Dealloc 实现 原理
当对象的引用计数Wie0时, 系统会调用对象的dealloc方法释放
- (void)dealloc {
_objc_rootDealloc(self);
}在内部
void
_objc_rootDealloc(id obj)
{
assert(obj);
obj->rootDealloc();
}继续调用了rootDealloc方法
显然调用顺序为:先调用当前类的dealloc,然后调用父类的dealloc,最后到了NSObject的dealloc.
inline void
objc_object::rootDealloc()
{
//判断对象是否采用了Tagged Pointer技术
if (isTaggedPointer()) return; // fixme necessary?
//判断是否能够进行快速释放
//这里使用了isa指针里的属性来进行判断.
if (fastpath(isa.nonpointer && //对象是否采用了优化的isa计数方式
!isa.weakly_referenced && //对象没有被弱引用
!isa.has_assoc && //对象没有关联对象
!isa.has_cxx_dtor && //对象没有自定义的C++析构函数
!isa.has_sidetable_rc //对象没有用到sideTable来做引用计数
))
{
//如果以上判断都符合条件,就会调用C函数 free 将对象释放
assert(!sidetable_present());
free(this);
}
else {
//如果以上判断没有通过,做下一步处理
object_dispose((id)this);
}
}内部做了一些判断, 如果满足这五个条件,直接调用free函数,进行内存释放.
当一个最简单的类(没有任何成员变量,没有任何引用的类),这五个判断条件都是成立的,直接free.
id
object_dispose(id obj)
{
if (!obj) return nil;
objc_destructInstance(obj);
free(obj);
return nil;
}调用objc_destructInstance函数来析构对象obj,再free(obj)释放内存.
objc_destructInstance内部函数会销毁C++析构函数以及移除关联对象的操作.
继续调用objc_object的clearDeallocating函数做下一步处理
objc_object::clearDeallocating()
{
if (slowpath(!isa.nonpointer)) {
// Slow path for raw pointer isa.
// 如果要释放的对象没有采用了优化过的isa引用计数
sidetable_clearDeallocating();
}
else if (slowpath(isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc)) {
// Slow path for non-pointer isa with weak refs and/or side table data.
// 如果要释放的对象采用了优化过的isa引用计数,并且有弱引用或者使用了sideTable的辅助引用计数
clearDeallocating_slow();
}
assert(!sidetable_present());
}根据是否采用了优化过的isa做引用计数分为两种:
1. 要释放的对象没有采用优化过的isa引用计数:
会调用sidetable_clearDeallocating() 函数做进一步处理
void
objc_object::sidetable_clearDeallocating()
{
// 在全局的SideTables中,以this指针(要释放的对象)为key,找到对应的SideTable
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
// clear any weak table items
// clear extra retain count and deallocating bit
// (fixme warn or abort if extra retain count == 0 ?)
table.lock();
//在散列表SideTable中找到对应的引用计数表RefcountMap,拿到要释放的对象的引用计数
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
if (it != table.refcnts.end()) {
//如果要释放的对象被弱引用了,通过weak_clear_no_lock函数将指向该对象的弱引用指针置为nil
if (it->second & SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED) {
weak_clear_no_lock(&table.weak_table, (id)this);
}
//从引用计数表中擦除该对象的引用计数
table.refcnts.erase(it);
}
table.unlock();
}2. 如果该对象采用了优化过的isa引用计数
并且该对象有弱引用或者使用了sideTable的辅助引用计数,就会调用clearDeallocating_slow()函数做进一步处理.
NEVER_INLINE void
objc_object::clearDeallocating_slow()
{
assert(isa.nonpointer && (isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc));
// 在全局的SideTables中,以this指针(要释放的对象)为key,找到对应的SideTable
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
table.lock();
if (isa.weakly_referenced) {
//要释放的对象被弱引用了,通过weak_clear_no_lock函数将指向该对象的弱引用指针置为nil
weak_clear_no_lock(&table.weak_table, (id)this);
}
//使用了sideTable的辅助引用计数,直接在SideTable中擦除该对象的引用计数
if (isa.has_sidetable_rc) {
table.refcnts.erase(this);
}
table.unlock();
}
以上两种情况都涉及weak_clear_no_lock函数, 它的作用就是将被弱引用对象的弱引用指针置为nil.
void
weak_clear_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id)
{
//获取被弱引用对象的地址
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
// 根据对象地址找到被弱引用对象referent在weak_table中对应的weak_entry_t
weak_entry_t *entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent);
if (entry == nil) {
/// XXX shouldn't happen, but does with mismatched CF/objc
//printf("XXX no entry for clear deallocating %p\n", referent);
return;
}
// zero out references
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
size_t count;
// 找出弱引用该对象的所有weak指针地址数组
if (entry->out_of_line()) {
referrers = entry->referrers;
count = TABLE_SIZE(entry);
}
else {
referrers = entry->inline_referrers;
count = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;
}
// 遍历取出每个weak指针的地址
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
objc_object **referrer = referrers[i];
if (referrer) {
// 如果weak指针确实弱引用了对象 referent,则将weak指针设置为nil
if (*referrer == referent) {
*referrer = nil;
}
// 如果所存储的weak指针没有弱引用对象 referent,这可能是由于runtime代码的逻辑错误引起的,报错
else if (*referrer) {
_objc_inform("__weak variable at %p holds %p instead of %p. "
"This is probably incorrect use of "
"objc_storeWeak() and objc_loadWeak(). "
"Break on objc_weak_error to debug.\n",
referrer, (void*)*referrer, (void*)referent);
objc_weak_error();
}
}
}
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
}这里也表明了为什么被weak修饰的对象在释放时, 所有弱引用该对象的指针都被设置为nil.
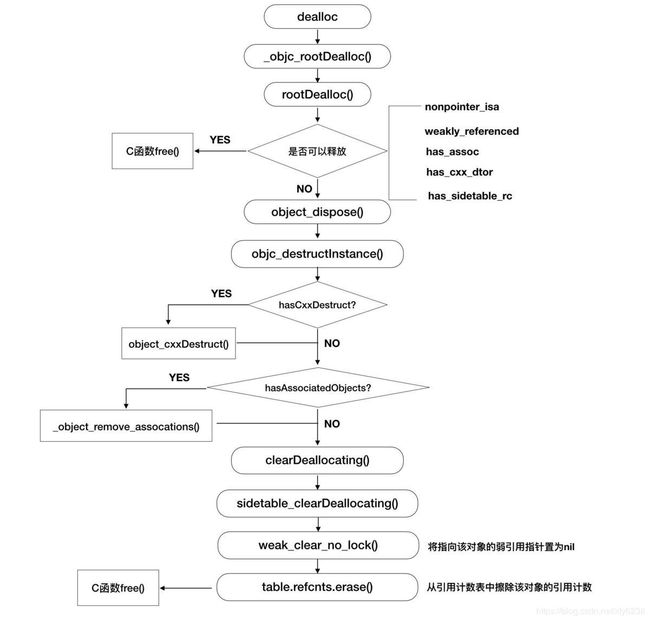
dealloc整个方法释放流程如下图:
看流程图发现,如果五个条件不满足.内存无法进行快速释放.在上面中,我看到博客里关于 objc_destructInstance 这个方法只是概述而过,所以我找了相关资料来了解一下.
void *objc_destructInstance(id obj)
{
if (obj) {
Class isa_gen = _object_getClass(obj);
class_t *isa = newcls(isa_gen);
// Read all of the flags at once for performance.
bool cxx = hasCxxStructors(isa);
bool assoc = !UseGC && _class_instancesHaveAssociatedObjects(isa_gen);
// This order is important.
if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj);
if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj);
if (!UseGC) objc_clear_deallocating(obj);
}
return obj;
}总共干了三件事::
1. 执行了object_cxxDestruct 函数
2. 执行_object_remove_assocations,去除了关联对象.(这也是为什么category添加属性时,在释放时没有必要remove)
3.就是上面写的那个,清空引用计数表并清除弱引用表,将weak指针置为nil
object_cxxDestruct是由编译器生成,这个方法原本是为了++对象析构,ARC借用了这个方法插入代码实现了自动内存释放的工作.
这个释放.
现象:
1. 当类拥有实例变量时,这个方法会出现,且父类的实例变量不会导致子类拥有这个方法.
2. 出现这个方法和变量是否被赋值,赋值成什么没有关系.
根据博客内容总结, 我们可以认为这个方法就是用来释放该类中的属性的. weak修饰的属性应该不包含在内.
参考资料:
Dealloc实现原理
https://www.cnblogs.com/wfwenchao/p/4569079.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u012413955/article/details/89979562
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0abad3b06600