AbstractRoutingDataSource动态数据源切换,AOP实现动态数据源切换
AbstractRoutingDataSource动态数据源切换
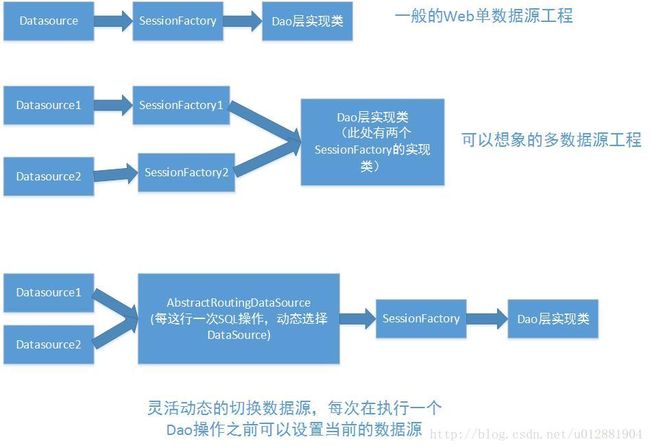
上周末,室友通宵达旦的敲代码处理他的多数据源的问题,搞的非常的紧张,也和我聊了聊天,大概的了解了他的业务的需求。一般的情况下我们都是使用SSH或者SSM框架进行处理我们的数据源的信息。
操作数据一般都是在DAO层进行处理,可以选择直接使用JDBC进行编程(http://blog.csdn.net/yanzi1225627/article/details/26950615/)
或者是使用多个DataSource 然后创建多个SessionFactory,在使用Dao层的时候通过不同的SessionFactory进行处理,不过这样的入侵性比较明显,一般的情况下我们都是使用继承HibernateSupportDao进行封装了的处理,如果多个SessionFactory这样处理就是比较的麻烦了,修改的地方估计也是蛮多的
最后一个,也就是使用AbstractRoutingDataSource的实现类通过AOP或者手动处理实现动态的使用我们的数据源,这样的入侵性较低,非常好的满足使用的需求。比如我们希望对于读写分离或者其他的数据同步的业务场景
单数据源的场景(一般的Web项目工程这样配置进行处理,就已经比较能够满足我们的业务需求)
- 多数据源多SessionFactory这样的场景,估计作为刚刚开始想象想处理在使用框架的情况下处理业务,配置多个SessionFactory,然后在Dao层中对于特定的请求,通过特定的SessionFactory即可处理实现这样的业务需求,不过这样的处理带来了很多的不便之处,所有很多情况下我们宁愿直接使用封装的JDBC编程,或者使用Mybatis处理这样的业务场景
使用AbstractRoutingDataSource 的实现类,进行灵活的切换,可以通过AOP或者手动编程设置当前的DataSource,不用修改我们编写的对于继承HibernateSupportDao的实现类的修改,这样的编写方式比较好,至于其中的实现原理,让我细细到来。我们想看看如何去应用,实现原理慢慢的说!
编写AbstractRoutingDataSource的实现类,HandlerDataSource就是提供给我们动态选择数据源的数据的信息,我们这里编写一个根据当前线程来选择数据源,然后通过AOP拦截特定的注解,设置当前的数据源信息,也可以手动的设置当前的数据源,在编程的类中。
package com.common.utils.manydatasource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
/**
* descrption: 多数据源的选择
* authohr: wangji
* date: 2017-08-21 10:32
*/
public class MultipleDataSourceToChoose extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
/**
* @desction: 根据Key获取数据源的信息,上层抽象函数的钩子
* @author: wangji
* @date: 2017/8/21
* @param:
* @return:
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return HandlerDataSource.getDataSource();
}
}
- 设置动态选择的Datasource,这里的Set方法可以留给AOP调用,或者留给我们的具体的Dao层或者Service层中手动调用,在执行SQL语句之前。
package com.common.utils.manydatasource;
/**
* descrption: 根据当前线程来选择具体的数据源
* authohr: wangji
* date: 2017-08-21 10:36
*/
public class HandlerDataSource {
private static ThreadLocal handlerThredLocal = new ThreadLocal();
/**
* @desction: 提供给AOP去设置当前的线程的数据源的信息
* @author: wangji
* @date: 2017/8/21
* @param: [datasource]
* @return: void
*/
public static void putDataSource(String datasource) {
handlerThredLocal.set(datasource);
}
/**
* @desction: 提供给AbstractRoutingDataSource的实现类,通过key选择数据源
* @author: wangji
* @date: 2017/8/21
* @param: []
* @return: java.lang.String
*/
public static String getDataSource() {
return handlerThredLocal.get();
}
/**
* @desction: 使用默认的数据源
*/
public static void clear() {
handlerThredLocal.remove();
}
}
- 设置拦截数据源的注解,可以设置在具体的类上,或者在具体的方法上,dataSource是当前数据源的一个别名用于标识我们的数据源的信息。
package com.common.utils.manydatasource;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @description: 创建拦截设置数据源的注解
* Created by wangji on 2017/8/21.
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DynamicSwitchDataSource {
String dataSource() default "";
}
- AOP拦截类的实现,通过拦截上面的注解,在其执行之前处理设置当前执行SQL的数据源的信息,HandlerDataSource.putDataSource(….),这里的数据源信息从我们设置的注解上面获取信息,如果没有设置就是用默认的数据源的信息。
package com.common.utils.manydatasource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* descrption: 使用AOP拦截特定的注解去动态的切换数据源
* authohr: wangji
* date: 2017-08-21 10:42
*/
@Aspect
@Slf4j
@Component
@Order(1)
public class HandlerDataSourceAop {
//@within在类上设置
//@annotation在方法上进行设置
@Pointcut("@within(com.common.utils.manydatasource.DynamicSwitchDataSource)||@annotation(com.common.utils.manydatasource.DynamicSwitchDataSource)")
public void pointcut() {}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint)
{
Method method = ((MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
DynamicSwitchDataSource annotationClass = method.getAnnotation(DynamicSwitchDataSource.class);//获取方法上的注解
if(annotationClass == null){
annotationClass = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getAnnotation(DynamicSwitchDataSource.class);//获取类上面的注解
if(annotationClass == null) return;
}
//获取注解上的数据源的值的信息
String dataSourceKey = annotationClass.dataSource();
if(dataSourceKey !=null){
//给当前的执行SQL的操作设置特殊的数据源的信息
HandlerDataSource.putDataSource(dataSourceKey);
}
log.info("AOP动态切换数据源,className"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName()+"methodName"+method.getName()+";dataSourceKey:"+dataSourceKey==""?"默认数据源":dataSourceKey);
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after(JoinPoint point) {
//清理掉当前设置的数据源,让默认的数据源不受影响
HandlerDataSource.clear();
}
}
- 配置数据源在Spring 核心容器中配置
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc2.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/datasource2
<bean id="dataSource0" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close" init-method="init">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="10"/>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource1" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close" init-method="init">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc2.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="10"/>
bean>- 配置之前我们实现的数据源选择的中间层AbstractRoutingDataSource的实现类,这里的key就是数据源信息的别名,通过这个key可以选择到数据源的信息。MultipleDataSourceToChoose就是上面写的数据源选择器的实现类
bean id="dataSource" class="com.common.utils.manydatasource.MultipleDataSourceToChoose" lazy-init="true">
<description>数据源description>
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String" value-type="javax.sql.DataSource">
<entry key="datasource0" value-ref="dataSource0" />
<entry key="datasource1" value-ref="dataSource1" />
map>
property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource0" />
bean>- SessionFactory的配置还是照旧,使用以前的配置,只不过当前选择的数据源是datasource,也就是数据源选择的中间层MultipleDataSourceToChoose,因为当前的中间层中实现了DataSource这个接口,所以可以看做为DataSource的是实现类啦,所以配置不会出现问题。
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialectprop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">falseprop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">falseprop>
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">updateprop>
<prop key="hibernate.autoReconnect">trueprop>
<prop key="hibernate.jdbc.batch_size">50prop>
<prop key="hibernate.connection.autocommit">falseprop>
<prop key="hibernate.connection.release_mode">after_transactionprop>
<prop key="hibernate.bytecode.use_reflection_optimizer">falseprop>
props>
property>
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>com.modulevalue>
list>
property>
bean>- 简单的使用AOP进行测试一下,这里测试的结果时不同的,所以是生效的,使用了不同的数据源,但是底层的实现没有进行任何的修改处理。
@Service
@Slf4j
public class UserInfoService implements IUserInfoService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
private CommonHibernateDao commonDao;
@TestValidateParam
public User getUserInfoById(Integer id) {
return userDao.findById(id);
}
@DynamicSwitchDataSource(dataSource = "datasource0")
public void save(User user) {
userDao.save(user);
}
@DynamicSwitchDataSource(dataSource = "datasource1")
public List findAll(){
String sql = "select u.userName as name,u.userAge as age,u.userAddress as address,u.id from user u";
List list =commonDao.findListBySQL(sql,User.class);
return list;
}
} - 也可以不适用AOP,直接在编程中实现,通过测试,结果分别为两个数据库中的信息
public void test(){
HandlerDataSource.putDataSource("datasource1");
String sql = "select u.userName as name,u.userAge as age,u.userAddress as address,u.id from user u";
List list =commonDao.findListBySQL(sql,User.class);
HandlerDataSource.putDataSource("datasource0");
commonDao.deleteById("2",User.class);
}
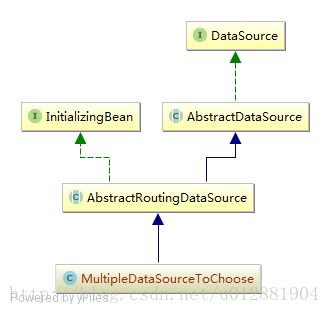
- 实现原理,MultipleDataSourceToChoose的继承结构图,之前说过他是DataSource的子类,由于无论我们是使用Mybatis还是使用Hibernate进行SQL操作的时候总会执行getConnection(),无论我们的数据源是否使用了数据库连接池,因为数据库连接池的主要作用就是保持一堆的Connection不进行关闭的处理,节省我们的关闭和打开连接的开销。http://blog.csdn.net/shuaihj/article/details/14223015/ 浅谈数据库连接池说的简单易懂。 Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;所以这句话总是要执行的,只是AbstractRoutingDataSource这个类给我们进行了一些中介的处理,在获取Connection的时候会去寻找保存的DataSource的引用,到底是选择哪个DataSource进行处理,看代码!
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.common.utils.manydatasource.MultipleDataSourceToChoose" lazy-init="true">
<description>数据源description>
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String" value-type="javax.sql.DataSource">
<entry key="datasource0" value-ref="dataSource0" />
<entry key="datasource1" value-ref="dataSource1" />
map>
property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource0" />
bean>targetDataSources,是一个Map对于数据源的引用
public void setTargetDataSources(Map targetDataSources) {
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
} 对于实现SQL的Connection getConnection() throws SQLException的实现,其实就是代理模式找到之前Map的引用,通过key,而这个key就是我们灵活配置的key,通过这个key就可以寻找到这个值。
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}这里说的非常的详细,通过钩子函数让子类去实现,寻找特定的key,然后选择DataSource 的时候就可以很灵活的使用啦!
/**
* Retrieve the current target DataSource. Determines the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key}, performs
* a lookup in the {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map,
* falls back to the specified
* {@link #setDefaultTargetDataSource default target DataSource} if necessary.
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
}这个就是模板方法模式中常见的钩子函数,在HttpServlet中也有类似的使用钩子,非常的棒,不过这个是必须实现,httpServlet不是必须实现,只是添加一些补充。由于每次执行数据库的调用,总会执行这个getConnection方法,每次都查看AOP中是否设置了当前的数据源,然后找到Map的引用的代理的数据源的Connection方法,原理没有变化的。
/**
* Determine the current lookup key. This will typically be
* implemented to check a thread-bound transaction context.
* Allows for arbitrary keys. The returned key needs
* to match the stored lookup key type, as resolved by the
* {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey} method.
*/
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();这里就是我们的实现的数据源的选择哦!
/**
* descrption: 多数据源的选择
* authohr: wangji
* date: 2017-08-21 10:32
*/
public class MultipleDataSourceToChoose extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
/**
* @desction: 根据Key获取数据源的信息,上层抽象函数的钩子
* @author: wangji
* @date: 2017/8/21
* @param:
* @return:
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return HandlerDataSource.getDataSource();
}
}- 但是这个由于有多个数据源导致我们只能管理默认的数据源的事务!
- http://blog.csdn.net/erixhao/article/details/52133153/
- https://github.com/WangJi92/mybatits-study/blob/master/mybatis-study/study-7-spring-Hibernate%20-manydatasource/src/main/java/com/common/utils/manydatasource/MultipleDataSourceToChoose.java/ 源码地址