python 按图形打印二叉树
需求:
python代码实现
1. 按层打印二叉树
2. 需要打印二叉树层与层之间的斜线
3. 结点的下一层如果没有子节点,以‘N’代替
方法:
- 使用namedtuple表示二叉树
- 使用StringIO方法,遍历时写入结果,最后打印出结果
- 打印结点值时,如果为空,StringIO()写入‘N ’
- 递归获取树的深度
- 将遍历树时候每层的node当做list元素存入list中
- 根据树的深度设置每层node应该pad的空格数量:
2 **(深度-1)-1 - 打印每层之间的斜线,需处理:
- 每两层之间的斜线应有 “2 **(深度-1)”层
- 每层的左斜线与右斜线之间的空格数量有变化,每深一层加2
python代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from collections import namedtuple
from io import StringIO
import math
# define the node structure
Node = namedtuple('Node', ['data', 'left', 'right'])
# initialize the tree
tree = Node(1,
Node(2,
Node(4,
Node(7, None, None),
None),
Node(5, None, None)),
Node(3,
Node(6,
Node(8, None, None),
Node(9, None, None)),
None))
class Queue(object):
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def enqueue(self, b):
self.queue.insert(0, b)
def dequeue(self):
return self.queue.pop()
def isEmpty(self):
return self.queue == []
def getheight(node):
if not node:
return 0
else:
return max(getheight(node.left), getheight(node.right)) + 1
def add_padding(str, pad_length_value):
str = str.strip()
return str.center(pad_length_value, ' ')
# sotre node , space and slashes in list first, then print out
def pretty_print(tree):
output = StringIO()
pretty_output = StringIO()
current_level = Queue()
next_level = Queue()
current_level.enqueue(tree)
depth = 0
# get the depth of current tree
# get the tree node data and store in list
if tree:
while not current_level.isEmpty():
current_node = current_level.dequeue()
output.write('%s ' % current_node.data if current_node else 'N ')
next_level.enqueue(
current_node.left if current_node else current_node)
next_level.enqueue(
current_node.right if current_node else current_node)
if current_level.isEmpty():
if sum([i is not None for i in next_level.queue]
): # if next level has node
current_level, next_level = next_level, current_level
depth = depth + 1
output.write('\n')
print('the tree print level by level is :')
print(output.getvalue())
print("current tree's depth is %i" % (depth+1))
# add space to each node
output.seek(0)
pad_length = 3
keys = []
spaces = int(math.pow(2, depth))
while spaces > 0:
skip_start = spaces * pad_length
skip_mid = (2 * spaces - 1) * pad_length
key_start_spacing = ' ' * skip_start
key_mid_spacing = ' ' * skip_mid
keys = output.readline().split(' ') # read one level to parse
padded_keys = (add_padding(key, pad_length) for key in keys)
padded_str = key_mid_spacing.join(padded_keys)
complete_str = ''.join([key_start_spacing, padded_str])
pretty_output.write(complete_str)
# add space and slashes to middle layer
slashes_depth = spaces
print('current slashes depth im_resize:')
print(spaces)
print("current levle's list is:")
print(keys)
spaces = spaces // 2
if spaces > 0:
pretty_output.write('\n') # print '\n' each level
cnt = 0
while cnt < slashes_depth:
inter_symbol_spacing = ' ' * (pad_length + 2 * cnt)
symbol = ''.join(['/', inter_symbol_spacing, '\\'])
symbol_start_spacing = ' ' * (skip_start-cnt-1)
symbol_mid_spacing = ' ' * (skip_mid-2*(cnt+1))
pretty_output.write(''.join([symbol_start_spacing, symbol]))
for i in keys[1:-1]:
pretty_output.write(''.join([symbol_mid_spacing, symbol]))
pretty_output.write('\n')
cnt = cnt + 1
print(pretty_output.getvalue())
if __name__ == '__main__':
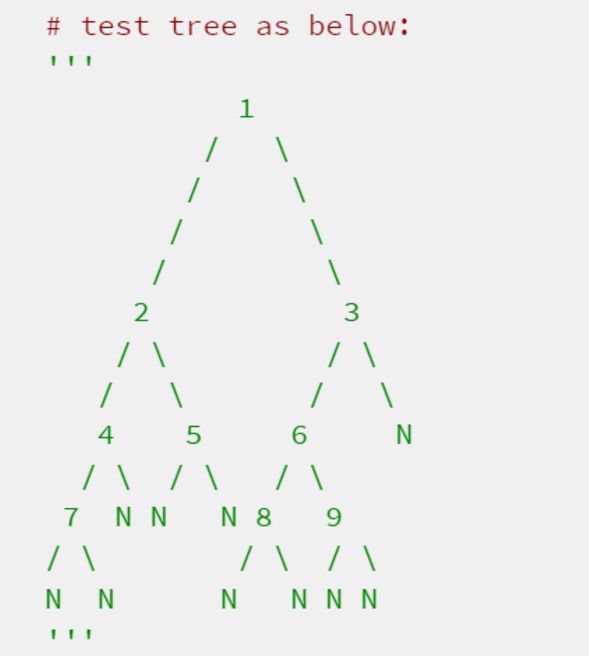
pretty_print(tree)测试用的tree如下:
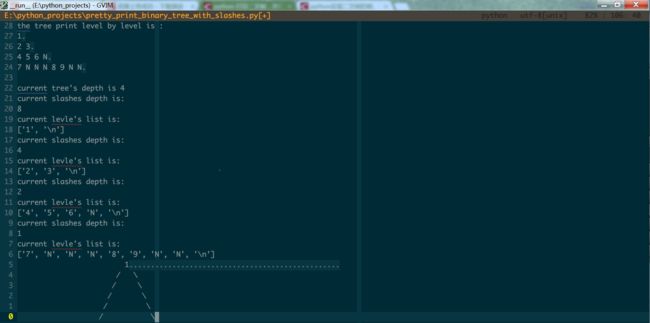
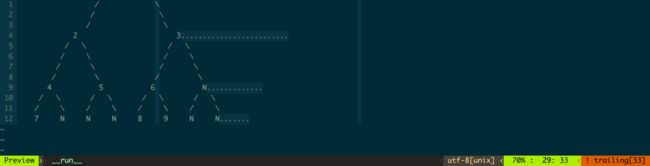
运行结果如下:
参考:
StringIO 模块用于在内存缓冲区中读写数据
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13484943/print-a-binary-tree-in-a-pretty-way
http://articles.leetcode.com/how-to-pretty-print-binary-tree/#comment-114851