SpringBoot集成WebSocket发送 文本 对象 集合
WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议。可实现由服务端主动推送消息至客户端,使之持续链接的一种双向通信协议
实现WebSocket主动推送的需求一般在用户实时聊天,音视频通话等IM项目
第一步: 先引入坐标
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-websocket
第二步: 编写WebSocket映射类 注意包结构
package com.rf.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig{
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter()
{
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
第三步: 编写WebSocket服务端链接路由
package com.rf.component;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.rf.domain.dto.WebSocketParam;
import com.rf.utils.WebSocketDecoder;
import com.rf.utils.WebSocketEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.websocket.OnClose;
import javax.websocket.OnMessage;
import javax.websocket.OnOpen;
import javax.websocket.Session;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
@Component
//此注解相当于你得服务端路径 IP+端口+/web/websocket/{phone} 序列化与反序列化,后面代码我会贴出
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/web/websocket/{phone}" , decoders = { WebSocketDecoder.class }, encoders = { WebSocketEncoder.class })
public class WebSocket {
private Session session;
private static CopyOnWriteArraySet webSockets =new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
private static Map sessionPool = new HashMap();
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam(value="phone")String phone) {
this.session = session;
webSockets.add(this);
//将对象保存到session,以Map的形式
sessionPool.put(phone, session);
System.out.println("【websocket消息】有新的连接 当前连接总数为:"+webSockets.size());
}
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
webSockets.remove(this);
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message) throws IOException {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
}
// 此为广播消息
public void sendAllMessage(String message) {
for(WebSocket webSocket : webSockets) {
try {
webSocket.session.getAsyncRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public int sendTextMessage(String phone, String message) {
//get 的是个Map 的key
Session session = sessionPool.get(phone);
if (session != null) {
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 500;
}
}else{
return 500;
}
return 200;
}
//这是我的一个实体类 如果你向前台发送的是一个实体类,则需要序列化
public int sendTextMessage(WebSocketParam param) throws IOException {
Session session = sessionPool.get(param.getRecPhone());
if(session != null){
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(param));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 500;
}
}else{
return 500;
}
return 200;
}
// 此为单点消息 (发送对象)
public int sendObjMessage(String phone, Object param) {
Session session = sessionPool.get(phone);
if (session != null) {
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendObject(param);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 500;
}
}else{
return 500;
}
return 200;
}
}
在此介绍一下websocket的注解
@OnOpen: 当链接成功之后所需要进行的操作
@OnClose: 关闭链接后可能进行的某些操作
@OnMessage: 这是接受客户端或其他发送来的文本消息 可以有多个 该注解可以重载 不同参数对应不同类型
@OnError: 当发生错误时需要进行操作或有可能的操作
此类中我引用了Hutool的工具包
cn.hutool
hutool-all
4.5.7
@ServerEndpoint(value = “/web/websocket/{phone}” , decoders = { WebSocketDecoder.class }, encoders = { WebSocketEncoder.class })
该注解内的参数可提供发送对象的功能,分别是将对象序列化与反序列化
首先: 需要序列化的实体类
package com.rf.domain.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Getter
@Setter
//抑制序列化成Json后控制台报错
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"hibernateLazyInitializer","handler"})
public class WebSocketParam implements Serializable {
private Long type;
private String content;
private String recPhone;
private String sendPhone;
}
我用了lombok插件 也可以用原始的Get 和 Set 方法
工具类:
package com.rf.utils;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.rf.domain.dto.WebSocketParam;
import javax.websocket.DecodeException;
import javax.websocket.EndpointConfig;
public class WebSocketDecoder implements javax.websocket.Decoder.Text {
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
@Override
public void init(EndpointConfig arg0) {
}
@Override
public WebSocketParam decode(String user) throws DecodeException {
return JSON.parseObject(user, WebSocketParam.class);
}
@Override
public boolean willDecode(String arg0) {
return true;
}
}
package com.rf.utils;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.rf.domain.dto.WebSocketParam;
import javax.websocket.EncodeException;
import javax.websocket.EndpointConfig;
public class WebSocketEncoder implements javax.websocket.Encoder.Text {
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
@Override
public void init(EndpointConfig arg0) {
}
@Override
public String encode(WebSocketParam param) throws EncodeException {
return JSON.toJSONString(param);
}
}
工具类的Json包引用的是 阿里的Json工具包
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.6
此时我们可以写一个接口来模拟一下双方通信
@ApiOperation(value = "测试给另一个对象发送Text消息")
@PostMapping(value = "/sendTextMessage")
public CommonResult sendTextMessage(String phone ,String message){
webSocket.sendTextMessage(phone,message);
return CommonResult.success(message);
}
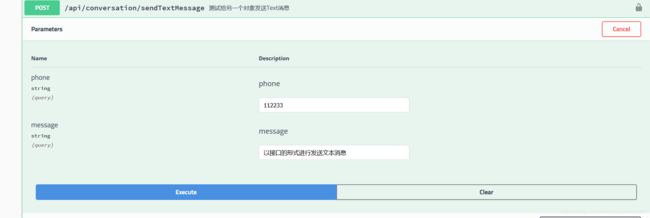
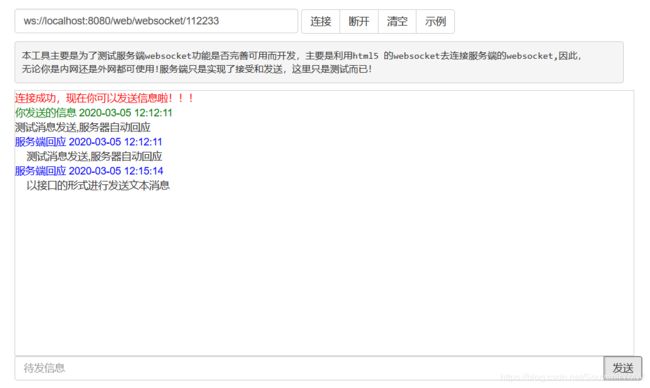
那么既然可以发送文本消息,已经将对象序列化了,测试一下发送一个序列化之后的对象
@ApiOperation(value = "发送对象")
@PostMapping(value = "/sendObjMessage")
public CommonResult sendObjMessage(String sendPhone, String recPhone ,String content,Long type) throws IOException {
WebSocketParam param = new WebSocketParam();
param.setSendPhone(sendPhone);
param.setContent(content);
param.setType(type);
//接收者手机号/Id
param.setRecPhone(recPhone);
webSocket.sendTextMessage(param);
return CommonResult.success(param);
}
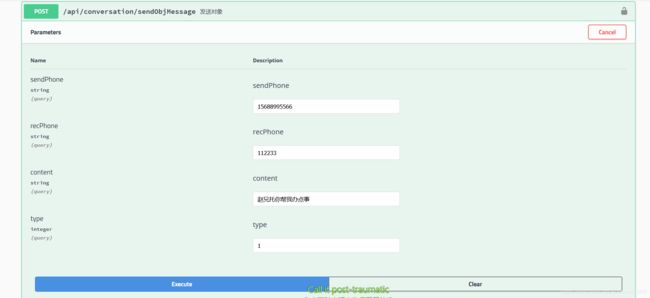
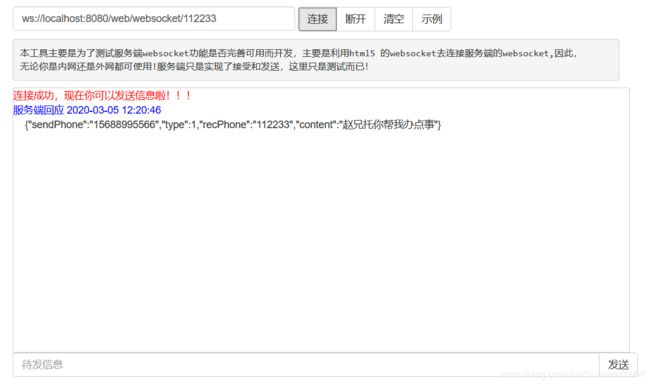 在此客户端收到的是String类型,可以以逗号分割成数组,也可以使用Json反序列,
在此客户端收到的是String类型,可以以逗号分割成数组,也可以使用Json反序列,
服务端只需要使用工具类中的encode进行反向序列化便得到一个对象!

