Map
官方声明如下:
public interface Map
此时可以看到,Map是一个接口,其中有泛型K、V两个。描述如下:
An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value.
将键映射到值的对象。映射不能包含重复的键;因此,Map不能包含重复的键。每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
Map内部的方法
- Put 与 Get 方法
/**
* 研究 Map 中方法的使用
* 1、 put 方法的作用 和 返回值的意义
* 2、 get 方法的作用
*/
public class TestMap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
// put 将 key 和 value 放入到 map 集合中,并返回这个”键值对“的“值” 这句话不对
// 将指定的值与此映射中的指定键关联(可选操作)
// put 将制定的值 8000.0 与此映射的制定的键"ThinkPadE530"关联
// 如果制定的键"ThinkPad E530" 曾经在当前的 map 中存在,则用新的值替换老的值
// put 方法返回的是 指定的键对应的老值(前提是这个键在 map 中是存在的,否则返回 null)
Double v = map.put("ThinkPad E530", 8000.0);
System.out.println(v);
System.out.println(map.toString());
v = map.put("IdeaPad Yaga", 7000.0);
System.out.println(v);
System.out.println(map.toString());
v = map.put("ThinkPad E530", 800.0);
System.out.println("v = " + v);
System.out.println(map.toString());
// 根据 key 取出相应的 value
Double value = map.get("ThinkPad E530");
System.out.println(value);
value = map.get("张无忌");
System.out.println(value);
}
}
- ContainsKey 与 ContainsValue
/**
* 研究 Map 中方法的使用
* 1、 containsKey 的作用(内部采用 key 的 equals 比较)
* 2、 containsValue 的作用(内部采用 value 的 equals 比较)
*/
public class TestMap3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("ThinkPad E530", 8000.0);
map.put("IdeaPad Yaga", 7000.0);
System.out.println(map.containsKey("张无忌")); // 判断时采用 key 对象的 equals 方法比较
System.out.println(map.containsKey("ThinkPadE530"));// 判断某个键存在于 map 中
System.out.println(map.containsValue(9000.0)); // 判断某个值存在于 map 中
// 8000 自动包装成 Integer 对象
System.out.println(map.containsValue(8000)); // 判 断时采用 value 对象的 equals 方法比较
}
}
- isEmpty、 remove、 clear
/**
* 研究 Map 中方法的使用:
* 1、 isEmpty
* 2、 remove
* 3、 clear
*/
public class TestMap4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map books = null;
System.out.println(books == null) ; // 集合变量 books是空的(栈中 books 没有存储数据,存储的是 null)
books = new HashMap<>(); // 创建 HashMap 对象,并赋值给 books 变量,此时 books 一定不是 null,但是集合中什么都没有,因此是个空集
System.out.println(books.isEmpty()) ; // 判断 map 集合是否是空的
books.put(0001, "Java 从入门到精通");
books.put(0002, "Java 编程思想");
books.put(0003, "java 数据结构与算法");
books.put(0004, "深入 java 虚拟机(第二版) ");
books.put(0005, "疯狂 Java 讲义(第三版) ");
System.out.println(books.isEmpty()) ; // 判断 map 集合是否是空的
String value = books.get(1); // 获得 key 是 1 的那个 value
System.out.println(value);
value = books.remove(1); // 根据制定的 key 删除“键值对”,并且返回“值”
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(books);
books.clear(); // 清空集合
System.out.println(books);
}
}
迭代 map
/**
* 研究 Map 中方法的使用
* 1、 entrySet
* 2、 keySet
* 3、 values77
*/
public class TestMap5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map books = new HashMap<>();
books.put(0001, "你不知道的 JavaScript");
books.put(0002, "Java 编程思想");
books.put(0003, "java 数据结构与算法");
books.put(0004, "深入 java 虚拟机(第二版) ");
books.put(0005, "疯狂 Java 讲义(第三版) ");
/*
Set entries = books.entrySet();
System.out.println(entries);
// 用 foreach 或 iterator 来迭代 Set 集合
for (Object object : entries) {
System.out.println(object);
}
*/
// Set> entries = books.entrySet(); 确定 set 中存放 Entry
Set> entries =
books.entrySet(); // Integer String 确定 Entry 中存放的是什么
// 迭代时 每次循环都可以获得一个 entry 对象,也就是一组键值对,因此可以直接得到 key,同时也可以得到 value
for (Map.Entry e : entries) {
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " : " + e.getValue());
}
// 也可以用迭代器迭代(entries.iterator() )
System.out.println("<---------------------------------------------------->");
// 得到所有的 key 组成的 Set 集合
Set keys = books.keySet();
for (Integer i : keys) {
// 可以根据 key 取出 value
System.out.println(books.get(i) + " : " + i);
}
System.out.println("<---------------------------------------------------->");
Collection c = books.values();
for (String string : c) {
System.out.println(string);
// 能不能根据 Value 获取的 key?
}
System.out.println(c instanceof Set); // false79
System.out.println(c instanceof List); // false
System.out.println(c.getClass()); // HashMap$Values
}
}
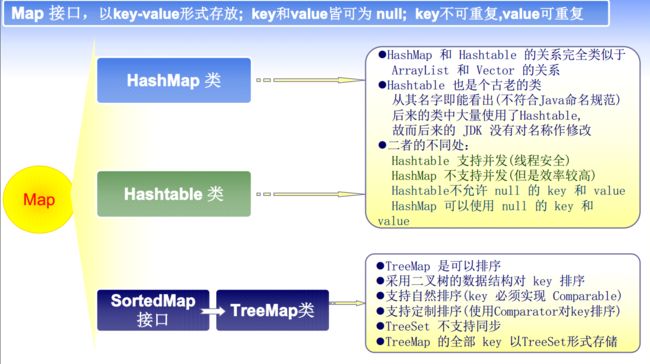
java.util.HashMap
HashMap仅仅查看构造方法,不做过多的描述。
HashMap():Constructs an empty HashMap with the default initial capacity (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
HashMap(int initialCapacity):Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor):Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial capacity and load factor.
HashMap(Map m):Constructs a new HashMap with the same mappings as the specified Map.
可以看到,HashMap具体的构造方法与HashSet的构造方法是差不多的,那么在这里就不进行具体的翻译了。
示例如下:
/**
* 1、 HashMap 内部采用哈希表来存储“键值对”
* HashMap 中提供了一个 hash 方法,用来根据 key 计算“键值对”的 hash 值
* 2、创建 HashMap 实例是,并没有直接创建数组对象
* 3、在调用 put 方法时,如果是第一次调用,就创建内部的哈希 表,并将元素放入其中
* 如果不是第一次,则需要考虑是否要扩大容量(根据加载 因子来确定)
*/
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// HashMap 的 默 认 容 量 是 16(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
// 创建一个加载因子为 0.75f 的 HashMap 实例
HashMap map = new HashMap<>(); // 容量是 16 加载因子是 0.75
// 第一次向 map 中放入键值对时,才创建内部数组(即哈希表)
map.put("男生", 20);
map.put("女生", 15);
map.put("老师", 6);
// 创建 HashMap 实例时,并没有直接创建内部的哈希表
HashMap books = new
HashMap<>(10,0.5f); // 容量是 10,加载因子是 0.5
// 第一次向 map 中放入键值对时,才创建内部数组(即哈希表)
books.put("Java 编程思想", 10);
books.put("深入 Java 虚拟机", 20);
}
}
java.util.TreeMap
TreeMap与TreeSet 的使用基本是一样的,因为TreeSet内部是由TreeMap实现的。
【I】 java.util.SortedMap:表示根据 key 进行排序的”键值对(key-value) “集合
【C】 java.util.TreeMap : 基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)的NavigableMap 实现81
TreeMap 实现了 NavigableMap 接口; NavigableMap 继承了SortedMap 接口
根据 key 进行排序:
自然顺序: Key 对应的那个类必须实现 java.lang.Comparable
(compareTo)
比较器顺序:在 java.util.Comparator 中的 compare 方法实现比
较
示例如下:
public class Bear {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private char gender;
public Bear() {
super();
}
public Bear(Integer id, String name, char gender) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
}
// getter and setter
}
/**
* 1、使用 TreeMap 的无参构造创建的对象是以 key 的自然顺序
为排序依据
* 2、如果 key 对应的类没有实现自然排序,则需要在创建
TreeMap 对象时,指定比较器
* 3、 TreeMap 内部基于红黑树实现(自己挑战)
*/
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map tm = new TreeMap<>();
tm.put("hello", 1.5);
tm.put("ipad", 2.5);
System.out.println(tm);
tm.put("apple", 4.8);
System.out.println(tm);
Comparator c = new Comparator(){
@Override
public int compare(Bear o1, Bear o2) {
int x = 0 ;
if(o1!=null && o2!=null && o1.getId()!=null &&
o2.getId()!=null){
x = o1.getId() - o2.getId();83
}
return x;
}
};
Map foods = new TreeMap<>(c);
System.out.println(foods);
Bear b1 = new Bear(1,"熊大",'男');
foods.put(b1, 30.0);
Bear b2 = new Bear(2,"熊二",'男');
foods.put(b2, 300.0);
Set> entries =
foods.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry e : entries) {
Bear bear = e.getKey();
System.out.println(bear.getId()+":" +
bear.getName() + " : " + e.getValue());
}
}
}