Android Jetpack组件学习 ViewModel & LiveData
一、简介
- ViewModel - 提供了一种创建和检索绑定到特定生命周期的对象的方法。
ViewModel通常存储视图数据的状态,并与其他组件通信,例如数据存储库或处理业务逻辑层。 - LifecycleOwner / LifecycleRegistryOwner -无论是
LifecycleOwner和LifecycleRegistryOwner都是AppCompatActivity和Support Fragment类实现的接口。您可以将其他组件订阅到实现这些接口的所有者对象,以观察对所有者生命周期的更改。 - LiveData - 允许您观察应用程序的多个组件之间的数据更改,而无需在它们之间创建明确,严格的依赖关系路径。
LiveData尊重应用程序组件的复杂生命周期,包括activity,fragment,service或任何定义在app中的LifecycleOwner。LiveData通过暂停对已停止的LifecycleOwner对象的订阅以及取消对已完成的LifecycleOwner对象的订阅。
二、实践
1、使用viewModel
先写一个有一个计时器的activity
<Chronometer
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/hello_textview"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:id="@+id/chronometer"/>
Chronometer chronometer = findViewById(R.id.chronometer);
chronometer.start();
如果配置更改(例如屏幕旋转)破坏活动时会发现计时器被重置
添加ViewModel
使用 ViewModel在activity或fragment的整个生命周期中保留数据。要管理应用程序数据,activity是一个糟糕的选择。如之前所示activity和fragment是短暂的对象,当用户与应用程序交互时,这些对象会频繁创建和销毁。此外ViewModel还更适合管理与网络通信相关的任务,以及数据操作和持久性。
public class ChronometerViewModel extends ViewModel {
@Nullable
private Long mStartTime;
@Nullable
public Long getStartTime() {
return mStartTime;
}
public void setStartTime(final long startTime) {
this.mStartTime = startTime;
}
}
在activity中添加代码
//ViewModelStore提供了一个新的视图模型或之前创建的视图模型。
ChronometerViewModel chronometerViewModel
= ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(ChronometerViewModel.class);
if (chronometerViewModel.getStartTime() == null) {
//它是一个新的ViewModel
long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
chronometerViewModel.setStartTime(startTime);
chronometer.setBase(startTime);
} else {
//否则保留了视图模型,将chronometer初始化
chronometer.setBase(chronometerViewModel.getStartTime());
}
这时会发现计时器的状态没有被重置
this指的是一个LifecycleOwner实例。只要LifecycleOwner的作用域是活动的,框架就保持ViewModel的活动状态。如果其所有者因配置更改(例如屏幕旋转)而被销毁,ViewModel不会被销毁。所有者的新实例重新连接到现有的ViewModel,如下图所示:
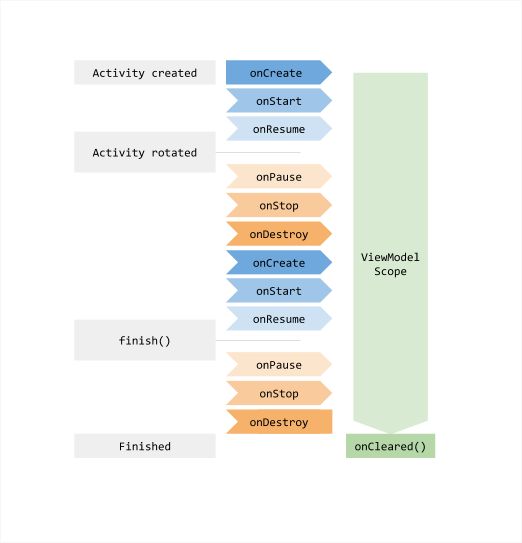
注意
activity或fragment的范围从created到finished(或terminated),您不能将其与已destroyed混淆。请记住,当设备旋转时,activity将被销毁,但与之关联的任何ViewModel实例不会被销毁。
系统在生命周期所有者的整个生命周期(例如activity或fragment)中将ViewModel实例保存在内存中。系统不会将ViewModel实例持久化到持久存储中。
#####2、使用LiveData包装数据
现在使用Timer自定义一个计时器,此逻辑添加到LiveDataTimerViewModel类中,并使activity专注于管理用户和UI之间的交互。
当计时器通知时,activity会更新UI。为了避免内存泄漏,ViewModel不包括对活动的引用。例如,配置更改(例如屏幕旋转)可能导致ViewModel中的引用被引用到应该进行垃圾回收的activity 。系统将保留ViewModel的实例,直到相应的activity或生命周期所有者不再存在。
注意
在ViewModel中存储对 Context或View的引用可能导致内存泄漏,避免使用引用Context或View类实例的字段,onCleared()方法对于取消订阅或清除对具有更长生命周期的其他对象的引用非常有用,但不能用于清除对Context或View对象的引用。
您可以将活动或片段配置为观察数据源,在更改时接收数据,而不是直接从ViewModel修改视图。这称为观察者模式。要将数据公开为可观察对象,请将该类型包装在LiveData类中。如果您使用了数据绑定库或其他响应库(如RxJava),您可能熟悉观察者模式。 LiveData是一个特殊的可观察类,它能感知生命周期,并只通知活跃的观察者。
新建一个LifecycleActivity ,它可以提供生命周期的状态 ,LifecycleRegistryOwner用于将ViewModel和LiveData实例的生命周期绑定到activity 或fragment(26.1.0 高版本后的 Activity 已经实现了LifecycleOwner 接口,可以不用手动实现)
public class LifecycleActivity extends FragmentActivity
implements LifecycleRegistryOwner {...}
新建LiveDataTimerViewModel
public class LiveDataTimerViewModel extends ViewModel {
private static final int ONE_SECOND = 1000;
private MutableLiveData<Long> mElapsedTime = new MutableLiveData<>();
private long mInitialTime;
public LiveDataTimerViewModel() {
mInitialTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
Timer timer = new Timer();
// Update the elapsed time every second.
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
final long newValue = (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - mInitialTime) / 1000;
// setValue() cannot be called from a background thread so post to main thread.
mElapsedTime.postValue(newValue);
}
}, ONE_SECOND, ONE_SECOND);
}
public LiveData<Long> getElapsedTime() {
return mElapsedTime;
}
}
activity中调用
public class ChronoActivity3 extends AppCompatActivity {
private LiveDataTimerViewModel mLiveDataTimerViewModel;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.chrono_activity_3);
mLiveDataTimerViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(LiveDataTimerViewModel.class);
subscribe();
}
private void subscribe() {
final Observer<Long> elapsedTimeObserver = new Observer<Long>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(@Nullable final Long aLong) {
String newText = ChronoActivity3.this.getResources().getString(
R.string.seconds, aLong);
((TextView) findViewById(R.id.timer_textview)).setText(newText);
Log.d("ChronoActivity3", "Updating timer");
}
};
mLiveDataTimerViewModel.getElapsedTime().observe(this, elapsedTimeObserver);
}
}
可以发现计时器不会随着屏幕旋转而重置
3、订阅生命周期事件
如果没有在相应生命周期取消订阅或停止组件或库,可能会导致内存泄漏。
可以将lifecycle owner对象传递给具有lifecycle-aware组件的新实例,以确保它们知道生命周期的当前状态,可以使用以下语句查询生命周期的当前状态
lifecycleOwner.getLifecycle().getCurrentState()
上面的语句返回一个状态,例如Lifecycle.State.RESUMED,或Lifecycle.State.DESTROYED。
实现的生命周期感知对象LifecycleObserver还可以观察生命周期所有者状态的变化
lifecycleOwner.getLifecycle().addObserver(this);
您可以对对象使用注解,以指示它在需要时调用适当的方法
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.EVENT.ON_RESUME)
void addLocationListener() { ... }
下面创建一个activity,使用LoactionManager获取当前经纬度显示给用户,订阅更改并使用LiveData自动更新UI,根据activity状态的更改,创建注册和注销LocationManager。
一般我们会在onStart(),onResume()中注册监听,onStop(),onPause()中取消注册
@Override
protected void onResume() {
mLocationManager.requestLocationUpdates(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER, 0, 0, mListener);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
mLocationManager.removeUpdates(mListener);
}
下面新建一个类BoundLocationManager,要让类观察活动的生命周期,必须将其添加为观察者。为此,将BoundLocationManager对象通过将以下代码添加到其构造函数来观察生命周期
lifecycleOwner.getLifecycle().addObserver(this);
要在发生生命周期更改时调用方法,可以使用@OnLifecycleEvent注解。使用BoundLocationListener类中的以下注解更新addLocationListener()和removeLocationListener()方法:
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_RESUME)
void addLocationListener() {
...
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_PAUSE)
void removeLocationListener() {
...
}
public class BoundLocationManager {
public static void bindLocationListenerIn(LifecycleOwner lifecycleOwner,
LocationListener listener, Context context) {
new BoundLocationListener(lifecycleOwner, listener, context);
}
@SuppressWarnings("MissingPermission")
static class BoundLocationListener implements LifecycleObserver {
private final Context mContext;
private LocationManager mLocationManager;
private final LocationListener mListener;
public BoundLocationListener(LifecycleOwner lifecycleOwner,
LocationListener listener, Context context) {
mContext = context;
mListener = listener;
lifecycleOwner.getLifecycle().addObserver(this);
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_RESUME)
void addLocationListener() {
// Note: Use the Fused Location Provider from Google Play Services instead.
// https://developers.google.com/android/reference/com/google/android/gms/location/FusedLocationProviderApi
mLocationManager =
(LocationManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
mLocationManager.requestLocationUpdates(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER, 0, 0, mListener);
Log.d("BoundLocationMgr", "Listener added");
// Force an update with the last location, if available.
Location lastLocation = mLocationManager.getLastKnownLocation(
LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER);
if (lastLocation != null) {
mListener.onLocationChanged(lastLocation);
}
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_PAUSE)
void removeLocationListener() {
if (mLocationManager == null) {
return;
}
mLocationManager.removeUpdates(mListener);
mLocationManager = null;
Log.d("BoundLocationMgr", "Listener removed");
}
}
}
public class LocationActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final int REQUEST_LOCATION_PERMISSION_CODE = 1;
private LocationListener mGpsListener = new MyLocationListener();
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions,
@NonNull int[] grantResults) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
if (grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED
&& grantResults[1] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
bindLocationListener();
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "This sample requires Location access", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
private void bindLocationListener() {
BoundLocationManager.bindLocationListenerIn(this, mGpsListener, getApplicationContext());
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.location_activity);
if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED && ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this,
new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION},
REQUEST_LOCATION_PERMISSION_CODE);
} else {
bindLocationListener();
}
}
private class MyLocationListener implements LocationListener {
@Override
public void onLocationChanged(Location location) {
TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.location);
textView.setText(location.getLatitude() + ", " + location.getLongitude());
}
@Override
public void onStatusChanged(String provider, int status, Bundle extras) {
}
@Override
public void onProviderEnabled(String provider) {
Toast.makeText(LocationActivity.this,
"Provider enabled: " + provider, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onProviderDisabled(String provider) {
}
}
}
4、在fragment之间共享ViewModel
下面创建一个activity和2个fragment,每个都有一个seekBar,一个单例的ViewModel,同时应该使用activity作为生命周期所有者,因为每个fragment的生命周期是独立的。
public class SeekBarViewModel extends ViewModel {
public MutableLiveData<Integer> seekbarValue = new MutableLiveData<>();
}
在一个activity中包含2个Fragment_step5
public class Fragment_step5 extends Fragment {
private SeekBar mSeekBar;
private SeekBarViewModel mSeekBarViewModel;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
View root = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_step5, container, false);
mSeekBar = root.findViewById(R.id.seekBar);
mSeekBarViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity()).get(SeekBarViewModel.class);
subscribeSeekBar();
return root;
}
private void subscribeSeekBar() {
// SeekBar改变时更新ViewModel
mSeekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(new SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress, boolean fromUser) {
if (fromUser) {
Log.d("Step5", "Progress changed!");
mSeekBarViewModel.seekbarValue.setValue(progress);
}
}
@Override
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) { }
@Override
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) { }
});
// ViewModel改变时更新SeekBar
mSeekBarViewModel.seekbarValue.observe(getActivity(), new Observer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(@Nullable Integer value) {
if (value != null) {
mSeekBar.setProgress(value);
}
}
});
}
}
