aaa");
System.out.println("我从服务调用着端获得的数据是:"+remoteData);
RpcContext.getServerContext().getAttachments().put("bbb","ccc");
return "test";
}
}
2.4 测试
我们这里测试一下,然后从服务提供者日志中可以看到
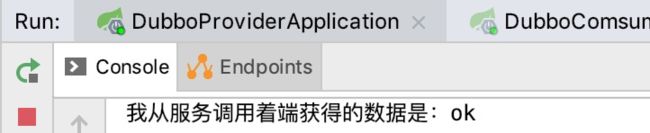
从服务调用者的日志可以看到:

2.5 这个能干啥
在我们普通的开发中,RpcContext基本用不到,但是在某些框架在做dubbo兼容适配的时候会用到,我这里举两个例子,分布式链路追踪是怎样将traceId,spanId,pId传到服务调用者的,其实就是用了这个context。再就是分布式事务是怎样将全局事务id传到子事务的,其实还是用这个传的,只不过他们在做的时候优雅一下,不会明着调用,可能会使用Filter来往里面塞,也可能是aop的形式往里面塞。
3.原理解析
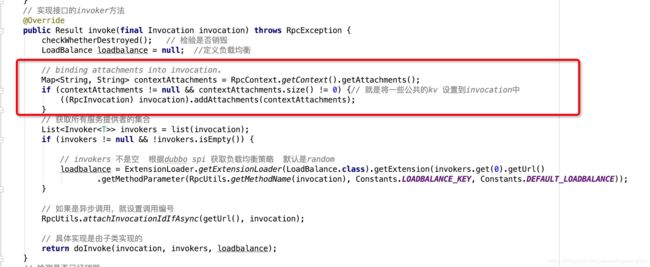
在上面的小节中我们讲解了RpcContext,还用RpcContext在服务调用者与服务提供者做了信息传递。那么这个功能是怎样实现的呢,其实很简单。首先我们得了解一下Rpc调用传输的实体RpcInvocation与Result,在进行服务调用者调用往服务提供者端发送请求就是发送的Request对象,将Request对象序列化成二进制,然后传到服务提供者端,服务提供者端就会将二进制反序列化成Request对象,这个request对象中包的就是这个RpcInvocation (调用实体),然后服务提供者进行对应方法调用(对应方法 参数 其实都在RpcInvocation实体中封装着)将执行结果放到RpcResult实体中,然后包上一层Response,序列化成二进制发送给服务调用者端,服务调用者端反序列化成Response,再将Response这层皮拨开,取出RpcResult,这个RpcResult就封装着调用结果集。其实不管是RpcInvocation 还是RpcResult里面都有共同的成员变量,那就是attachments,这个就是存放附加参数的,我们上面塞到Context中的数据,其实都会被封装到这个成员中传输。我们可以看到,他其实就是个map

那么怎么从RpcContext中封装到这两个实体中的呢?其实这里是用了dubbo Filter来做的,在服务调用着端有个ConsumerContextFilter过滤器,专门将RpcResult中的attachments 塞到本地的RpcServerContext中,最后会清了本次调用context中的attachments,我们来看下实现:
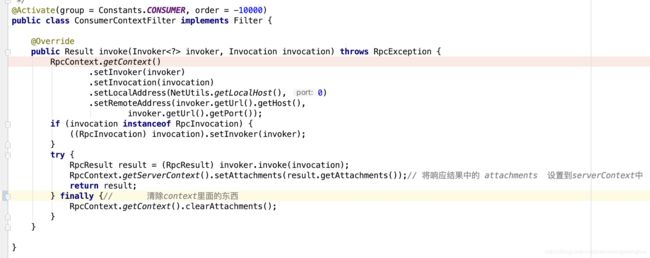
在服务提供者端有个ContextFilter 过滤器,它会在调用前,将调用者端传过来的attachments ,塞到context中,同时在调用完成后,将serverContext中的attachments 塞到RpcResult 中,最后移除context与清空serverContext,我们来看下源码实现。
其实这里还有个问题就是在服务调用者端,是在哪里将context中的附加参数添加到invocation里面的,这个其实是在调用的时候,会经过clusterInvoker,然后有个抽象父类里面实现的invoke方法,这个类就是AbstractClusterInvoker,就是在这个类里面将context中的附加参数添加到invocation里面的,我们稍微看下: