人脸特征点检测(一)
人脸特征点检测(Facial landmark detection),即人脸特征点定位、人脸对齐(Face Alignment),是在人脸检测的基础上进行的,对人脸上的特征点例如嘴角、眼角等进行定位。
人脸特征点检测有很多用途,例如:
(1)改善人脸识别:通过人脸特征点检测将人脸对齐到平均脸,对齐后的人脸图像识别算法更加有效。
(2)人脸平均:利用人脸特征点检测的结果,将多个人脸进行融合成新的平均人脸。尝试做了一下2017年巴塞罗那足球俱乐部FCB一线队所有成员的平均脸,如下图,哈哈,很帅有木有?!
(3)人脸交换:利用人脸特征点检测的结果,对两张人脸进行无缝换脸,将一张人脸换到另一张上,做了下把贝克汉姆的脸换到梅西上的效果,如下图所示。
(4)人脸化妆&装扮:这方面的应用很多,感觉也是最具有商业应用价值的。可以做很多有趣的事情,日常生活中常见的,例如给你的脸上加上猫猫狗狗的小胡须、兔耳朵,涂上腮红、带上圣诞帽等装扮。还有美图秀秀美妆相机、美颜相机等,例如粉底、腮红、唇彩、眼影眼线、睫毛、双眼皮、美瞳、亮眼、大眼、鼻子高挺、自动瘦脸、眉毛等人脸化妆,都是在人脸特征点检测的基础上实现的。不得不说,现在的PS技术很强大,而且还是提供了傻瓜式的,用户量很大…
上述这些人脸特征点检测的应用,说明特征点的检测确实很有用很重要。特征点检测的又快又准,接下来的工作才好开展。
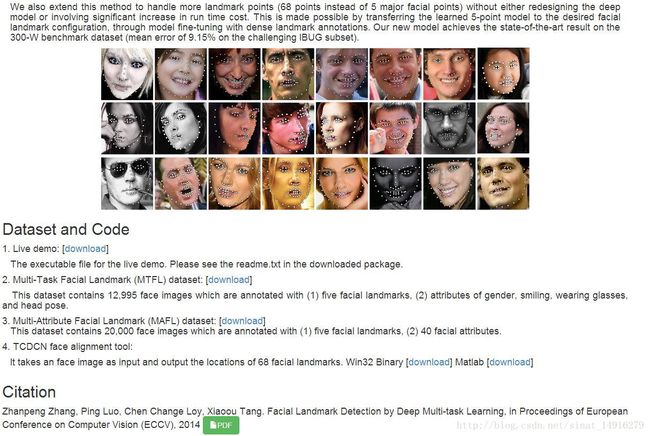
论文Facial Landmark Detection by Deep Multi-task Learning对人脸特征点检测有很好的效果,如下图所示,鲁棒性很强,但只公布了演示程序,没有公布源码及提供使用借口,无法实际使用,且论文实现和训练起来难度很大。
在Happynear大神github主页有论文Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Neural Networks的实现代码,暂时还没用到。
Seetaface中科院计算所山世光研究员带领的人脸识别研究组研发,代码基于C++实现,不依赖第三方库,开源免费,其人脸对齐模块支持5个人脸关键点的检测,其采用的是一种由粗到精的自编码器网络(Coarse-to-Fine Auto-encoder Networks, CFAN)来求解这个复杂的非线性映射过程。Dlib库实现了2014年一篇非常经典的人脸特征点检测的论文:Face Alignment at 3000 FPS via Regression Local Binary Features,其人脸特征点检测又快又准。深圳大学于仕祺老师公布的免费的libfacedetect,人脸特征点检测也非常快,效果也不错,和Dlib一样为68特征点检测,但鲁棒性不如Dlib。Seetaface、Dlib和libfacedetect都提供了人脸特征点检测的接口。
下面仅介绍三种方式来实现人脸特征点检测。
1.级联回归CNN人脸特征点检测
2.Dlib人脸特征点检测
3.libfacedetect人脸特征点检测
4.Seetaface人脸特征点检测方法
1.级联回归CNN人脸特征点检测
采用该Cascade级联回归CNN方法来定位一个人脸中的5个特征点,在我的机器上(GTX 1060)耗时7ms,算比较快了(然而,dlib、libfacedetect等做人脸68个特征点检测的速度比这都还要快…),目前人脸特征点检测的耗时主要还是在之前的要做的人脸检测上。用caffe训练网络实现该方法所用到的数据集样本、制作数据集和预测特征点的python脚本打包地址:下载链接
人脸特征点检测实际上是在人脸检测的基础上,在人脸框中预测特征点的位置。很多人脸数据集都提供了图像样本中人脸框的位置及特征点的坐标,我们需要做的是训练能预测特征点在人脸框中相对位置的网络。在实际预测时,我们首先通过人脸检测方法获取人脸框位置,然后在人脸框中预测特征点坐标。
卷积神经网络可以用于分类和回归任务,做分类任务时最后一个全连接层的输出维度为类别数,接着Softmax层采用Softmax Loss计算损失函数,而如果做回归任务,最后一个全连接层的输出维度则是要回归的坐标值的个数,采用的是欧几里何损失Euclidean Loss。
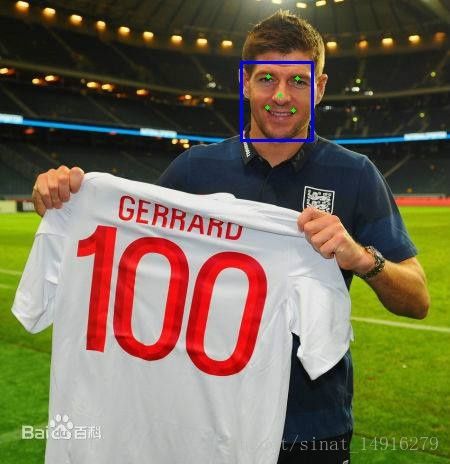
训练卷积神经网络来回归特征点坐标,这里博主只做了人脸中5个特征点的检测(如上图所示)。如果只采用一个网络来做回归训练,会发现得到的特征点坐标并不够准确,为了更加快速、准确的定位人脸特征点,采用级联回归CNN的方法,借鉴级联CNN中的级联思想,进行分段式特征点定位,其具体思路为:
(1)首先在整个人脸图像(蓝色框)上训练一个网络来对人脸特征点坐标进行粗回归,实际采用的网络其输入大小为39x39的人脸区域灰度图,预测时可以得到特征点的大致位置。
(2)设计另一个回归网络,以人脸特征点周围的局部区域图像(红色框)作为输入进行训练,实际采用的网络其输入大小为15x15的特征点局部区域灰度图,以预测到更加准确的特征点位置。
需要注意的是,由于采用的是欧几里何损失,在计算坐标时,使用的是相对坐标而不是绝对坐标,例如,在(1)中使用的是鼻子点在人脸框(蓝色框)中的相对坐标(0~1),在(2)中使用的是鼻子点在选定的周围区域框(红色框)中的相对坐标,这样能够促进模型收敛,避免网络训练发散。
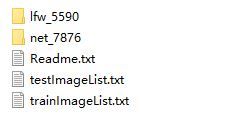
在理解思路后,准备制作数据集并设计或选取网络了,首先是数据集制作。采用的是MTFL人脸数据库,在data\face_fp文件夹下,如图lfw_5590和net_7876文件夹中包括了所有的样本(包括训练集和验证集),训练集和测试集的标签文本trainImageList.txt或testImageList.txt中的每一行,依次对应图像路径、人脸框坐标值和五个特征点的坐标值标签,具体参照Readme.txt。
在第一阶段训练时,对数据集进行了增广(只针对训练集),除了做镜像之外,还对人脸框位置做了两组缩放和四组平移(实际检测时检测出到的人脸框位置可能不够准确,为了克服这种影响,提高泛化能力),然后将图像中的人脸框区域裁剪出来,并统一缩放到39x39大小,这样数据增广了3x5=15倍,会增加训练耗时,但不影响测试时间。事实证明以上的数据增广使得第一阶段预测的特征点更加准确,实际上博主还尝试了对人脸框做两组随机的小角度旋转,但最后对特征点位置预测的准确性并没有多大提高。在做数据增广的时候,对应的特征点坐标也要变换过来,而且要转化为相对坐标(第一阶段是相对人脸框,0~1)。
使用caffe训练CNN网络,由于是回归问题,多标签,而lmdb不支持多标签(虽然可以修改caffe源码以支持多标签,但这里没有必要),因此使用hdf5格式以支持多标签,在data\face_fp下的stage1.py脚本可以执行生成第一阶段的经过数据增广的hdf5格式的训练集和验证集以及对应的标签文本,输出到data\face_fp\1F文件夹下。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon May 15 21:34:35 2017
@author: Administrator
"""
import os
from os.path import join, exists
import cv2
import numpy as np
import h5py
from common_utils import shuffle_in_unison_scary, logger,processImage, getDataFromTxt, BBox
from utils import flip, rotate
import time
###第一阶段,大致确定关键点位置
TRAIN = './'
OUTPUT = './1_F'
if not exists(OUTPUT):
os.mkdir(OUTPUT)
assert(exists(TRAIN) and exists(OUTPUT))
###生成hdf5文件,训练集做数据增广
def generate_hdf5(ftxt, output, mode='train', augment=False): #输入参数:(原始图像和关键点坐标标签文本,h5文件输出目录,h5文件名,是否数据增广)
data = getDataFromTxt(ftxt) #读取存放了文件路径和人脸框及其关键点的标签文本,坐标转换成相对坐标,返回读取结果(图像完整路径,人脸框,关键点绝对坐标)
F_imgs = [] #人脸框图
F_landmarks = [] #相对坐标
if not augment: #如果不做数据增广
for (imgPath, bbox, landmarkGt) in data:
img = cv2.imread(imgPath)
assert(img is not None) #检查img是否存在
logger("process %s" % imgPath) #打印信息
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
f_bbox = bbox
f_face = gray[f_bbox.top:f_bbox.bottom+1,f_bbox.left:f_bbox.right+1] #人脸框图像
landmarkGt_p = f_bbox.projectLandmark(landmarkGt) #转换成相对人脸框相对坐标
### 原图
f_face = cv2.resize(f_face, (39, 39))
F_imgs.append(f_face.reshape((1, 39, 39)))
F_landmarks.append(landmarkGt_p.reshape(10))
else:
for (imgPath, bbox, landmarkGt) in data:
img = cv2.imread(imgPath)
assert(img is not None) #检查img是否存在
logger("process %s" % imgPath) #打印信息
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
height,width = gray.shape
for exp in range(3): #5x3共15种变换,3种外扩
bbox_e = bbox.expand(0.1*exp) #分别往外扩0.0,0.1,0.2
for ori in range(5): #5种平移
if ori == 1:
bbox_s = bbox_e.subBBox(0.1,1.1,0.0,1.0) #向右平移0.1
elif ori == 2:
bbox_s = bbox_e.subBBox(-0.1,0.9,0.0,1.0) #向左平移0.1
elif ori == 3:
bbox_s = bbox_e.subBBox(0.0,1.0,0.1,1.1) #向下平移0.1
elif ori == 4:
bbox_s = bbox_e.subBBox(0.0,1.0,-0.1,0.9) #向上平移0.1
else:
bbox_s = bbox_e
f_bbox = BBox([int(bbox_s.left),int(bbox_s.right),int(bbox_s.top),int(bbox_s.bottom)]) #人脸框
if (f_bbox.top < 0 or f_bbox.left < 0 or f_bbox.bottom + 1 > height or f_bbox.right + 1 > width) : #如果人脸框超出图像边界,忽略之
continue
f_face = gray[f_bbox.top:f_bbox.bottom+1,f_bbox.left:f_bbox.right+1] #人脸框图像
landmarkGt_p = f_bbox.projectLandmark(landmarkGt) #转换成相对人脸框相对坐标
#水平镜像
face_flipped, landmark_flipped = flip(f_face, landmarkGt_p) #将人脸框图像和关键点坐标同时镜像
face_flipped = cv2.resize(face_flipped, (39, 39)) #人脸框图像缩放到统一大小,默认双线性插值
F_imgs.append(face_flipped.reshape((1, 39, 39))) #opencv读取的图像shape为(h,w,c),转变为(c,h,w)
F_landmarks.append(landmark_flipped.reshape(10)) #将5x2的标签reshape成一维
### 原图
f_face = cv2.resize(f_face, (39, 39))
F_imgs.append(f_face.reshape((1, 39, 39)))
F_landmarks.append(landmarkGt_p.reshape(10))
length = len(F_imgs)
print 'length = %d' % length
F_imgs, F_landmarks = np.asarray(F_imgs), np.asarray(F_landmarks) #转化成array
F_imgs = processImage(F_imgs) #图像预处理:去均值、归一化
shuffle_in_unison_scary(F_imgs, F_landmarks) #乱序
logger("generate %s" % output) #打印日志
num = length / 100000
h5files = []
for index in range(num):
suffix = '_%d.h5' % index
h5file = join(output,mode + suffix) #拼接成h5文件全路径
h5files.append(h5file)
with h5py.File(h5file, 'w') as h5: #以“写”方式打开h5文件
h5['data'] = F_imgs[index*100000 : (index + 1)*100000].astype(np.float32) #数据转换成float32类型,存图像
h5['landmark'] = F_landmarks[index*100000 : (index + 1)*100000].astype(np.float32) #数据转换成float32类型,存坐标标签
suffix = '_%d.h5' % num
h5file = join(output,mode + suffix) #拼接成h5文件全路径
h5files.append(h5file)
with h5py.File(h5file, 'w') as h5: #以“写”方式打开h5文件
h5['data'] = F_imgs[num*100000 : length].astype(np.float32) #数据转换成float32类型,存图像
h5['landmark'] = F_landmarks[num*100000 : length].astype(np.float32) #数据转换成float32类型,存坐标标签
#将h5文件全路径,存放到文本文件中
with open(join(OUTPUT, mode + '.txt'), 'w') as fd:
for h5file in h5files:
fd.write(h5file + '\n')
if __name__ == '__main__':
np.random.seed(int(time.time())) #seed指定随机数生成时所用算法开始的整数值,使随机值的产生随时间而变化,而不会每次产生的随机数都相同
# train data
train_txt = join(TRAIN,'trainImageList.txt') #join函数相当于matlab中的fullfile函数,用来连接目录和文件名,得到完整文件路径
generate_hdf5(train_txt,OUTPUT,'train',True) #输入参数:(原始图像和关键点坐标标签文本,h5文件输出目录,h5文件名,是否数据增广)
test_txt = join(TRAIN,'testImageList.txt')
generate_hdf5(test_txt, OUTPUT, 'test')准备好了第一阶段的数据集,下面看第一阶段所使用的网络1_F_train.prototxt,网络的输入层大小为39x39的单通道灰度图像,最后一个全连接层的输出维度为10,代表5个特征点的坐标值,而最后一层使用的是欧几里何Euclidean Loss,计算的是网络预测的坐标值与真实值(都是相对值)之间的均方误差的累积。
# This file gives the CNN model to predict all landmark in Stage1
name: "landmark_1_F"
layer {
name: "hdf5_train_data"
type: "HDF5Data"
top: "data"
top: "landmark"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
hdf5_data_param {
source: "../../data/face_fp/1_F/train.txt"
batch_size: 128
}
}
layer {
name: "hdf5_test_data"
type: "HDF5Data"
top: "data"
top: "landmark"
include {
phase: TEST
}
hdf5_data_param {
source: "../../data/face_fp/1_F/test.txt"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 4
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "conv1"
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 40
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "conv2"
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "conv3"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 60
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu3"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv3"
top: "conv3"
}
layer {
name: "pool3"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv3"
top: "pool3"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv4"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool3"
top: "conv4"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 80
kernel_size: 2
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu4"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv4"
top: "conv4"
}
layer {
name: "pool3_flat"
type: "Flatten"
bottom: "pool3"
top: "pool3_flat"
}
layer {
name: "conv4_flat"
type: "Flatten"
bottom: "conv4"
top: "conv4_flat"
}
layer {
name: "concat"
type: "Concat"
bottom: "pool3_flat" ###
bottom: "conv4_flat" ###
top: "faker"
concat_param {
concat_dim: 1
}
}
layer {
name: "fc1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "faker"
top: "fc1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 120
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu_fc1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "fc1"
}
layer {
name: "fc2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "fc2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu_fc2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc2"
top: "fc2"
}
layer {
name: "error"
type: "EuclideanLoss"
bottom: "fc2"
bottom: "landmark"
top: "error"
include {
phase: TEST
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "EuclideanLoss"
bottom: "fc2"
bottom: "landmark"
top: "loss"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
}设置训练超参数文件1_F_solver.prototxt如下,然后就可以开始训练了,训练迭代200000次后,loss就降得就很小了。
net: "./1_F_train.prototxt"
test_iter: 55 #3466/64=55
test_interval: 1000
base_lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
#lr_policy: "step"
#gamma: 0.1
#stepsize: 50000
display: 200
max_iter: 500000
snapshot: 20000
snapshot_prefix: "./1_F/"
test_compute_loss: true
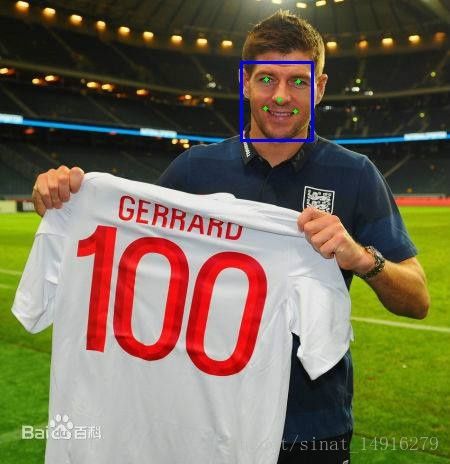
solver_mode: GPU准备好1_F_deploy.prototxt,我们首先看看只用第一阶段训练来做预测的结果,如下图所示,可以看到第一阶段能够大致预测到特征点位置,但仍不够准确,接下来需要我们进行第二阶段的训练。
第二阶段训练,共5个特征点,每个特征点做两组数据集,即第一组数据集取以特征点为中心,局部框大小为(2*0.18*W,2*0.18*H),其中W、H为人脸框的大小,并对此局部框做随机的微小平移使得特征点在局部框中的位置随机,裁剪出局部框图像并统一到15x15大小,第二组数据集和第一组数据集制作过程一样,只是局部框取得是(2*0.16*W,2*0.16*H)。对每个特征点,针对这两组数据集采用同样的网络模型进行训练,可以得到两组训练好的模型,在预测时,采取两组模型预测的均值作为预测结果,提高预测的准确性。
上述第二阶段数据集的制作代码在stage2.py脚本中,同样需要注意的是需要将特征点的坐标值标签变换为相对于局部框的相对坐标(0~1),最后生成hdf5格式的数据集文件及对应的train.txt、test.txt。
import time
from collections import defaultdict
import cv2
import numpy as np
import h5py
from common_utils import logger, createDir, getDataFromTxt, getPatch, processImage
from common_utils import shuffle_in_unison_scary
from utils import randomShiftWithArgument #,randomShift
types = [(0, 'LE1', 0.16),
(0, 'LE2', 0.18),
(1, 'RE1', 0.16),
(1, 'RE2', 0.18),
(2, 'N1', 0.16),
(2, 'N2', 0.18),
(3, 'LM1', 0.16),
(3, 'LM2', 0.18),
(4, 'RM1', 0.16),
(4, 'RM2', 0.18)] #5个关键点,两种padding
for t in types:
d = './2_%s' % t[1]
createDir(d)
def generate(ftxt, mode, augment=False):
"""
Generate Training Data for LEVEL-2
mode = train or test
"""
data = getDataFromTxt(ftxt) #读取存放了文件路径和人脸框及其关键点的标签文本,坐标转换成相对坐标,返回读取结果(图像完整路径,人脸框,关键点绝对坐标)
trainData = defaultdict(lambda: dict(patches=[], landmarks=[])) #数据字典
for (imgPath, bbox, landmarkGt) in data:
img = cv2.imread(imgPath, cv2.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE) #读取灰度图像
assert(img is not None) #检查图像是否存在
logger("process %s" % imgPath)
landmarkGt_p = bbox.projectLandmark(landmarkGt) #绝对坐标投影到相对于人脸框的相对坐标
landmarkPs = randomShiftWithArgument(landmarkGt_p, 0.05, 2) #对关键点相对坐标的位置做2组随机平移,得到2组“新的关键点”,0.05表示关键点相对于人脸框相对坐标的最大平移度
if not augment:
landmarkPs = [landmarkPs[0]] #测试集只做一组随机平移
for landmarkP in landmarkPs: #对做的2组随机平移,将所有局部框图像和关键点相对于局部框的相对坐标送入到数据字典trainData
for idx, name, padding in types: #对每个关键点和padding
patch, patch_bbox = getPatch(img, bbox, landmarkP[idx], padding) #根据随机平移过的关键点相对坐标和padding得到局部框图像和局部框
patch = cv2.resize(patch, (15, 15)) #局部框图像缩放到15x15
patch = patch.reshape((1, 15, 15)) #每个patch为c,h,w,append之后就变成了n,c,h,w
trainData[name]['patches'].append(patch)
_ = patch_bbox.project(landmarkGt[idx]) #‘真’关键点相对人脸框相对坐标反投影到绝对坐标,再投影到局部框得到相对局部框的相对坐标
trainData[name]['landmarks'].append(_)
for idx, name, padding in types:
logger('writing training data of %s'%name)
patches = np.asarray(trainData[name]['patches']) #从数据字典中取出
landmarks = np.asarray(trainData[name]['landmarks'])
patches = processImage(patches) #预处理,去均值、归一化
shuffle_in_unison_scary(patches, landmarks) #乱序
with h5py.File('./2_%s/%s.h5'%(name, mode), 'w') as h5: #生成mode.h5(train/test)
h5['data'] = patches.astype(np.float32)
h5['landmark'] = landmarks.astype(np.float32)
with open('./2_%s/%s.txt'%(name, mode), 'w') as fd: #生成mode.txt(train/test),写入h5文件路径
fd.write('./2_%s/%s.h5'%(name, mode))
if __name__ == '__main__':
np.random.seed(int(time.time())) #seed指定随机数生成时所用算法开始的整数值,使随机值的产生随时间而变化,而不会每次产生的随机数都相同
# trainImageList.txt
generate('./trainImageList.txt', 'train', augment=True) #生成train.h5和train.txt,训练集做数据增强(实际上只是多做了一组随机平移)
# testImageList.txt
generate('./testImageList.txt', 'test') #生成test.h5和test.txt
# Done总共5个特征点,每个特征点使用了两种数据集,使用的是同一个网络,最终训练得到10个模型。以下为第二阶段左眼第一组数据集的训练模型2_LE1_train.prototxt,其它训练网络只需修改数据集路径即可。
# This file gives the CNN model to predict landmark in Stage2
name: "landmark_2_LE1"
layer {
name: "hdf5_train_data"
type: "HDF5Data"
top: "data"
top: "landmark"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
hdf5_data_param {
source: "../../data/face_fp/2_LE1/train.txt"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "hdf5_test_data"
type: "HDF5Data"
top: "data"
top: "landmark"
include {
phase: TEST
}
hdf5_data_param {
source: "../../data/face_fp/2_LE1/test.txt"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 4
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "conv1"
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 40
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "conv2"
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "fc1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "fc1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 60
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu_fc1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "fc1"
}
layer {
name: "fc2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "fc2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu_fc2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc2"
top: "fc2"
}
layer {
name: "error"
type: "EuclideanLoss"
bottom: "fc2"
bottom: "landmark"
top: "error"
include {
phase: TEST
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "EuclideanLoss"
bottom: "fc2"
bottom: "landmark"
top: "loss"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
}对应的网络超参数文件2_LE1_solver.prototxt,需要注意的是对不同特征点,可能需要尝试不同的初始学习率来使得模型更好的收敛。因此,需要训练10个小网络,还是挺繁琐的…
net: "./2_LE1_train.prototxt"
test_iter: 55 #3466/64=55
test_interval: 1000
base_lr: 0.005
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
#lr_policy: "step"
#gamma: 0.1
#stepsize: 50000
display: 200
max_iter: 100000
snapshot: 20000
snapshot_prefix: "./2_LE1/"
test_compute_loss: true
solver_mode: GPU接下来就可以开始训练,训练迭代100000次后,loss也降得差不多了。然后接着把剩下的9个都训练完,注意可能要调下学习率,batchsize不用调。
然后准备好预测用的2_LE1_deploy.prototxt,剩下9个deploy.prototxt与其完全一致。现在可以来看看级联后的特征点预测结果了,如图所示,可以看到预测结果更加准确了,但鲁棒性还不够强。
如果采取更大的网络,特征点的预测会更加准确鲁棒,但耗时多,为了在速度和性能上做找到平衡点,使用较小的网络,并采用级联的思想,先进行粗检测,然后微调特征点位置。
下面是最终预测人脸特征点的landmarks_detection.py,其中人脸检测采用的是级联CNN或者opencv人脸检测,在人脸检测的基础上预测人脸特征点位置,并将预测的相对位置转换成图像上的绝对坐标。
#coding:utf-8
import os
from os.path import join
import cv2
import caffe
import numpy as np
from face_detection_functions import *
from load_model_functions import *
import time
#定义一个CNN类,初始化网络,以及前向传播返回结果
class CNN(object):
"""
Generalized CNN for simple run forward with given Model
"""
def __init__(self, net, model):
self.net = net
self.model = model
self.cnn = caffe.Net(net, model, caffe.TEST) # failed if not exists
def forward(self, data, layer='fc2'):
print data.shape
fake = np.zeros((len(data), 1, 1, 1))
self.cnn.set_input_arrays(data.astype(np.float32), fake.astype(np.float32)) #指定一块连续的数据
self.cnn.forward() #前向传播
result = self.cnn.blobs[layer].data[0] #获取指定layer结果
t = lambda x: np.asarray([np.asarray([x[2*i], x[2*i+1]]) for i in range(len(x)/2)]) #定义匿名函数t,将输入的10x1坐标数组转换成5x2矩阵
result = t(result)
return result
class BBox(object): #BoundingBox类
"""
Bounding Box of face
"""
def __init__(self, bbox):
self.left = int(bbox[0])
self.right = int(bbox[1])
self.top = int(bbox[2])
self.bottom = int(bbox[3])
self.x = bbox[0]
self.y = bbox[2]
self.w = bbox[1] - bbox[0]
self.h = bbox[3] - bbox[2]
def expand(self, scale=0.05): #向外扩展
bbox = [self.left, self.right, self.top, self.bottom]
bbox[0] -= int(self.w * scale)
bbox[1] += int(self.w * scale)
bbox[2] -= int(self.h * scale)
bbox[3] += int(self.h * scale)
return BBox(bbox)
def project(self, point): #投影变换,将点坐标转换为相对于BBox框的相对坐标
x = (point[0]-self.x) / self.w
y = (point[1]-self.y) / self.h
return np.asarray([x, y])
def reproject(self, point): #投影逆变换,将点相对于BBox框的相对坐标转换成点的绝对坐标值
x = self.x + self.w*point[0]
y = self.y + self.h*point[1]
return np.asarray([x, y])
def reprojectLandmark(self, landmark): #投影逆变换,将所有关键点相对于BBox框的相对坐标转换成点的绝对坐标值
print len(landmark)
if not len(landmark) == 5:
landmark = landmark[0]
p = np.zeros((len(landmark), 2))
for i in range(len(landmark)):
p[i] = self.reproject(landmark[i])
return p
def projectLandmark(self, landmark): #投影变换,将所有点坐标转换为相对于BBox框的相对坐标
p = np.zeros((len(landmark), 2))
for i in range(len(landmark)):
p[i] = self.project(landmark[i])
return p
def subBBox(self, leftR, rightR, topR, bottomR):
leftDelta = self.w * leftR
rightDelta = self.w * rightR
topDelta = self.h * topR
bottomDelta = self.h * bottomR
left = self.left + leftDelta
right = self.left + rightDelta
top = self.top + topDelta
bottom = self.top + bottomDelta
return BBox([left, right, top, bottom])
def cropImage(self, img): #根据BBox返回裁剪图像
"""
crop img with left,right,top,bottom
**Make Sure is not out of box**
"""
return img[self.top:self.bottom+1, self.left:self.right+1]
class Landmarker(object):
"""
class Landmarker wrapper functions for predicting facial landmarks
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize Landmarker with files under VERSION
"""
#model_path = join(PROJECT_ROOT, VERSION)
deploy_path = "../../models/face_fp"
model_path = "../../models/face_fp"
CNN_TYPES = ['LE1', 'RE1', 'N1', 'LM1', 'RM1', 'LE2', 'RE2', 'N2', 'LM2', 'RM2']
level1 = [(join(deploy_path, '1_F_deploy.prototxt'), join(model_path, '1_F/_iter_200000.caffemodel'))]
level2 = [(join(deploy_path, '2_%s_deploy.prototxt'%name), join(model_path, '2_%s/_iter_100000.caffemodel'%name)) \
for name in CNN_TYPES]
self.level1 = [CNN(p, m) for p, m in level1] #初始化第一阶段网络
self.level2 = [CNN(p, m) for p, m in level2] #初始化第二阶段网络
def detectLandmark(self, image, bbox):
"""
Predict landmarks for face with bbox in image
apply level-1 and level-2
"""
#if not isinstance(bbox, BBox) or image is None:
#return None, False
face = bbox.cropImage(image) #裁剪出人脸框图像
#face = image
#print face.shape
face = cv2.resize(face, (39, 39)) #缩放人脸框图像到39x39
#print face.shape
face = face.reshape((1, 1, 39, 39)) #人脸框图像数据矩阵->[n,c,h,w]
face = self._processImage(face) #人脸框图像预处理,归一化
# level-1, only F in implemented
landmark = self.level1[0].forward(face) #第一阶段,直接调用CNN类Level1[0]的前向传播函数,返回第一阶段回归结果(相对人脸框的相对坐标)
# level-2
landmark = self._level(image, bbox, landmark, self.level2, [0.16, 0.18]) #第二阶段,根据padding和前一阶段的关键点回归结果,重新取人脸框中的局部框,继续回归
return landmark
def _level(self, img, bbox, landmark, cnns, padding):
"""
LEVEL-?
"""
for i in range(5): #五个关键点
x, y = landmark[i] #获取上一阶段预测结果的关键点坐标
patch, patch_bbox = self._getPatch(img, bbox, (x, y), padding[0]) #根据第一种padding获取局部框图像patch、局部框patch_bbox
patch = cv2.resize(patch, (15, 15)).reshape((1, 1, 15, 15)) #局部小窗口框缩放到15x15
patch = self._processImage(patch) #预处理,归一化
d1 = cnns[i].forward(patch) #第一种padding每个关键点对应的网络,前向传播,返回的是相对于局部框的相对坐标
patch, patch_bbox = self._getPatch(img, bbox, (x, y), padding[1]) #根据第二种padding获取局部框图像patch、局部框patch_bbox
patch = cv2.resize(patch, (15, 15)).reshape((1, 1, 15, 15))
patch = self._processImage(patch)
d2 = cnns[i+5].forward(patch) #第二种padding每个关键点对应的网络,前向传播,返回的是相对于局部框的相对坐标
d1 = bbox.project(patch_bbox.reproject(d1[0])) #对第一padding,相对局部框patch_size的相对坐标->绝对坐标->相对于人脸的相对坐标
d2 = bbox.project(patch_bbox.reproject(d2[0])) #对第一padding,相对局部框patch_size的相对坐标->绝对坐标->相对于人脸的相对坐标
landmark[i] = (d1 + d2) / 2
return landmark
def _getPatch(self, img, bbox, point, padding): #根据相对坐标和padding获取局部框图像patch、局部框patch_bbox
"""
Get a patch iamge around the given point in bbox with padding
point: relative_point in [0, 1] in bbox
"""
point_x = bbox.x + point[0] * bbox.w
point_y = bbox.y + point[1] * bbox.h
patch_left = point_x - bbox.w * padding
patch_right = point_x + bbox.w * padding
patch_top = point_y - bbox.h * padding
patch_bottom = point_y + bbox.h * padding
patch = img[patch_top: patch_bottom+1, patch_left: patch_right+1]
patch_bbox = BBox([patch_left, patch_right, patch_top, patch_bottom])
return patch, patch_bbox #返回局部框图像patch、局部框patch_bbox
def _processImage(self, imgs): #预处理,归一化
"""
process images before feeding to CNNs
imgs: N x 1 x W x H
"""
imgs = imgs.astype(np.float32)
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
m = img.mean()
s = img.std()
imgs[i] = (img - m) / s
return imgs
def drawLandmark(img, landmark):
for x, y in landmark:
cv2.circle(img, (int(x), int(y)), 2, (0,255,0), -1)
return img
#利用opencv的harr + adaboost人脸检测算法进行人脸检测
def detectFaces(cascadeCls,img):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = cv2.equalizeHist(gray)
faces = cascadeCls.detectMultiScale(gray,1.1,3,0,(64,64),(256,256)) #多尺度人脸检测
return faces
if __name__ == '__main__':
#cascade级联CNN人脸检测+分段式特征点检测
# ================== load models ======================================
net_12c_full_conv, net_12_cal, net_24c, net_24_cal, net_48c, net_48_cal = load_face_models(loadNet=True)
nets = (net_12c_full_conv, net_12_cal, net_24c, net_24_cal, net_48c, net_48_cal)
min_face_size = 48
stride = 5
get_landmark = Landmarker()
result_folder = './result-folder/'
test_folder = './test-folder/'
test_images = os.listdir(test_folder)
start_time = time.time()
for test_image in test_images:
imgPath = test_folder + test_image
img = cv2.imread(imgPath)
assert(img is not None)
print 'imgPath: %s' % imgPath
print img.shape
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_forward = np.array(img,dtype=np.float32)
img_forward -= np.array((104,117,123)) #去均值,级联CNN训练时减去的是ImageNet数据集均值
rects = detect_faces_net(nets,img_forward,min_face_size,stride,True,1.414,0.85) #调用级联CNN人脸检测方法
for rect in rects:
cv2.rectangle(img,(rect[0],rect[1]),(rect[2],rect[3]),(255,0,0),2)
bbox = BBox([rect[0],rect[2],rect[1],rect[3]])
final_landmark = get_landmark.detectLandmark(gray,bbox)
final_landmark = bbox.reprojectLandmark(final_landmark)
img = drawLandmark(img,final_landmark)
cv2.imwrite(result_folder + test_image,img)
end_time = time.time()
print 'the time of face detection and feature points location per image:',(end_time - start_time)*1000/len(test_images),'ms'
'''
###opencv(harr+adaboost)视频中人脸检测 + 分段式特征点提取
xmlPath = 'D:/OPENCV2.4.9/opencv/sources/data/haarcascades/haarcascade_frontalface_alt2.xml'
cascadeCls = cv2.CascadeClassifier(xmlPath) #加载xml人脸检测文件,获取CascadeClassifier对象
get_landmark = Landmarker() #定义一个关键点类
video = cv2.VideoCapture('himetan.avi')
if video.isOpened():
success,frame = video.read()
while success:
faces = detectFaces(cascadeCls,frame)
if len(faces) == 0:
cv2.imshow('image',frame)
else:
img = frame.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
for face in faces:
bbox = BBox([face[0],face[0]+face[2],face[1],face[1]+face[3]])
cv2.rectangle(img,(bbox.left,bbox.top),(bbox.right,bbox.bottom),(255,0,0),2)
final_landmark= get_landmark.detectLandmark(gray, bbox) #调用关键点检测函数,返回检测到的相对坐标
final_landmark = bbox.reprojectLandmark(final_landmark) #反投影得到检测到的关键点绝对坐标
img = drawLandmark(img, final_landmark) #在图像上标出所有关键点
cv2.imshow('image',img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) > 0:
break
success,frame = video.read()
video.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
'''
'''
###opencv(harr+adaboost)文件夹下图像中人脸检测 + 分段式特征点提取
xmlPath = 'D:/OPENCV2.4.9/opencv/sources/data/haarcascades/haarcascade_frontalface_alt2.xml'
cascadeCls = cv2.CascadeClassifier(xmlPath) #加载xml人脸检测文件,获取CascadeClassifier对象
result_folder = './result-folder/'
test_folder = './test-folder/'
test_images = os.listdir(test_folder)
get_landmark = Landmarker() #定义一个关键点类
start_time = time.time()
for image in test_images:
img = cv2.imread(test_folder+image)
#bbox = BBox([320,391,55,152]) #人脸框位置,left,right,top,bottom
faces = detectFaces(cascadeCls,img)
if len(faces) == 0:
break
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
for face in faces:
bbox = BBox([face[0],face[0] + face[2],face[1],face[1] + face[3]])
cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox.left, bbox.top), (bbox.right, bbox.bottom), (0,0,255), 2)
#cv2.resize(gray,(256,256))
final_landmark= get_landmark.detectLandmark(gray, bbox) #调用关键点检测函数,返回检测到的相对坐标
final_landmark = bbox.reprojectLandmark(final_landmark) #反投影得到检测到的关键点绝对坐标
img = drawLandmark(img, final_landmark) #在图像上标出所有关键点
#cv2.imwrite(result_folder+'level1-'+image, img)
#cv2.imwrite(result_folder+'level2-'+image, img)
end_time = time.time()
print 'the time of face detection and feature points location per image:',(end_time - start_time)*1000/len(test_images),'ms'
'''