DFS(深搜)和BFS(广搜)
DFS(深搜)和BFS(广搜)
DFS
深度优先搜索属于图算法的一种,英文缩写为DFS即Depth First Search.其过程简要来说是对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个节点只能访问一次.
举例说明:
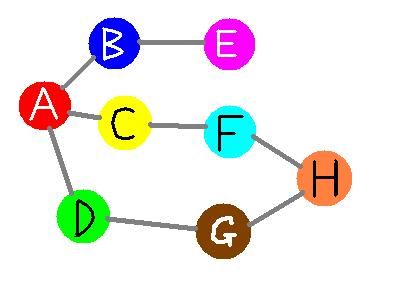
上图是无向图,从A节点开始进行深度优先搜索(以下的访问次序并不是唯一的,第二个点既可以是B也可以是C,D),则我们可能得到如下的一个访问过程:
A->B->E(没有路了!回溯到B,发现还是没路,回溯到A)->C->F->H->G->D(没有路,最终回溯到A,发现A也没路了)本次搜索结束。
注意:每次到最后一个没有路的节点时,标记已经走过,上图例子中第一个没有路的节点时E,然后回溯到B,发现B也没有路了,标记走过,再回溯到A,以此类推。
举例
题目描述
在一个 w∗h的矩形广场上,每一块 1∗1的地面都铺设了红色或黑色的瓷砖。小明现在站在某一块黑色的瓷砖上,他可以从此处出发,移动到上下左右四个相邻的且是黑色的瓷砖上。现在,他想知道,通过重复上述移动所能经过的黑色瓷砖数。
输入
第一行两个正整数 h,w。(2≤h,w≤50)
接下来输入一个二维字符矩阵,每个字符为 “.”,"#","@",分别代表黑色瓷砖,红色瓷砖,初始位置。
输出
输出一个整数,表示可以到达的瓷砖数。
样例输入
11 9
.#.........
.#.#######.
.#.#.....#.
.#.#.###.#.
.#.#..@#.#.
.#.#####.#.
.#.......#.
.#########.
.........
样例输出
59
数据规模与约定
时间限制:1 s
内存限制:256 M
100% 的数据保证 2≤h,w≤50
思路:从一个起点找到可走路径,标记已走过,递归调用
注意:需将此处的行列与坐标纸上的x,y区分开
#include 上述题目的解法一般用在求图中黑色的数量,波数等问题。
题目描述
给出 n 件物品,每个物品有一个体积 Vi,从中取出若干件物品能够组成的不同的体积和有多少种可能。例如,n=3 , Vi={1,3,4},那么输出 6 种不同的体积和为 1,3,4,5,7,8。
输入
第一行一个正整数 n。(n≤20)
第二行 n 个整数,表示 Vi。(1≤Vi≤50)
输出
输出一个整数,表示不同体积的组合数。
样例输入
3
1 3 4
样例输出
6
数据规模与约定
时间限制:1 s
内存限制:256 M
100% 的数据保证 n≤20
#include DFS可以解决集合问题
题目描述
有很多人在门口排队,每个人将会被发到一个有效的通行密码作为门票。一个有效的密码由 L 个小写字母组成,至少有一个元音 (a,e,i,o,u)和两个辅音,并且是按字母表顺序出现的,例如 abc 是有效的,而 cba 不是。
现在给定一个期望长度 L 和 C 个小写字母,输出所有有效密码。
输入
第一行两个正整数 L,C。(3≤L≤15,C≤26)
接下来一行输入 C个小写字母。
输出
按照字母表顺序输出所有密码,一行一个,若密码超过 2500025000 时,只输出前 2500025000 个密码。
样例输入
4 6
a t c i s w
样例输出
acis
acit
aciw
acst
acsw
actw
aist
aisw
aitw
astw
cist
cisw
citw
istw
数据规模与约定
时间限制:1 s
内存限制:256 M
100% 的数据保证 3≤L≤15,C≤26
#include 题目描述
读入一个用邻接矩阵存储的无向图,输出它的深度优先遍历序列。(以 1为起点,按照编号越小权值越大的规则)
输入
第一行一个正整数 NN,表示节点个数。(5≤N≤20)
接下来输入一个邻接矩阵,a[i,j]=0表示 i,j之间不存在边,=1 说明存在边。
输出
格式参照样例
样例输入
8
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
样例输出
1-2-4-6-5-3-7-8
#include BFS
广度优先搜索(BFS) 广度优先搜索在进一步遍历图中顶点之前,先访问当前顶点的所有邻接结点。 a .首先选择一个顶点作为起始结点,并将其染成灰色,其余结点为白色。 b. 将起始结点放入队列中。 c. 从队列首部选出一个顶点,并找出所有与之邻接的结点,将找到的邻接结点放入队列尾部,将已访问过结点涂成黑色,没访问过的结点是白色。如果顶点的颜色是灰色,表示已经发现并且放入了队列,如果顶点的颜色是白色,表示还没有发现 d. 按照同样的方法处理队列中的下一个结点。
模板
#include题目描述
小明刚刚参加完期中考试,“这次又能得班级第一了”,他沾沾自喜,想起之前一直努力学习的自己,他决定去西城红场看个电影放松一下。现在小明想从学校走到电影院,因为市政大力修路和挖地铁,有些道路不允许步行,请判断小明能否走到电影院(只能朝上下左右四个方向行走),如果能到,则输出最短步数,如果不能到,则输出 No.
输入
第 1 行两个数 n 和 m 表示地图有 n 行 m 列 2≤n,m≤500 第 2 行至第 n+1 行为地图,其中 s 表示学校 g表示电影院 . 为步行可以通过的点 # 为步行不可通过的点
输出
能走到电影院输出最少步数 不能走到电影院输出 No
样例输入
4 4
…s
…##
…
.g…
样例输出
5
数据规模与约定
时间限制:1 s
内存限制:256 M
100% 的数据保证 2≤n,m≤500
#include 带有条件的广搜
题目描述
小明看完了电影,是时候回家了,可是这时他突然得知小米之家的小米9现货开卖了,这款手机小明已经想了一个多月,知道这个消息后的他十分兴奋,一定要在回家之前先去小米之家买手机(城市中有一个或多个小米之家),请计算小明从电影院到任意一个小米之家买手机后回家的最短距离(只能朝上下左右四个方向行走,除了障碍物外,其他地方都可以通过),数据保证可以买完手机后回家。
输入
第 1 行两个数 n 和 m 表示地图有 n 行 m 列 2≤n,m≤2000 第 2 行至第 n+1 行为地图 其中 S 表示电影院 T 表示家 P 表示小米之家 . 为可以通过的点 # 为障碍物
输出
一个整数 表示小明从电影院去小米之家再回家的总距离
样例输入
5 5
.S…
###…
…T
.P##.
P…
样例输出
11
数据规模与约定
时间限制:5 s
内存限制:256 M
100% 的数据保证 2≤n,m≤2000
#include 广搜搜索树
559. N叉树的最大深度
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
//广搜
/*class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
queue q;
q.push(root);
int deep_max = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
deep_max++;
for(int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--){
Node * temp = q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto a : temp->children){
q.push(a);
}
}
}
return deep_max;
}
};*/
//深搜
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int deep_max = 0;
for(auto i : root->children){
int temp = maxDepth(i);
deep_max = max(deep_max,temp);
}
return deep_max+1;
}
};
Leetcode 剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> v;
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return v;
queue<TreeNode * > q;
q.push(root);
vector<int> vec;
while(!q.empty()){
for(int i = q.size(); i; i--){
TreeNode * temp = q.front();
vec.push_back(temp->val);
q.pop();
if(temp->left){
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(temp->right){
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
v.push_back(vec);
vec.clear();
}
return v;
}
};