SVM
文章目录
- 对偶问题和KKT条件
- 拉格朗日对偶问题
- 弱强对偶
- 互补松弛定理
- KKT
- 互补松弛
- kernel extension
- Key Ideas of Kernel Methods
- Basis Functions
对偶问题和KKT条件
标准形式
M i n f 0 ( x ) Min\qquad f_0(x) Minf0(x)
s . t . f i ( x ) ≤ 0 i = 1 , . . . , m s.t.\qquad f_i(x) \le 0 \quad i=1,...,m s.t.fi(x)≤0i=1,...,m
h i ( x ) = 0 i = 1 , . . . , p \qquad h_i(x)=0 \quad i=1,...,p hi(x)=0i=1,...,p
其中 x ∈ R n x \in R^n x∈Rn,定义域 D D D,最优值 p ∗ p^* p∗
拉格朗日: L : R n × R m × R p → R L:R^n \times R^m \times R^p \rightarrow R L:Rn×Rm×Rp→R
d o m ( L ) = D × R m × R p dom(L)=D \times R^m \times R^p dom(L)=D×Rm×Rp
L ( x , λ , ν ) = f 0 ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 m λ i f i ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 p ν i h i ( x ) L(x,\lambda,\nu)= f_0(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m}\lambda_if_i(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p}\nu_ih_i(x) L(x,λ,ν)=f0(x)+i=1∑mλifi(x)+i=1∑pνihi(x)

拉格朗日对偶函数:
g ( λ , ν ) = inf x ∈ D L ( x , λ , ν ) g(\lambda,\nu)=\inf \limits_{x \in D}L(x,\lambda,\nu) g(λ,ν)=x∈DinfL(x,λ,ν)
inf x ∈ D ( f 0 ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 m λ i f i ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 p ν i h i ( x ) ) \inf \limits_{x \in D}(f_0(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m}\lambda_if_i(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p}\nu_ih_i(x)) x∈Dinf(f0(x)+i=1∑mλifi(x)+i=1∑pνihi(x))
- g g g 凹 ,可能 负无穷 for some λ , ν \lambda,\nu λ,ν
- lower bound property:if λ ≥ 0 , \lambda \ge 0, λ≥0,就 g ( λ , ν ) ≤ p ∗ g(\lambda,\nu) \le p^* g(λ,ν)≤p∗
第二个为什么成立呢?
假设 D 子 集 D子集 D子集就是满足s.t.条件的 x x x集合,那么
p ∗ = inf D 子 集 f 0 ( x ) = p^*=\inf\limits_{D子集}f_0(x)= p∗=D子集inff0(x)=
inf D 子 集 f 0 ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 p ν i h i ( x ) ) ≥ \inf\limits_{D子集}f_0(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p}\nu_ih_i(x)) \ge D子集inff0(x)+i=1∑pνihi(x))≥
inf x ∈ D 子 集 ( f 0 ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 m λ i f i ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 p ν i h i ( x ) ) ≥ \inf \limits_{x \in D子集}(f_0(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m}\lambda_if_i(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p}\nu_ih_i(x)) \ge x∈D子集inf(f0(x)+i=1∑mλifi(x)+i=1∑pνihi(x))≥
inf x ∈ D ( f 0 ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 m λ i f i ( x ) + ∑ i = 1 p ν i h i ( x ) ) \inf \limits_{x \in D}(f_0(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{m}\lambda_if_i(x)+\sum_{i=1}^{p}\nu_ih_i(x)) x∈Dinf(f0(x)+i=1∑mλifi(x)+i=1∑pνihi(x))
= g ( λ , ν ) =g(\lambda,\nu) =g(λ,ν)
\
拉格朗日对偶问题
m a x g ( λ , ν ) max \qquad g(\lambda,\nu) maxg(λ,ν)
s . t . λ ≥ 0 s.t. \qquad \lambda \ge 0 s.t.λ≥0
- find best lower bound on p ∗ p^* p∗,ontained from 拉格朗日对偶函数
- a concave optimization problem with optimal value denoted as d ∗ d^* d∗

弱强对偶
- 弱: d ∗ ≤ p ∗ d^* \le p^* d∗≤p∗
-总是成立
可以用来去找困难问题的非平凡下界 - d ∗ = p ∗ d^*=p^* d∗=p∗
-一般并不成立
通常对于凸问题成立
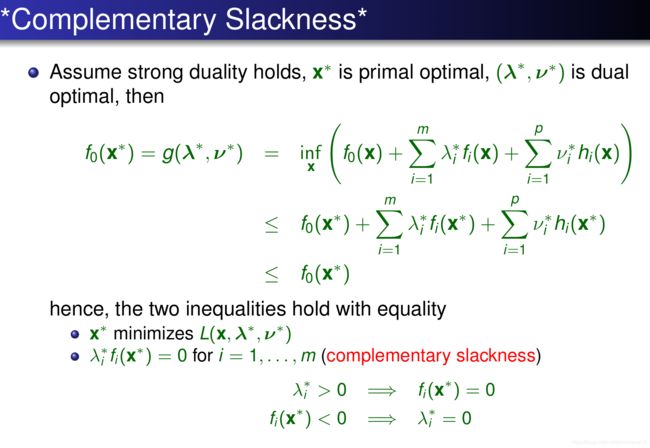
互补松弛定理
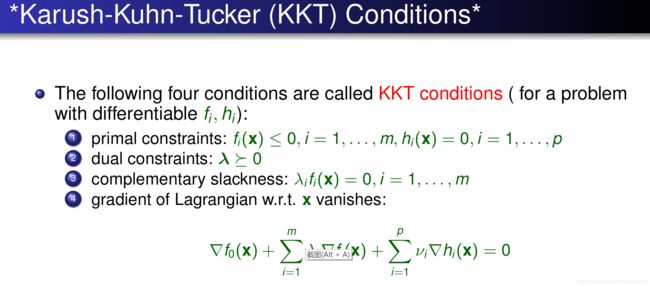
KKT
互补松弛
kernel extension
Key Ideas of Kernel Methods
- Instead of defining a nonlinear model in the original (input) space,
- the problem is mapped to a new (feature) space by performing a nonlinear transformation using suitably chosen basis functions.
- 基本函数不是核函数哦
- the problem is mapped to a new (feature) space by performing a nonlinear transformation using suitably chosen basis functions.
- A linear model is then applied in the new space.
- 新空间用线性SVM吧
- The basis functions are often defined implicitly via defining kernel functions directly.
- 先定义核函数,隐式的定义了基本函数
Basis Functions
- 基本函数
- z = ϕ ( x ) z=\phi(x) z=ϕ(x)
- 其中 z j = ϕ j ( x ) z_j=\phi_j(x) zj=ϕj(x), j = 1 , 2 , . . . , M j=1,2,...,M j=1,2,...,M
- M M M应该是维度吧
- 意思就是我z的每个分量是这样定的哦
- 判别函数
- g ( z ) = w T z g(z)=w^Tz g(z)=wTz
- g ( z ) = w T ϕ ( x ) = ∑ j = 1 M w j ϕ j ( x ) g(z)=w^T\phi(x)=\sum\limits_{j=1}^{M}w_j\phi_j(x) g(z)=wTϕ(x)=j=1∑Mwjϕj(x)