Android 进阶 - Activity服务启动分析
前面已经介绍了如何创建一个应用服务,如何创建一个系统服务,这里我把Android服务分为:应用服务(ActivityService),系统服务(SystemService),分类是否正确也不清楚,网上并没有资料明确定义,之所以这样分类,因为应用服务放在ActiveServices中管理,而系统服务放在ServiceManager中管理,两者存在明显的不同。由于Android设计时已经把中间层标准化了,我们实现一个服务时,只需要简单实现服务端(Native)和调用端(Proxy)即可。本文将详细描述ActiveService的启动全过程,有关Binder的部分没有详细介绍,后续文章再介绍。
1、Activity服务启动的几个阶段
Activity服务启动大致可以分为以下几个阶段:
- 准备阶段:做进程启动前的准备工作。
- 进程启动阶段:通过Zygote启动进程。(当服务已经启动时,此步骤略)
- Activity启动阶段:在新的进程里,启动Activity。
本文重点说明第1阶段和第3阶段,进程启动阶段参见前一篇文章《Android 进阶-进程启动分析》。所以,Activity服务与应用的启动过程大致相同。
2. 准备阶段
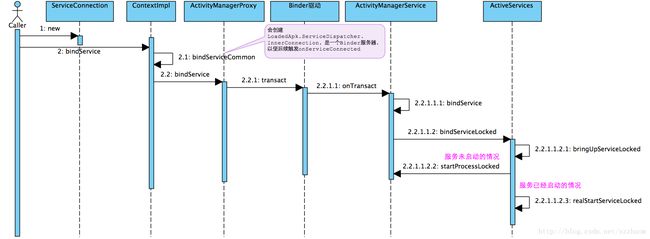
2.1 流程图
2.2 关键流程说明
上面的流程图,和Activity应用启动相似,最后都分为服务进程已经启动和服务进程未启动两种情况,服务进程已经启动的情况下,不需要进程启动,直接到服务启动步骤。
从先前服务实例中,我们知道,当要调用一个服务时,需要先创建一个ServiceConnection,并在OnServiceConnected函数中,保存服务的Binder接口,以便调用服务的各种接口。然后,再绑定服务,再调用服务。
2.2.1 ContextImpl.bindService
Client是调用Activity.bindService来绑定服务的,怎么会到ContextImpl.bindService中?上图中略去了一些步骤,这里结合代码说明:
Activity 继承自 ContextThemeWrapper ,而ContextThemeWrapper继承自 ContextWrapper,bindService就定义在ContextWraper中。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/ContextWrapper.java
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
public ContextWrapper(Context base) {
mBase = base;
}
...
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
...
}
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ContextThemeWrapper.java
public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {
...
public ContextThemeWrapper() {
super(null);
}
...
}
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public ActivityThread{
private Context createBaseContextForActivity(ActivityClientRecord r,
final Activity activity) {
ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl();
appContext.init(r.packageInfo, r.token, this);
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
...
Context baseContext = appContext;
...
return baseContext;
}
...
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// System.out.println("##### [" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "] ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(" + r + ")");
...
try {
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
...
if (activity != null) {
//创建上下文
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
//连接上下文
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);
...
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}
}public Activity{
...
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config) {
// 连接mBase
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachActivity(this, mContainer, null);
...
}
}
public class ContextThemeWrapper{
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
//连接mBase
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
mBase = newBase;
}
}
因此,上图从ContextImpl.bindService开始。
2.2.2 ContextImpl.bindServiceCommon
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
// 创建一个IServiceConnection对象,服务绑定后,需要调用此对象的connected函数,触发ServiceConnection.onServiceConnected事件
// 此对象是一个LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection对象,见后面的LoadedApk的代码解释
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
...
// 通过ActivieyManagerProxy.bindService,经由Binder调用ActivityManagerService.bindService
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(),
service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return false;
}
}public class LoadedApk{
...
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
...
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
...
}
...
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
// 返回一个InnerConnection连接
return mIServiceConnection;
}
}
...
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
// 创建ServiceDispatcher
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
// 返回ServiceDispatcher.getIServiceConnection()
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
...
} - 调用mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher创建IServiceConnection连接,返回的是ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection对象,此对象作为bindService的参数,传给后续实现者。此对象可以通过connected函数,来触发ServiceConection.onServiceConnected,来通知调用方,服务已经绑定了,并传入IBinder对象,可以调用方通过此对象来调用服务的各种操作;
- 通过ActivityManagerProxy.bindService,来调用ActivityManagerService中的bindService方法。说明:ActivityManagerNavite.getDefault()返回的是一个ActivityManagerProxy对象,这在《Android进阶- Activity应用启动分析》一文中已经有介绍。具体的过程见上图,Binder通信过程本文忽略。
需要注意的是,InnerConnection继承自IServiceConnection.Stub,即,新创建的InnerConnection是一个Binder服务端对象。
2.2.3 ActivityManagerProxy.bindService
public class ActivityManagerProxy{
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
// 写入connection的binder接口
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
}2.2.4 ActivityManagerService.bindService
流程走到ActivityManagerService.bindService中后,又有两个关键动作,即ActiveServices.realStartServiceLocked和ActiveServices.reuqestServiceBindLocked。
2.2.5 ActiveServices.bringUpServiceLocked
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
public class ActiveServices{
...
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
int intentFlags, boolean execInFg, boolean whileRestarting) {
...
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
// 如果服务进程已经启动
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
} else {
...
}
// Not running -- get it started, and enqueue this service record
// to be executed when the app comes up.
if (app == null) {
// 如果服务进程未启动
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
...
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
...
return null;
}
}
上面的函数流程很简单,就是判断如果服务进程已经启动,则直接调用realStartServiceLocked启动服务,否则调用ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked启动进程,进入进程启动阶段。
3. 进程启动阶段
略。详见《Android 进阶 - 进程启动分析》一文。
4. 服务启动阶段
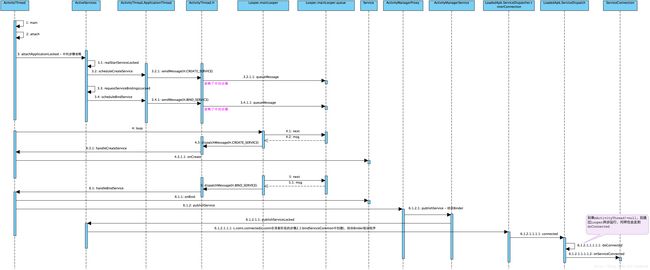
4.1 流程图
4.2 关键流程分析
上面的图看似比Activity启动要复杂,实际上大的步骤差不过,只不过,服务启动时,先要createService,再bindService,要发两次消息,而Activity启动只需要发一次消息。
如果服务进程已经启动的情况下,可直接从3.1:realStartServiceLocked一步往下看。
请先参看《Android 进阶 - Looper进程内通信》和《Android 进阶 -Activity应用启动分析》,从bindServiceLocked到sendMessage,再到消息进入到Looper.mainLooper.queue队列中,如果看了前面两篇文章,相信这一部分很容易看懂,这里不再讨论。流程主要发了两个消息H.CREATE_SERVICE和H.BIND_SERVICE,一个是创建服务的消息,一个是绑定服务的消息。这些消息会在Looper.loop函数依次处理。
4.2.1 handleCreateService
H.CREATE_SERVICE的消息,经由H.dispatchMessage,会进入ActivityThread.handleCreateService函数。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public clas ActivityThread{
...
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl();
context.init(packageInfo, null, this);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
context.setOuterContext(service);
// 连接服务上下文
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
// 触发服务的onCreate事件
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, 0, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// nothing to do.
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}4.2.2 handleBindService
H.BIND_SERVICE的消息,经由H.dispatchMessage,会进入ActivityThread.handleBindService函数。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public class ActivityThread{
...
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
// 触发服务的onBind事件
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
// 通过Binder,调用ActivityManagerService.publishService发布服务
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
...
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
}
}4.2.3 publishService
上节的源码中说明,服务绑定完成之后,会通过ActivityManagerProxy代理,经由Binder,调用ActivityManagerService的publishService函数。frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
pulbic class ActivityManagerService{
...
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
...
}
经由Binder驱动程序传输到ActivityManagerService后,service由服务端的Binder对象自动变了客户端的BinderProxy对象。
pulbic class ActiveServices{
...
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i
下面的代码是经由Binder远程接口传回至Activity调用端。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
public class LoadApk{
...
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
// 通知已经连接
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
// 进入下面的connected函数
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
...
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
// 进入下面的doConnected函数
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
...
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
...
// If there was an old service, it is not disconnected.
if (old != null) {
// 假如是服务,触发onServiceDisconnected事件
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
// 假如是新服务,则触发onServiceConnected。mConnection为在Activity.bindService是传入的参数,也即是绑定服务前用户创建的ServiceConnection类实例。
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
}
} 流程走到这里,就算是完成了,进入了调用者创建的ServiceConnection.onServiceConnected函数中,此函数会传回服务的IBinder接口,调用者可以保存此接口调用服务的各类操作。
5. 结语
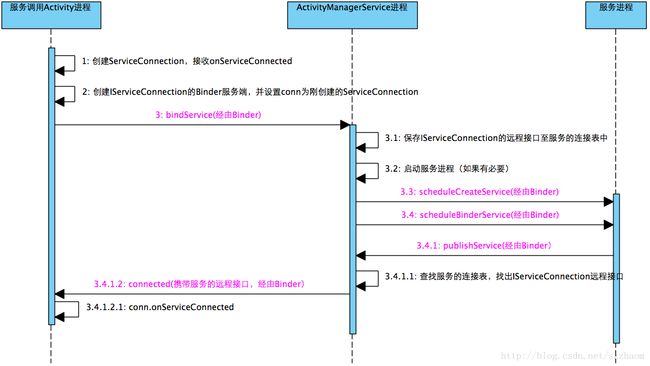
最后,我们总结一下,如下图。
上图是简化了的流程,只从三个进程来描述。从上图可以看出,Android已经屏蔽了进程概念,要在一个Activity里,绑定一个服务,其实是三个进程之间打交道,进程之间的数据,全部经由Binder传递。
- ServiceConnection在Activity里由调用方创建,实现onSeviceConnected事件,接收传回的service远程接口(BinderProxy);
- 创建IServiceConnection的Binder服务端,此步骤在ContextImpl.bindServiceCommon里创建,是一个LoadedApk.ServiceDistpatch.InnerConnection类的实例。
- binderService,此处经由Binder,传入到ActivityManagerService中,数据传递ActivityManagerService时,会将IServiceConnection服务端对象转换为BinderProxy的远程接口代理对象,此时,ActivityManagerService是Activity的客户端。
- 保存IServiceConnection至服务的连接列表中
- 如果有必要,启动服务进程
- 调用app.thread.scheduleCreateService创建服务,app.thread是一个基于ActivityThread.ApplicationThread的Binder远程接口,由此接口,可以与服务进程通讯,真正的操作在服务进程里。
- 同理,调用app.thread.scheduleBindService绑定服务,绑定操作在服务进程里
- 服务进程通过ActivityManagerProxy,经由Binder接口,将publishService转发至ActivityManagerService中。
- ActivityManagerService进程查找此服务的IServiceConnection远程Binder接口。
- 调用IServiceConnection远程Binder接口,进入到IServiceConnection服务端(即Activity服务调用进程),执行connected操作
- 最后执行ServiceConnection.onServiceConnected,通知Activity,服务绑定完成。并得到了服务的远程接口。