Java-利用Spring提供的Resource/ResourceLoader接口操作资源文件
- 背景
- 资源访问接口
- 主要方法
- 主要实现类
- 例子
- WritableResource ClassPathResource
- ServletContextResource
- 对资源文件编码
- 资源加载
- 资源地址表达式
- Spring支持的资源类型的地址前缀
- 注意事项 classpath 和 classpath
- Ant风格的资源地址
- 资源加载器
- 介绍
- 示例
- 资源地址表达式
- 注意事项
背景
JDK提供的访问资源的类(如java.net.URL、File等)并不能很好地满足各种底层资源的访问需求,比如缺少从类路径或者Web容器上下文中获取资源的操作类。
Spring提供了Resource接口,为应用提供了更强的底层资源访问能力,该接口拥有对应不同资源类型的实现类。
资源访问接口
主要方法
- boolean exists() 资源是否存在
- boolean isOpen() 资源是否打开
- URL getURL() throws IOException 如果底层资源可以表示成URL,则该方法放回对应的URL对象
- File getFile() throws IOException 如果底层资源对应一个文件,这返回对应的File对象
Spring框架使用Resource装载各种资源,包括配置文件资源、国际化属性文件资源等。
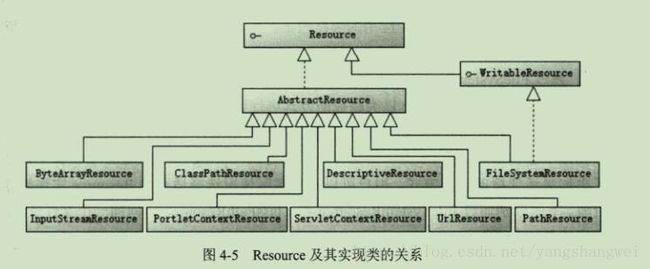
主要实现类
- WritableResource : 可写资源接口,Spring3.1新增的接口,有2个实现类: FileSystemResource和PathResource。 其中PathResource是Spring4.0提供的实现类
- ByteArrayResource:二进制数组表示的资源,二进制数组资源可以在内存中通过程序构造。
- ClassPathResource:类路径下的资源,资源以相对于类路径的方式表示,一般是以相对于根路径的方式
- FileSystemResouce:文件系统资源,资源以文件系统路径的方式表示
- InputStreamResource:以输入流返回标识的资源
- ServletContextResource:为访问Web容器上下文中的资源而设计的类,负责以相对于Web应用根目录的路径来加载资源。支持以流和URL的访问能行事,在war包解包的情况下,也可以通过File方式访问。 该类还可以直接从JAR包中访问资源。
- UrlResource:封装了java.net.URL,它使用户能够访问任何可以通过URL表示的资源,如文件系统的资源,HTTP资源,FTP资源
- PathResource : Spring4.0提供的读取资源文件的新类。Ptah封装了java.net.URL、java.nio.file.Path(Java 7.0提供)、文件系统资源,它四用户能够访问任何可以通过URL、Path、系统文件路径标识的资源,如文件系统的资源,HTTP资源,FTP资源
有了这个抽象的资源类后,就可以将Spring配置文件放在任何地方(如数据库、LDAP中),只要最终通过Resource接口返回配置信息即可。
Spring的Resource接口及其实现类可以在脱离Spring框架的情况下适用,比JDK更方便更强大.
例子
假设一个Web应用下有一个文件,用户可以通过以下几种方式对这个资源文件进行访问:
- 通过FileSystemResource以文件绝对路径的方式进行访问
- 通过ClassPathResource以类路径的方式进行访问
- 通过ServletContextResource以相对Web应用根目录的方式进行访问
WritableResource / ClassPathResource
package com.xgj.service;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.PathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.WritableResource;
/**
*
* @ClassName: ResourceLoadTest
* @Description: 跟这个模块无关,仅仅是为了测试 Resource接口操作文件
* @author: Mr.Yang
* @date: 2017年7月7日 下午11:38:19
*/
public class ResourceLoadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String filePath = "D:/workspace/workspace-jee/HelloSpring/hello-spring4/src/test/resources/resourcefiletest.txt";
// (1)使用系统文件路径加载文件
WritableResource res = new FileSystemResource(filePath);
// PathResource @since 4.0
//WritableResource res = new PathResource(filePath);
System.out.println(res.getFilename());
// (2)使用类路径方式加载spring-context.xml文件
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("spring-context.xml");
System.out.println(classPathResource.getFilename());
// (3)使用WritableResource接口写资源文件
OutputStream os = res.getOutputStream();
os.write("小工匠的使用Resource接口测试".getBytes());
os.close();
// (4)使用Resource接口读取资源文件
InputStream ins = res.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int i;
while ((i = ins.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(i);
}
System.out.println("读取的文件:" + res.getFilename() + ",内容:" + bos.toString());
// 读取spring-context.xml的内容
InputStream ins2 = classPathResource.getInputStream();
int j;
while ((j = ins2.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(j);
}
//System.out.println("读取的文件:" + classPathResource.getFilename() + ",内容:" + bos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出:
resourcefiletest.txt
spring-context.xml
读取的文件:resourcefiletest.txt,内容:小工匠的使用Resource接口测试
ServletContextResource
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<jsp:directive.page
import="org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletContextResource" />
<jsp:directive.page import="org.springframework.core.io.Resource" />
<jsp:directive.page import="org.springframework.web.util.WebUtils" />
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>ResourceTest,nothing to do with this moduletitle>
head>
<body>
<%
Resource res3 = new ServletContextResource(application, "/WEB-INF/classes/spring-context.xml");
out.print(res3.getFilename() + "
");
out.print(WebUtils.getTempDir(application).getAbsolutePath());
%>
body>
html>运行:
对资源文件编码
// (2)使用类路径方式加载spring-context.xml文件
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("spring-context.xml");
System.out.println(classPathResource.getFilename());
// 以UTF-8编码
EncodedResource ens = new EncodedResource(classPathResource ,"UTF-8");
String content = FileCopyUtils.copyToString(ens.getReader());
System.out.println("编码后的内容:\n" +content);资源加载
通过上面的例子,是不是发现 ,为了访问不同类型的资源,必须使用相应的Resource实现类。
是否可以在不显式使用Resource实现类的情况下,仅仅通过资源地址的特殊标示符就可以访问相应的资源? 答案是肯定的,Spring提供了一个强大的加载资源的方式,不仅能通过“classpath:”、“file:”等资源地址前缀识别不同的资源类型,还支持Ant风格带通配符的资源地址。
资源地址表达式
Spring支持的资源类型的地址前缀
| 地址前缀 | 实例 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/xgj/beans.xml | 从类不经中加载资源,classpath: 和 classpath:/ 是等价的,都是相对于类的根路径,资源文件可以在标准的文件系统中,也可以在jar或者zip的类包中 |
| file: | file:/conf/com/xgj/beans.xml | 使用UrlResource从文件系统目录中装载资源,可以采用绝对路径或者相对路径 |
| http:// | http://www.xgj.com/resource/beans.xml | 使用UrlResource从web服务器中加载资源 |
| ftp:// | ftp://www.xgj.com/resource/beans.xml | 使用UrlResource从FTP服务器中装载资源 |
| 没有前缀 | com/xgj/beans.xml | 根据ApplicationContext的具体实现类采用对应类型的Resource |
注意事项 classpath: 和 classpath*:
举个例子: 假设有多个Jar包或者文件系统类路径下拥有一个相同包名(com.xgj)
- classpath: 只会加载第一个加载的com.xgj包的类路径下查找
- classpath*: 会扫描到所有的这些jar包及类路径下出下的com.xgj类路径。
使用场景:
一般情况下,我们的应用都是有各个模块组成的,对于分模块打包的应用,假设我们有一个应用,分为N个模块,一个模块对应一个配置文件,分别为module1.xml 、module2xml、module3.xml….等,都放在了com.xgj的目录下,每个模块单独打成jar包。
我们可以使用 classpath*:com/xgj/module*.xml加载所有模块的配置文件。
如果使用classpath:com/xgj/module*.xml 只会加载一个模块的配置文件
Ant风格的资源地址
Ant风格的资源地址支持三种匹配符
?匹配文件名中的一个字符*匹配文件名中的任意字符**匹配多层路径
示例:
classpath:com/t?st.xml 匹配com类路径下的 com/test.xml com/tast.xml等
file:D:/conf/*.xml匹配文件系统D:/conf/目录下所有以.xml为后缀的文件
classpath:com/**/test.xml匹配com类路径下(当前目录及子孙目录)的test.xml
classpath:org/springframework/**/*.xml匹配类路径org/springframework/下是有的以.xml为后缀的文件
classpath:org/**/servlet/bla.xml 匹配类路径org任意层级的 /servlet/bla.xml的文件
资源加载器
介绍
Spring定义了一套资源加载的接口,并提供了实现类
ResourceLoader中的方法Resource getResource(String location);
可以根据一个资源地址加载文件资源, 不过ResourceLoader这个接口方法中的资源地址仅支持带资源类型前缀的表达式,不支持Ant风格的资源路径表达式。
不过 ResourcePatternResolver 扩展了 ResourceLoader接口,
ResourcePatternResolver 的getResource方法支持带资源类型前缀以及Ant风格的资源路径表达式。
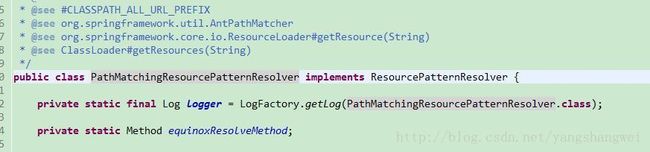
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是Spring提供的标准实现类。
示例
package com.xgj.service;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: ResourceLoaderTest
*
* @Description: 跟这个模块无关,仅仅是为了测试 ResourceLoa接口操作文件
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2017年7月9日 下午7:51:37
*/
public abstract class ResourceLoaderTest {
static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ResourceLoaderTest.class);
static ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
readFromClasspath();
readFromHttp();
readFromFile();
readFromFTP();
readFromNoPreFix();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: readFromClasspath
*
* @Description: 读取 classpath: 地址前缀的文件
*
* @throws IOException
*
* @return: void
*/
public static void readFromClasspath() throws IOException {
Resource[] resources = resourcePatternResolver.getResources("classpath*:com/xgj/conf/**/*.xml");
for (Resource resource : resources) {
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
readContent(resource);
}
}
public static void readFromNoPreFix() throws IOException {
Resource resource = resourcePatternResolver.getResource("spring-context.xml");
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
readContent(resource);
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: readFromFile
*
* @Description: 使用UrlResource从文件系统目录中装载资源,可以采用绝对路径或者相对路径
*
* @throws IOException
*
* @return: void
*/
public static void readFromFile() throws IOException {
Resource resource = resourcePatternResolver.getResource(
"file:/D:/workspace/workspace-jee/HelloSpring/hello-spring4/src/main/java/com/xgj/conf/conf2/test2.xml");
readContent(resource);
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: readFromHttp
*
* @Description: 使用UrlResource从web服务器中加载资源
*
* @throws IOException
*
* @return: void
*/
public static void readFromHttp() throws IOException {
Resource resource = resourcePatternResolver.getResource("http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello-spring4/index.jsp");
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
readContent(resource);
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: readFromFTP
*
* @Description: 这里只演示写法,因为这个服务器要求用户名和密码,其实是无法读取的。
*
* @throws IOException
*
* @return: void
*/
public static void readFromFTP() throws IOException {
Resource resource = resourcePatternResolver
.getResource("ftp://172.25.243.81/webserver/config/logback.xml");
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: readContent
*
* @Description: 读取获取到的资源文件的内容
*
* @param resource
* @throws IOException
*
* @return: void
*/
public static void readContent(Resource resource) throws IOException {
InputStream ins = resource.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int i;
while ((i = ins.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(i);
}
logger.debug("读取的文件:" + resource.getFilename() + ",/n内容:/n" + bos.toString());
}
}
注意事项
使用Resource操作文件时,如果资源的配置文件在项目发布的时候会打包到jar中,那么就不能使用Resource.getFile()方法,否则会抛出FileNotFoundException异常。
推荐使用 Resource.getInputStream()读取。
错误的方式
(new DefaultResourceLoader()).getResource("classpath:conf/sys.properties").getFile();正确的方式
(new DefaultResourceLoader()).getResource("classpath:conf/sys.properties").getInputStream();建议尽量使用流的方式读取,避免环境不同造成问题