Math、Data、Calendar、异常及其处理、IO流及其处理(JAVA小白进阶day11)
Math
final型
不能实例化,构造方法私有,
静态方法,可直接Math.方法名()
ceil()返回>=参数的最小整数值,转化为都double型
floor()返回<=参数的最大整数值,转化为都double型
random()输出大于等于0小于1(0<=x<1)的double类型的数
round())四舍五入为整数
Random类产生随机数:
Random random =new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(10);//[0,10)即0-9,1-10写为[0,10)+1
System.out.println(i);
Date
public static void test1() throws ParseException {
System.out.println(new Date());
//日期和字符串的转化
SimpleDateFormat sd = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sd.format(new Date()));
//按照sd设置的格式把字符串类型的日期转换为Date类型
String strDate = "2020年07月29日 10:34:59";
System.out.println(sd.parse(strDate));
}
Calendar
public static void test2() {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)+"-"
+(c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1+"-"
+c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)));
System.out.println(c.getTime());
}
异常
1、Throwable
Error:不能处理的XXXError
Exception:能处理的 xxxException
RunTimeException:运行时异常
NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOfBoundsException
StringIndexOfBoundsException

编译时异常
IOException,FileNotFoundException
InterruptedException,SQLException等

2、运行时异常不强制处理,如果代码写的严谨,可以避免运行时异常的产生
编译时异常必须处理
3、异常处理的两种方式
throws 抛出异常(声明异常)
try-catch块捕获异常:e.printStackTrace()//打印堆栈信息
//信息之间只差Exception in thread “main”
异常代码块:在日志文件里保存堆栈信息
外行,翻译异常信息
检查代码,直接打印堆栈信息
4、异常块的正确使用方式
try-catch
try-catch-finallly
try-catch-catch…finally
try-finally//语法正确,但不能捕获异常
//可多个catch块,不可多个try,每个try必须跟至少一个catch/finally
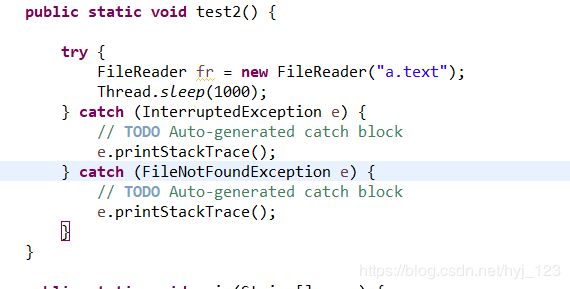

5、try-catch可以嵌套使用
6、执行过程
如果try中有异常,从异常语句开始不再执行后面语句
跳到catch执行
不管有无异常,finally都执行
public static int test6() {
try {
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return 2;
}finally {
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(test6());
}
//先输出结果,后返回函数值返回值,结果输出end,1
public static int test6() {
int i = 0;
try {
return i++;//当前 i = 0;后++
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return 2;
}finally {
i++;当前 i = 1;后++
System.out.println(i);当前 i = 2
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(test6());
}
//顺序执行,返回0,输出结果为2 end 0
public static int test6() {
int i = 0;
try {
return i++;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return 0;
}finally {
i++;
System.out.println("end");
return i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(test6());
}
//必须走finally,finally的返回值会覆盖之前所有的,输出结果end 2
♥finally 会覆盖/屏蔽异常
7、自定义异常类:继承现有异常
public interface Message{
String ageMessage
}
public static AgeException extends Exception{
public AgeException(){
//调用父类带参的构造函数,初始化错误信息
super(“请输入正确范围的年龄(1-150)”);
}
}
使用自定义的异常
throws new AgeException();//抛出异常
8、方法的重写
子类异常<=父类异常(运行时异常与编译时异常没有关系)
个数,继承关系
9、throw与throws的区别
throw throws
抛出异常 声明异常
在方法内 方法声明
+异常类对象 +异常类类型
后只能有一个异常类的对象 可跟多个异常类型,用","隔开
小结: 1、异常的继承关系 2、Exception 编译时异常/运行时异常 3、处理异常:throws/try…catch 4、try-catch多种语法格式 5、自定义异常 extends XXXException super(异常信息);
用:if(){throw 异常类对象} 6、方法重写的异常(编译时异常)
IO流
File类:创建对象时,不能创建文件夹和文件,只能描述文件的行为
File file = new File("d:\\a\\b\\a.txt");
File file2 = new File("d:\\a\\b","a.txt");
File path = new File("d:\\a\\b");
File file3 = new File(path,"a.txt");
文件夹的创建和删除
//单个文件夹文件夹的创建与删除
public static void test2() {
File file = new File("c:\\a");
if (!file.exists()) {
boolean b = file.mkdir();
System.out.println("创建"+b);
}else {
boolean b = file.delete();
System.out.println("删除"+b);
}
}
//创建多层文件夹mkdirs(),不可删除多个
public static void test21() {
File file = new File("c:\\a\\b\\c");
if (!file.exists()) {
boolean b = file.mkdirs();
System.out.println("创建"+b);
}else {
boolean b = file.delete();
System.out.println("删除"+b);
}
}
复习 1、String构造函数 2、String常用方法 3、matches,split,replaceAll可以使用正则表达式
4、正则表达式: [a-zA-Z0-9] [^abc] [0-9]<==> \d .一个任意字符 \.表示. [0-9]{6}
[0-9]{6,} [0-9]{6,8} [a-z]? [a-z]* [a-z]+
5、若字符串经常变化用StringBulider或StringBuffer StringBulider API 6、8种基本数据类型的封装类
byte short long float double boolean->第一个字母大写 int->Integer char->
Charater封箱 int ->Integer Intrger.valueOf() 拆箱 Integer ->int intValue
equals() ==hashCode() toString()


