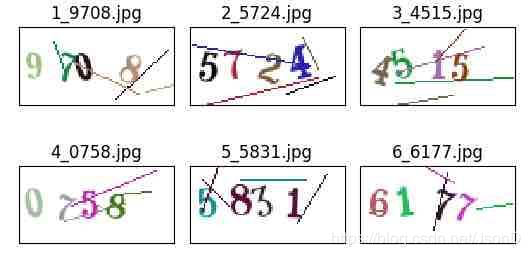
用了这招,复杂验证码识别率提高30%
免责声明:本栏内容只供学习交流使用,切勿用于非法用途。
一.验证码特点分析
二.图片预处理
三.整体模型训练
四.验证码分割
五.切分验证码训练
六.总结
一.验证码特点分析
1、该验证码由4位0~9的彩色数字组成
2、背景色位纯白色,存在多条彩色干扰线
3、数字会进行旋转操作
4、数字因为旋转和干扰线会黏连到一起
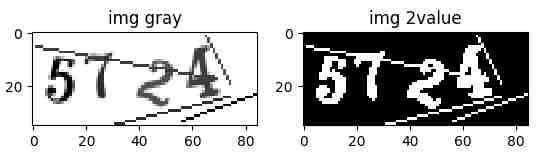
二.图片预处理
step1:
import cv2
##读取原始彩色图
img = cv2.imread(img_raw_dir + img_name, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
##把彩色图转化灰度图
img_gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
##图片剪裁
img_gray= img_gray[5:-5, 0:-5]
step2:
##把灰度图转化为反转二值图
th, img2b1 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 245, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
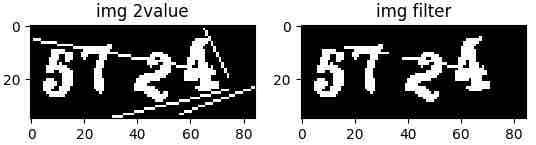
step3:
1、搜索图中所有白色连通域,广度遍历+队列+4连通域搜索
2、把低于30个点的连通域置黑。
from queue import Queue
##广度搜索连通域少于30的点并进行删除
def search_del_point(img, noise_count=30):
traveled = set()
surround = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
h, w = img.shape
threshold = 127
for i in range(h):
for j in range(w):
if img[i][j] > threshold and (i, j) not in traveled:
traveled.add((i, j))
q = Queue()
q.put((i, j))
searcher = [(i, j)]
while not q.empty():
point = q.get()
for k in range(4):
tar_x = point[0] + surround[k][0]
tar_y = point[1] + surround[k][1]
if tar_x >= 0 and tar_x < h and tar_y >= 0 and tar_y < w and \
img[tar_x, tar_y] > threshold and (tar_x, tar_y) not in traveled:
traveled.add((tar_x, tar_y))
q.put((tar_x, tar_y))
searcher.append((tar_x, tar_y))
if len(searcher) <= noise_count:
for point1 in searcher:
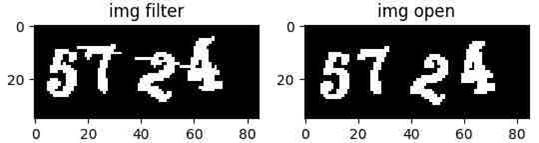
img[point1[0], point1[1]] = 0step4:
图片进行开运算,开运算=先腐蚀+再膨胀
开运算说明:https://blog.csdn.net/hanshanbuleng/article/details/80657148
##开运算=先腐蚀+再膨胀
k = np.ones((2, 2), np.uint8) ##卷积核函数2X2
img5 = cv2.morphologyEx(img4, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, k, iterations=1)
三.整体模型训练
step1:编写数据生成器代码,返回图片数组、label和图片名。
##单条训练/测试数据生成器
##输入参数说明
##img_gray_dir 预处理后的图片目录
##isTrain 当前生成的是训练集/测试机数据?
##split 训练集/测试集分割点,本例中11000张做为训练集,1000张做为测试集
##输出参数说明
##本方式使用的是Python的迭代器
##main_str 验证码字符串label
##train_image 验证码处理后图片
##current_file_name 图片文件名
def gen_captcha_text_and_image(img_dir=img_gray_dir, isTrain=True, split=11000):
list_name=listdir_s(img_dir)
list_name=sorted(list_name,key=lambda x:int(x.split('_')[0]))
files_sum=len(list_name)
if isTrain:
start_index=0
end_index= split-1
else:
start_index=split
end_index=files_sum-1
current_index=start_index
while True:
if current_index>=end_index:
current_index=start_index
current_file_name=list_name[current_index]
train_image =cv2.imread(img_dir+current_file_name,cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
th,train_image=cv2.threshold(train_image,127,1,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
main_str = current_file_name[current_file_name.rfind('_') +
1:current_file_name.rfind('.')]
yield main_str,train_image,current_file_name
current_index += 1step2:调用上步的生成器代码,批量生成训练数据和测试数据
##批量获取神经网络数据
##输入参数说明
##conv_shape 神经网络输入层形状
##batch_size 单次进入模型数据集大小
##max_captcha 验证码位数,本例为4
##img_width img_height 验证码图片长宽
## generator 上一步的图片生成器
##输出参数说明
##X 图片集合
##y label集合
##返回3 ctc输入长度
##返回4 ctc输出验证码长度
##返回5 单次训练的图片数
def gen_batch_captcha(conv_shape, batch_size=256, max_captcha=MAX_CAPTCHA, img_width=IMAGE_WIDTH, img_height=IMAGE_HEIGHT,
generator = gen_captcha_text_and_image(isTrain=True)):
char_set=get_char_str() ##验证码的字符集,本例为'0123456789'
X = np.zeros((batch_size, img_width, img_height, 1), dtype=np.ubyte)
y = np.zeros((batch_size, max_captcha), dtype=np.uint8)
while True:
for i in range(batch_size):
captcha_str,captch_img,current_file_name=next(generator)
X[i] = captch_img.reshape(img_width, img_height, 1)
y[i] = [char_set.index(x) for x in captcha_str]
yield [X, y, np.ones(batch_size) * int(conv_shape[1]-2),
np.ones(batch_size) * max_captcha], np.ones(batch_size)step3:把数据填入到模型里,每训练一个epoch,在测试数据上跑一遍。本例对完整图片的验证码识别使用的CRNN。原理可以参看这篇文章:一文读懂CRNN+CTC文字识别
##CRNN代码实现
##输入参数
##last_train_model 训练好的模型,在需要模型提升时候使用,初次训练不需要
##IMAGE_WIDTH IMAGE_HEIGHT 图片长、宽
##MAX_CAPTCHA 验证码字符数
##n_class 字符集数量,本例之10个数0~9,CRNN还得加个空格' ',n_class=11
##输出参数
##base_model 前向传播网络
##model 网络加入ctc损失函数计算
##conv_shape 卷积神经网络输出形状
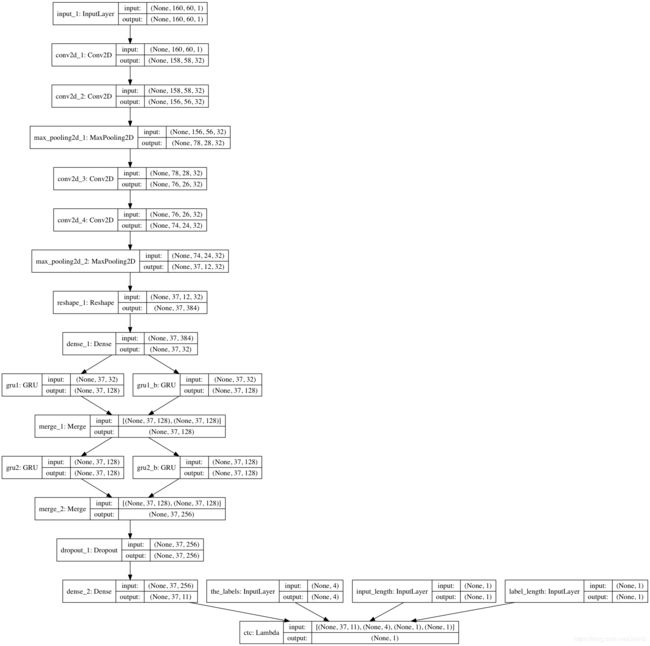
def image_to_sequence_net(last_train_model=None,IMAGE_WIDTH=160,IMAGE_HEIGHT=60,
MAX_CAPTCHA=4,n_class=n_class):
input_tensor = Input((IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT,1))
x = input_tensor
for i in range(2):
x = Convolution2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')(x)
x = Convolution2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
conv_shape = x.get_shape()
print('conv_shape====',conv_shape)
x = Reshape(target_shape=(int(conv_shape[1]), int(conv_shape[2]*conv_shape[3])))(x)
x = Dense(32, activation='relu')(x)
gru_1 = GRU(RNN_SIZE, return_sequences=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru1')(x)
gru_1b = GRU(RNN_SIZE, return_sequences=True, go_backwards=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru1_b')(x)
gru1_merged = add([gru_1, gru_1b])
gru_2 = GRU(RNN_SIZE, return_sequences=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru2')(gru1_merged)
gru_2b = GRU(RNN_SIZE, return_sequences=True, go_backwards=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru2_b')(gru1_merged)
x = concatenate([gru_2, gru_2b])
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
x = Dense(n_class, kernel_initializer='he_normal', activation='softmax')(x)
base_model = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=x)
labels = Input(name='the_labels', shape=[MAX_CAPTCHA], dtype='float32')
input_length = Input(name='input_length', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
label_length = Input(name='label_length', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
loss_out = Lambda(ctc_lambda_func, output_shape=(1,), name='ctc')([x, labels, input_length, label_length])
model = Model(inputs=[input_tensor, labels, input_length, label_length], outputs=[loss_out])
model.compile(loss={'ctc': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}, optimizer='adadelta')
if last_train_model:
model.load_weights(last_train_model)
return base_model,model,conv_shapestep4:设定模型保存阈值,当模型准确率大于阈值,则保存模型
##模型评估类
class Evaluate(Callback):
##base_model 前向传播网络
##model_save_dir 模型保存路径
##MAX_CAPTCHA 验证码位数
##model_save_acc 测试集准确率大于多少保存模型
def __init__(self,
base_model,model,generator,model_save_dir,MAX_CAPTCHA=4,model_save_acc=80):
self.accs = []
self.base_model=base_model
self.model=model
self.generator=generator
self.model_save_dir=model_save_dir
self.model_save_acc=model_save_acc
self.MAX_CAPTCHA=MAX_CAPTCHA
##预测准确率评估
def evaluate(self,base_model, generator, batch_num=1, MAX_CAPTCHA_=4):
batch_acc = 0
for i in range(batch_num):
[X_test, y_test, _, _], _ = next(generator)
y_pred = base_model.predict(X_test) ##前向传播网络,进行图像编码
shape = y_pred[:, 2:, :].shape
##ctc把图像编码解析为字
out = K.get_value(K.ctc_decode(y_pred[:, 2:, :], input_length=np.ones(shape[0]) * shape[1])[0][0])[:,:MAX_CAPTCHA_] 符串
print('out_shape====', out.shape)
if out.shape[1] == MAX_CAPTCHA_:
batch_acc += ((y_test == out).sum(axis=1) == MAX_CAPTCHA_).mean()
return batch_acc / batch_num
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
acc = self.evaluate(self.base_model,self.generator,MAX_CAPTCHA_=self.MAX_CAPTCHA) * 100
self.accs.append(acc)
print()
print('acc: %f%%' % acc)
if acc>self.model_save_acc: ##预测准确率大于某个阈值保存模型
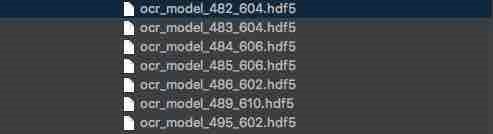
model_save_path =self.model_save_dir+"ocr_model_{0}_{1}.hdf5".format(epoch, int(acc))
self.model.save(model_save_path, overwrite=True)
step5:整体训练代码
def train_model():
##输入
##last_train_model 如果要提升模型训练效果,可以加载之前训练模型参数
##输出
##base_model 前向传播网络
##model 网络加入ctc损失函数计算
##conv_shape 前向传播网络输出shape
base_model, model, conv_shape=get_whole_model(last_train_model=model_whole_dir+'ocr_model_481_610.hdf5')
##获得训练集数据生成器
train_generator=gen_batch_captcha(conv_shape=conv_shape,generator=gen_captcha_text_and_image(split=11000))
##获得测试数据集生成器
test_generator=gen_batch_captcha(conv_shape=conv_shape,batch_size=500,generator=gen_captcha_text_and_image(isTrain=False,split=11000))
##定义模型评估类
evaluator = Evaluate(base_model, model, test_generator, model_whole_gray_dir, max_captcha=MAX_CAPTCHA, model_save_acc=60)
##开始训练
model.fit_generator(train_generator, steps_per_epoch=43, nb_epoch=10000,
callbacks=[EarlyStopping(patience=10), evaluator],workers=1)
##结果评估
evaluator.evaluate(base_model,test_generator)
step6:整体训练结果展示
文件命名结构:ocr_model_训练轮数_测试集准确率.模型文件后缀
总共训练500 epoch,测试集最高准确率61%,继续训练无法继续提升效果。
step7:问题分析与解决方案
原因:数字旋转和黏连降低了识别的准确性
解决方案1:获得更多有标注的验证码。
解决方案2:对验证码进行切割,降低问题复杂度。
四.验证码分割
获得更多有标注的验证码不太现实,本文采取的优化方法是对验证码进行切割。
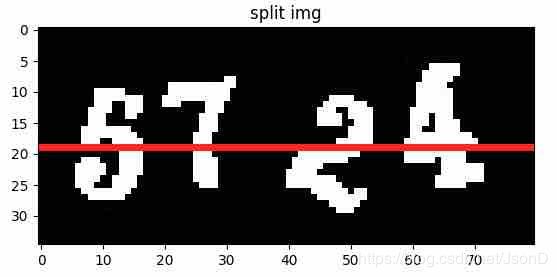
step1:图片切割展示
step2:图片切割方案
切割步骤:
1、计算图片垂直中心点,从左侧出发搜索获得连通图下标数组连通域。
2、使用numpy构建宽度30像素,原图高度的白板。
3、通过步骤1计算单个数字宽度,计算数字在白板中距离左侧距离。
##panel_width 白板宽度30px
##digit_width 数字宽度,可以计算
offset=(panel_width+1)//2-(digit_width+1)//2
4、计算数字在白板中实际坐标:h1=h,w1=w-digit_left+offset
step2:验证码切割异常1(3连通域,1黏连)
解决方案:
1、如果元素搜索目标连通域结果等于3,则出现了1个验证码的黏连。对宽度最大的元素进行超范围切割。
2、本例中分别截取左侧和右侧元素宽度的2/3映射到白板上
step3:验证码切割异常2(2连通域,2黏连)
解决方案:
1、如果元素搜索结果等于2,则可能1组3黏连或是2组2黏连,判断元素最大宽度,超过某个经验阈值则为3黏连。
2、2黏连情况按照异常2的切割方式切割分别切割。3黏连则在左侧、中间、右侧分别超范围切割出3个元素。
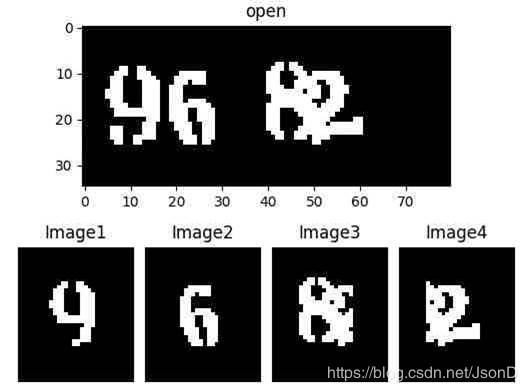
step4:切分结果展示
五.切分验证码训练
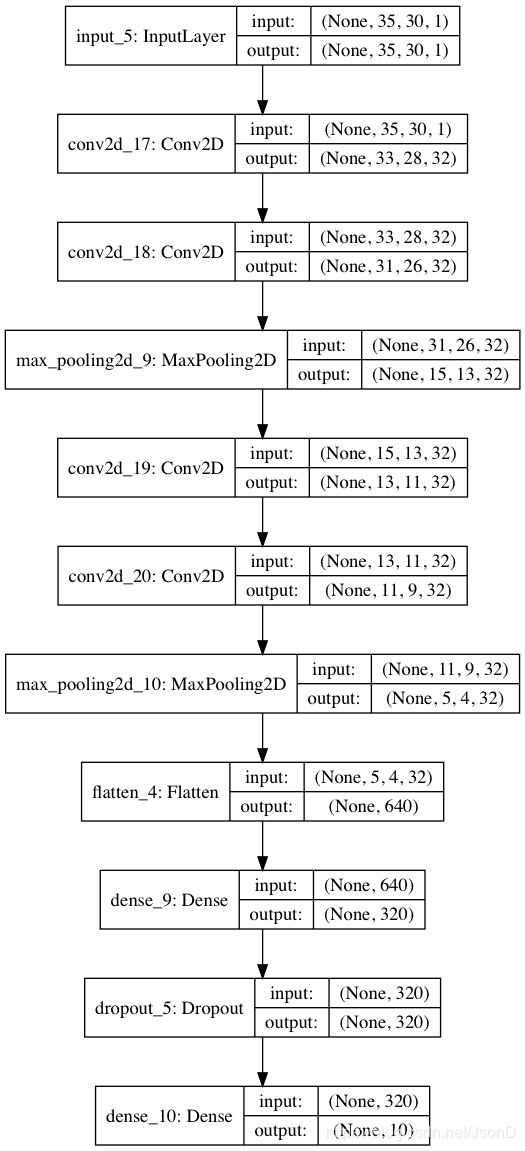
step1:验证码切分完毕后,提供数据的迭代器部分代码与完整训练基本相同。下面最提供Minist数据集识别用到的模型图与代码。
##Minist单字符ocr识别代码
##last_train_model 连续提升效果时倒入上次模型
def image_split_recognition(last_train_model=None, image_height=40, image_width=30, classes=10):
input_tensor = Input((image_height, image_width, 1))
x = input_tensor
for i in range(2):
x = Convolution2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')(x)
x = Convolution2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(512, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
x = Dense(classes, kernel_initializer='he_normal', activation='softmax')(x)
model = Model(inputs=input_tensor,outputs=x)
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adadelta', metrics=['accuracy'])
if last_train_model:
model.load_weights(last_train_model)
return modelstep2:切分验证码结果展示
总共训练不到30 epoch,测试集切分验证码准确率达到99.6%,
整张验证码识别准确率为98.4% (0.996^4=0.984)。
六.总结
通过字符切分和Minist识别网络,识别的准确率提升了37.4%(0.984-0.61=0.374)。CRNN网络是具有复杂的结构的强大算法,但最终却输给了简单的Minist单字符识别网络。可见在机器学习实践的过程中灵活变通的重要性。一些简单的算法,进行灵活的组合可以解决比较棘手的问题。