使用 Spring RestTemplate 访问 Rest 服务
RestTemplate简介
Spring's central class for synchronous client-side HTTP access.
It simplifies communication with HTTP servers, and enforces RESTful principles.
It handles HTTP connections, leaving application code to provide URLs(with possible template variables) and extract results.
上面这段是RestTemplate类中的简单介绍,RestTemplate是Spring3.0后开始提供的用于访问 Rest 服务的轻量级客户端,相较于传统的HttpURLConnection、Apache HttpClient、OkHttp等框架,RestTemplate大大简化了发起HTTP请求以及处理响应的过程。本文关注RestTemplate是如何使用的,暂不涉及内部的实现原理。
RestTemplate支持多种的请求方式,具体参考下表:
| HTTP method | RestTemplate methods |
|---|---|
| GET | getForObject、getForEntity |
| POST | postForObject、postForEntity、postForLocation |
| PUT | put |
| DELETE | delete |
| HEAD | headForHeaders |
| OPTIONS | optionsForAllow |
| PATCH | patchForObject |
| any | exchange、execute |
引入RestTemplate
- 方式一,使用无参构造器直接new一个对象
private RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
- 方式二,先注册成Spring的Bean对象,之后使用的时候直接注入
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
测试准备
新建User对象,用于下面不同请求方式的测试。
@Data
public class User {
/**
* id
*/
private Long id;
/**
* 用户名
*/
private String username;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
}
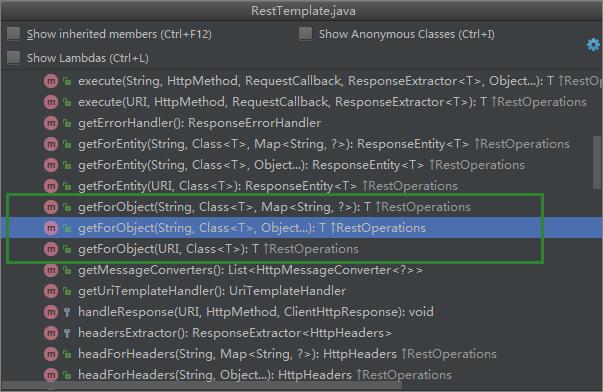
GET请求
GET请求对应两个方法,getForObject()和getForEntity(),每个方法又对应有具体的三个重载方法。这两者的区别在于getForObject()返回的是一个简单的对象,而getForEntity()响应的数据中,还额外包含有与HTTP相关的信息,如响应码、响应头等。
/**
* GET资源 (发送一个HTTP GET请求,返回的请求体将映射为一个对象)
*
* 1. 执行根据URL检索资源的GET请求
* 2. 根据responseType参数匹配为一定的类型
* 3. getForObject()只返回所请求类型的对象信息
*/
@Test
public void getForObject() {
long id = 0;
//URL中的{id}占位符最终将会用方法的id参数来填充
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user/{id}";
//重载1:最后一个参数是大小可变的参数列表,每个参数都会按出现顺序插入到指定URL的占位符中
User user = restTemplate.getForObject(url, User.class, id);
System.out.println("user = " + user);
//重载2:将id参数放到Map中,并以id作为key,然后将这个Map作为最后一个参数
Map urlParams = new HashMap<>(1);
urlParams.put("id", String.valueOf(id));
User user2 = restTemplate.getForObject(url, User.class, urlParams);
System.out.println("user2 = " + user2);
//重载3:构造URL对象,要在url上进行字符串拼接,不推荐使用
url = "http://localhost:9000/user/" + id;
User user3 = restTemplate.getForObject(URI.create(url), User.class);
System.out.println("user3 = " + user3);
}
/**
* GET资源 (发送一个HTTP GET请求,返回的ResponseEntity包含了响应体所映射成的对象)
*
* 1. 执行根据URL检索资源的GET请求
* 2. 根据responseType参数匹配为一定的类型
* 3. getForEntity()方法会返回请求的对象以及响应相关的额外信息
*/
@Test
public void getForEntity() {
long id = 1;
//URL中的{id}占位符最终将会用方法的id参数来填充
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user/{id}";
//重载1:同getForObject(),只不过返回的类型是ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity userResponseEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, User.class, id);
User user = userResponseEntity.getBody();
HttpStatus statusCode = userResponseEntity.getStatusCode();
int statusCodeValue = userResponseEntity.getStatusCodeValue();
HttpHeaders headers = userResponseEntity.getHeaders();
System.out.println("user = " + user + "; statusCode = " + statusCode + "; statusCodeValue = " + statusCodeValue + "; headers = " + headers);
//重载1:同getForObject(),只不过返回的类型是ResponseEntity
Map urlParams = new HashMap<>(1);
urlParams.put("id", String.valueOf(id));
ResponseEntity userResponseEntity2 = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, User.class, urlParams);
System.out.println("userResponseEntity2 = " + userResponseEntity2);
//重载3:同getForObject(),只不过返回的类型是ResponseEntity
url = "http://localhost:9000/user/" + id;
ResponseEntity userResponseEntity3 = restTemplate.getForEntity(URI.create(url), User.class);
System.out.println("userResponseEntity3 = " + userResponseEntity3);
}
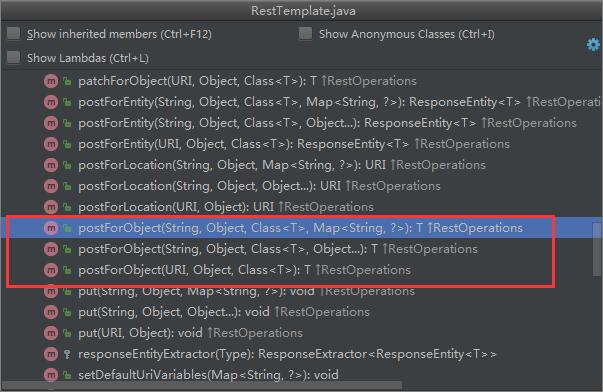
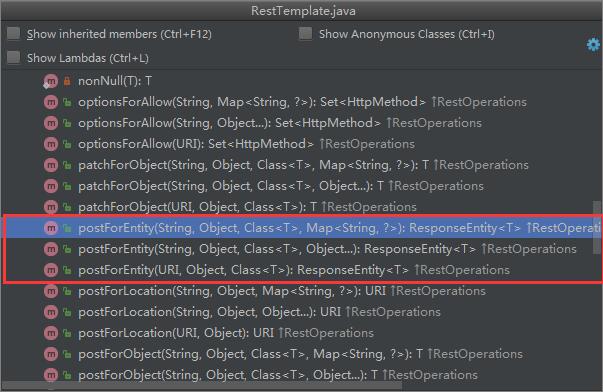
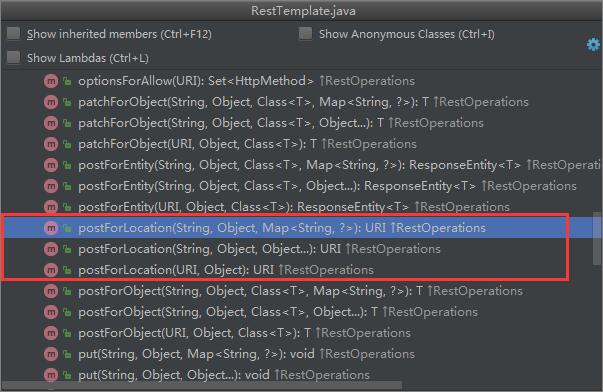
POST请求
POST请求对应三个方法,postForObject()、postForEntity()和postForLocation(),每个方法同样对应有三个具体的重载方法。postForObject()、postForEntity()类似于getForObject()和postForEntity(),postForLocation()返回的是一个URI对象。
/**
* POST资源 (POST数据到一个URL,返回根据响应体匹配形成的对象)
*/
@Test
public void postForObject() {
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user";
//重载1 & 重载2
User user1 = new User();
user1.setAge(20);
user1.setUsername("张三");
//第4个参数可以是Object... uriVariables 或者 Map uriVariables
User u1 = restTemplate.postForObject(url, user1, User.class);
System.out.println("user1 = " + u1);
//重载3
User user2 = new User();
user2.setAge(30);
user2.setUsername("李四");
User u2 = restTemplate.postForObject(URI.create(url), user2, User.class);
System.out.println("user2 = " + u2);
}
/**
* POST资源 (POST数据到一个URL,返回包含一个对象的ResponseEntity,这个对象是从响应体中映射得到的)
*/
@Test
public void postForEntity() {
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user";
// 重载1 & 重载2
User user3 = new User();
user3.setAge(25);
user3.setUsername("王五");
// 第4个参数可以是Object... uriVariables 或者 Map uriVariables
ResponseEntity userResponseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, user3, User.class);
User userBody = userResponseEntity.getBody();
HttpStatus statusCode = userResponseEntity.getStatusCode();
int statusCodeValue = userResponseEntity.getStatusCodeValue();
HttpHeaders headers = userResponseEntity.getHeaders();
System.out.println("user = " + userBody + "; statusCode = " + statusCode + "; statusCodeValue = " + statusCodeValue + "; headers = " + headers);
// 重载3
User user4 = new User();
user4.setAge(35);
user4.setUsername("陆六");
ResponseEntity userResponseEntity2 = restTemplate.postForEntity(URI.create(url), user4, User.class);
System.out.println("userResponseEntity2 = " + userResponseEntity2);
}
/**
* POST资源 (POST数据到一个URL)
* 如果服务端在响应的Location头信息中返回新资源的URL,接下来postForLocation()会以String的格式返回该URL
*/
@Test
public void postForLocation() {
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user";
User user = new User();
user.setAge(28);
user.setUsername("七七");
// 重载1 & 重载2
// 第3个参数可以是Object... uriVariables 或者 Map uriVariables
URI uri = restTemplate.postForLocation(url, user);
if (Objects.nonNull(uri)) {
String location = uri.toString();
System.out.println("location = " + location);
}
// 重载3
URI uri1 = restTemplate.postForLocation(URI.create(url), user);
if (Objects.nonNull(uri1)) {
String location = uri1.toString();
System.out.println("location = " + location);
}
}
PUT请求
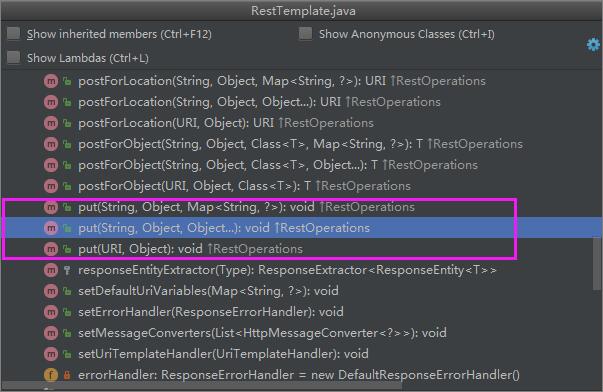
PUT请求只有一个方法:put(),对应三个具体的重载方法,put请求返回值为void。
/**
* PUT资源 (PUT资源到特定的URL)
*/
@Test
public void put() {
long id = 1;
//URL中的{id}占位符最终将会用方法的id参数来填充
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user/{id}";
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername("update 张三");
user.setAge(99);
//重载1
restTemplate.put(url, user, id);
//重载2
Map urlParams = new HashMap<>(1);
urlParams.put("id", String.valueOf(id));
restTemplate.put(url, user, urlParams);
//重载3
restTemplate.put(URI.create("http://localhost:9000/user/" + id), user);
}
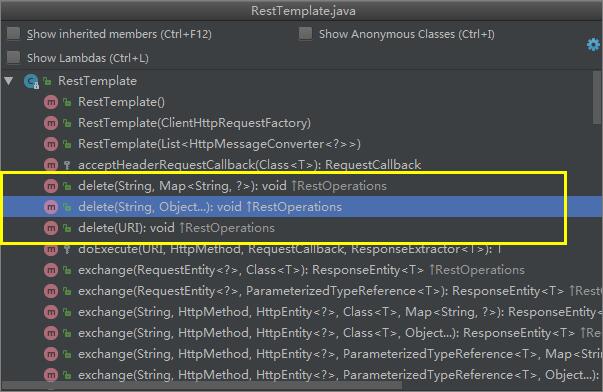
DELETE请求
DELETE请求同样只有一个方法:delete(),对应有三个具体的重载方法,delete请求返回值为void。
/**
* DELETE资源 (在特定的URL上对资源执行HTTP DELETE操作)
*/
@Test
public void delete() {
long id = 1;
//URL中的{id}占位符最终将会用方法的id参数来填充
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user/{id}";
//重载1
restTemplate.delete(url, id);
//重载2
Map urlParams = new HashMap<>(1);
urlParams.put("id", String.valueOf(id));
restTemplate.delete(url, urlParams);
//重载3
restTemplate.delete(URI.create("http://localhost:9000/user/" + id));
}
HEAD & OPTIONS & PATCH 请求
这几种请求方式比较少见和少用,这里就不再说明了。
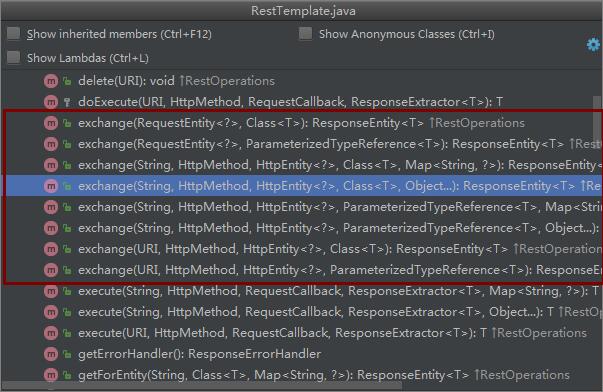
any(通用)请求
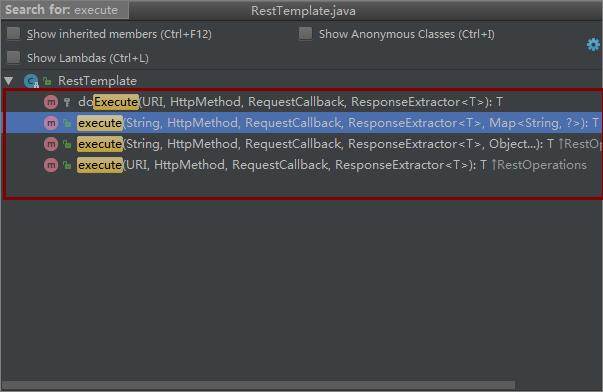
通用的请求主要是指execute()和exchange()方法,这两个方法又分别对应有三个和八个具体的重载方法。
/**
* 交换资源 (在URL上执行特定的HTTP方法,返回包含对象的ResponseEntity,这个对象是从响应体中映射得到的)
* 允许在发送给服务端的请求中设置头信息
* 支持GET、POST、PUT、DELETE...
*/
@Test
public void exchange() {
long id = 1;
String url = "http://localhost:9000/user/{id}";
//GET资源
//参数3是请求头部分;参数4是响应数据要转成对象;最后一个参数用于替换URL中的占位符
ResponseEntity userResponseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, null, User.class, id);
System.out.println("exchange = " + userResponseEntity + "; response body = " + userResponseEntity.getBody());
//POST资源
String url2 = "http://localhost:9000/user";
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
String jsonParams = "{\"username\":\"123\",\"age\":23}";
HttpEntity httpEntity = new HttpEntity(jsonParams, headers);
ResponseEntity responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url2, HttpMethod.POST, httpEntity, User.class);
System.out.println("exchange = " + responseEntity + "; response body = " + responseEntity.getBody());
//PUT and DELETE请求请自行测试
}
execute()的操作相对而言会比较麻烦,建议大家多使用exchange(),这里就不再贴代码进行说明了。
补充说明
以上测试代码可以在我的GitHub仓库中找到。