OnlineJudge项目简介
项目简介
仿照 leetcode 来写一个在线判题系统的项目。用户可以实现通过url在浏览器访问试题列表、选中相关题目并编写代码、提交到服务器编译运行、将运行结果反馈给浏览器展示在页面上等相应操作
开发环境
- CentOS7
- g++7.3.0(升级办法,详见Linux下gcc/g++升级-CSDN)
- jsoncpp (Json格式解析库)
- cpp-httplib (轻量级HTTP/HTTPS C++客户端服务器框架)
- ctemplate (网页模板类库)
项目源码
详见GitHub:OnlineJudge
项目设计思路
将本项目设计为四个模块,分别为:服务器模块、试题管理模块、编译运行模块 和 工具类
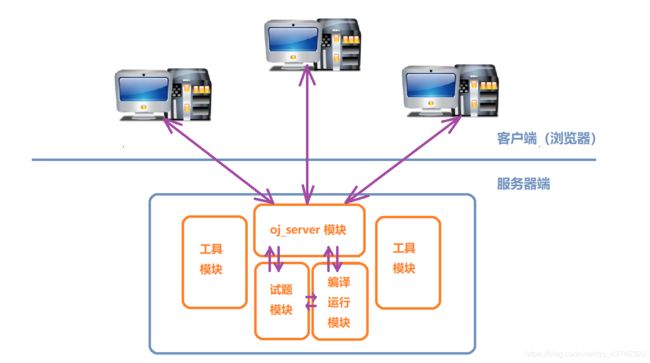
将需求进行细分,如下:
- 在浏览器中展示题目(oj_server,试题模块)
- 用户选择题目、编写代码并提交后台(oj_server,试题模块)
- 解析、合并代码并编译(编译运行模块)
- 后台执行编译出来的可执行程序(编译运行模块)
- 对编译、执行结果进行打包(编译运行模块)
- 将结果返回给浏览器客户端(oj_server)
一、服务器模块oj_server(Controller层)
作用:提供HTTP服务,串连试题模块和编译运行模块
步骤:
- 提交题目列表
- 提交题目描述和题目代码框架
- 提交代码执行结果
API和核心逻辑框架
服务器模块这边使用现有的 cpp-httplib 库进行搭建,并执行这一模块相关的逻辑:
// oj_server
#include "httplib.h"
int main()
{
using namespace httplib;
Server server;
OJ_Model oj_model;
server.Get("/all_questions", [&oj_model](const Request& req, Response& resp) {
// 提交题目列表
});
// 正则表达式:\b:单词的分界 *:匹配任意字符串 \d:匹配一个数字 ():分组应用
// 源码转义:特殊字符就按照字符字面源码来编译 形如:R"(string)"
server.Get(R"(/question/(\d+))", [&oj_model](const Request& req, Response& resp) {
// 提交题目描述和题目代码框架
});
server.Post(R"(/question/(\d+))", [&oj_model](const Request& req, Response& resp) {
// 提交代码执行结果
});
LOG(INFO, "Listen in 0.0.0.0:9094") << std::endl;
LOG(INFO, "Server ready!") << std::endl;
server.listen("0.0.0.0", 9094);
return 0;
}
具体实现
oj_server中 提交题目列表接口 完整代码如下:
// oj_server.cpp
server.Get("/all_questions", [&oj_model](const Request& req, Response& resp) {
(void)req;
std::vector<Question> ques;
oj_model.GetAllQuestions(&ques);
// 使用模板技术填充 html 页面,用以替代上述固定方法填充, 如下:
std::string html;
OJ_View::RenderAllQuestionsHTML(&html, ques);
// LOG(INFO, html);
resp.set_content(html, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
});
oj_view 中利用 ctemplate 模板库渲染题目页表的页面代码如下:
// 渲染 HTML 页面,并将该页面返回给调用者
static void RenderAllQuestionsHTML(std::string* html, std::vector<Question>& question)
{
// 1 获取数据字典-->将拿到的试题数据按照一定顺序保存在内存当中
ctemplate::TemplateDictionary dict("all_questions");
for(const auto& e : question)
{
ctemplate::TemplateDictionary* section_dict = dict.AddSectionDictionary("question");
section_dict->SetValue("id", e._id);
section_dict->SetValue("name", e._name);
section_dict->SetValue("difficulty", e._difficulty);
}
// 2 获取模板类指针,加载预定义的 HTML 页面到内存当中去
ctemplate::Template* temp_pointer = ctemplate::Template::GetTemplate("./WebPageTemplate/all_questions.html", ctemplate::DO_NOT_STRIP);
// 3 渲染:用模板类的指针,将数据字典中的数据更新到 HTML 页面的内存中去
temp_pointer->Expand(html, &dict);
}
./WebPageTemplate/all_questions.html 中代码如下(简陋版,只实现功能)
<html>
<head>
<title>Online Judgetitle>
head>
<body>
{{#question}}
<div>
<a href="/question/{{id}}"><h2>{{id}}.{{name}} {{difficulty}}h2>a>
div>
{{/question}}
body>
html>
二、试题模块
步骤:
- 从配置文件中加载题目
- 配置文件格式,约定在配置文件中对题目的描述(题目编号、题目名称、题目路径、难度)
- 加载题目配置文件,使用数据结构 (unordered_map) 保存加载出来的题目介绍信息
- 针对每道题目而言,根据路径加载数据文件:
- desc.txt:题目描述
- header.cpp:代码头文件及框架
- tail.cpp:测试文件
- 获取全部题目接口:提供给 oj_server 一个可以获取所有试题信息的接口,用以在界面上进行展示
- 获取单个题目接口:提供给 oj_server 一个可以获取单个试题信息的接口,用以在界面上进行展示
试题管理方式
-
每一个试题对应一个目录(放在 oj_data 下, 例如 oj_data/1/)
-
目录中包含了三个文件
- header.cpp: .cpp 文件的上半部分, 主要是头文件包含 + 代码模板 + 用户要实现的代码主体
- tail.cpp: .cpp 文件的末尾, 包含了测试用例代码和测试用例的执行过程(用例如何组织, 以及通过/失败的输出日志需要满足一定的约定)
- desc.txt: 题目要求的详细描述.
-
有一个总的配置文件(oj_config.cfg), 是一个 行文本文件, 记录了每个题目的id, 标题, 路径, 难度信息(字段之间用 \t 分割)
-
该文件需要实现一个 OjModel 类, 提供以下接口:
- 获取所有题目列表
- 获取某个题目的题面信息(也就是只包含 oj1.header部分的信息)
- 获取某个题目的完整信息(也就是 header + tail 拼接成的完整 cpp)
-
tail.cpp 文件编写约定:
- 每个用例是一个函数, 函数构造输入并获取校验输出.
- 每个用例从标准输出输出一行日志
- 如果用例通过, 统一打印 [TestName] ok!
- 如果用例不通过, 统一打印 [TestName] failed! 并且给出合适的提示.
这样风格来设计, 可能对后期的多语言扩展不利. 但是不用引入额外的标准输入输出的配置文件,
实现风格更简洁好理解.
API及核心代码设计(Model 层)
// 试题信息描述
typedef struct TestQuestionDescription
{
std::string _id;
std::string _name;
std::string _path; // 保存路径
std::string _difficulty; // 难易程度
}Question;
class OJ_Model
{
public:
OJ_Model()
{
LoadAllQuestions("./config.cfg");
}
// 加载 unordered_map 中的所有试题,用以展示在页面中
bool GetAllQuestions(std::vector<Question>* question)
{
for(const auto& kv : QuesMap_)
{
question->push_back(kv.second);
}
std::sort(question->begin(), question->end(), [](const Question& left, const Question& right) {
return std::stoi(left._id) < std::stoi(right._id); // 在数组中按照升序进行排序
});
return true;
}
// 加载指定 id 的试题
bool GetOneQuestion(const std::string& id, std::string* description, std::string* header, Question* question)
{
// 根据 id 去查找对应题目的信息,即它的路径
auto iter = QuesMap_.find(id);
if(iter == QuesMap_.end())
{
LOG(ERROR, "Not Found Question id is ") << id << std::endl;
return false;
}
*question = iter->second;
// 加载具体单个题目信息,从保存的路径上去加载
// description 描述信息
int ret = FileTools::ReadDataFromFile(DescPath(iter->second._path), description);
if(ret == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Read description failed!") << std::endl;
return false;
}
// header 头部信息
ret = FileTools::ReadDataFromFile(HeaderPath(iter->second._path), header);
if(ret == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Read header failed!") << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 拼接代码
// 将用户提交的代码 和 本地测试代码合并成一份,等待后续写入并编译执行
bool SplicingCode(std::string user_code, const std::string& ques_id, std::string& code)
{
code.clear();
// 查找对应id的试题是否存在
auto iter = QuesMap_.find(ques_id);
if(iter == QuesMap_.end())
{
LOG(ERROR, "Cannot find question id is ") << ques_id << std::endl;
return false;
}
std::string tail_code;
int ret = FileTools::ReadDataFromFile(TailPath(iter->second._path), &tail_code); // 获取测试代码
if(ret < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Open tail.cpp failed!");
return false;
}
code = user_code + tail_code; // 合并
return true;
}
private:
// 将 oj_config.cfg 文件中的所有题目信息组织进 unordered_map 中
bool LoadAllQuestions(const std::string& ConfigPath)
{
std::ifstream input_file(ConfigPath.c_str());
if(!input_file.is_open())
{
return false;
}
std::string line;
while(std::getline(input_file, line))
{
// 1.切割字符串
// 切割原型:题号 名称 路径 难度
std::vector<std::string> info;
StringTools::Split(line, " ", &info);
if(4 != info.size())
{
// 当前切分出错,但不能直接退出,转而加载其他题目信息
continue;
}
// 2.将切分后的内容保存到 unordered_map 中去
Question ques;
ques._id = info[0];
ques._name = info[1];
ques._path = info[2];
ques._difficulty = info[3];
QuesMap_[ques._id] = ques;
}
input_file.close();
return true;
}
// 问题描述文件
std::string DescPath(const std::string& ques_path)
{
return ques_path + "desc.txt";
}
// 头文件----代码框架文件
std::string HeaderPath(const std::string& ques_path) {...}
// 尾文件----代码测试文件
std::string TailPath(const std::string& ques_path) {...}
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, Question> QuesMap_;
};
三、编译运行模块
功能:将用户提交的代码写入到文件中去,编译源码文件,运行编译出来的可执行文件
步骤:
- 编译
- 将用户提交的代码写入文件中去
- fork子进程,进程程序替换为 g++ 程序,进行编译源码文件
- 获取编译结果,写入标准输出文件或者标准错误文件
- 运行
- 若代码能执行到此处,说明一定编译出可执行程序。fork子进程,进程程序替换为执行编译出来的可执行程序
- 将运行结果,写入标准输出或者标准错误文件
API及核心代码设计
输入:
- json 数据
- code 字段:需要编译的源代码
- stdin 字段:标准输入的内容
输出: - json 格式
- errorno 字段:值为0表示编译正确,运行无异常;1表示编译出错;2表示运行时异常;3表示输入参数错误;4表示内存错误
- reason 字段:存放程序运行状态或者出错原因
- stdout 字段:表示程序标准输出的结果
- stderr 字段:表示程序标准错误输出的结果
** 临时文件命名约定 **
在核心代码设计中,会涉及到很多的临时文件,比如编译运行后保存错误信息的文件 和 程序运行结果的文件等等,因此需要对临时文件进行一定的规范
此处,对其名称进行约束,规定:统一以 “tmp_时间戳 . 文件后缀” 格式进行组织
// compiler.hpp
enum ErrorNo
{
OK = 0, // 编译运行没有错误
COMPILE_ERROR, // 编译错误
RUN_ERROR, // 运行错误
PRAM_ERROR, // 参数错误
INTERNAL_ERROR // 内存错误
};
class Compiler
{
public:
static void CompileAndRun(Json::Value req, Json::Value* resp)
{
// 1. 判空
// {"code":"xxx", "stdin":"xxxx"}
if(req["code"].empty())
{
(*resp)["errerno"] = PRAM_ERROR;
(*resp)["reason"] = "Pram error";
LOG(ERROR, "Request Command is Empty!") << std::endl;
return ;
}
// 2.将完整代码 (用户代码 + 测试代码) 写到文件中去,对文件名称进行约定:tmp_时间戳.cpp
std::string code = req["code"].asString();
std::string tmp_filename = WriteTmpFile(code);
if(tmp_filename == "")
{
(*resp)["errorno"] = INTERNAL_ERROR;
(*resp)["reason"] = "Create file failed";
LOG(ERROR, "Write Source failed!") << std::endl;
return ;
}
// 3.编译
if(!Compile(tmp_filename))
{
(*resp)["errorno"] = COMPILE_ERROR;
std::string reason;
FileTools::ReadDataFromFile(ErrorPath(tmp_filename), &reason);
(*resp)["reason"] = reason;
LOG(ERROR, "Compile Error!") << std::endl;
return ;
}
// 4.运行
int ret = Run(tmp_filename);
if(ret != 0)
{
(*resp)["errorno"] = RUN_ERROR;
(*resp)["reason"] = "Program exit by ret " + std::to_string(ret);
LOG(ERROR, "Run Error!") << std::endl;
return ;
}
// 5.构造响应
(*resp)["errorno"] = OK;
(*resp)["reason"] = "Compile and run is okay";
std::string stdout_reason;
FileTools::ReadDataFromFile(StdoutPath(tmp_filename), &stdout_reason);
(*resp)["stdout"] = stdout_reason;
std::string stderr_reason;
FileTools::ReadDataFromFile(StderrPath(tmp_filename), &stderr_reason);
(*resp)["stderr"] = stderr_reason;
// Clean(tmp_filename);
return ;
}
private:
static std::string WriteTmpFile(const std::string& code)
{
// 1.组织文件名称
std::string tmp_filename = "/tmp_" + std::to_string(TimeTools::TimeStamp());
// 写文件
int ret = FileTools::WriteDataToFile(SrcPath(tmp_filename), code);
if(ret < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Write code to source failed!") << std::endl;
return "";
}
return tmp_filename;
}
static std::string SrcPath(const std::string& filename)
{
return "./tmp_files" + filename + ".cpp";
}
static std::string ErrorPath(const std::string& filename) {...}
static std::string ExePath(const std::string& filename) {...}
static std::string StdoutPath(const std::string& filename) {...}
static std::string StderrPath(const std::string& filename) {...}
static bool Compile(const std::string& filename)
{
// 1.构造编译命令 --> g++ src -o [exec] -std=c++11
const int commandcount = 20;
char buf[commandcount][50] = {{0}};
char* command[commandcount] = {0};
for(int i = 0; i < commandcount; i++)
{
command[i] = buf[i];
}
snprintf(command[0], 49, "%s", "g++");
snprintf(command[1], 49, "%s", SrcPath(filename).c_str());
snprintf(command[2], 49, "%s", "-o");
snprintf(command[3], 49, "%s", ExePath(filename).c_str());
snprintf(command[4], 49, "%s", "-std=c++11");
snprintf(command[5], 49, "%s", "-D");
snprintf(command[6], 49, "%s", "CompileOnline");
command[7] = NULL;
// 2.创建子进程
// 父进程 --> 等待子进程退出
// 子进程 --> 进程程序替换
int pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Create child process failed!") << std::endl;
return false;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
// child
int fd = open(ErrorPath(filename).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0664);
if(fd < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Open Compile errorfile failed:") << ErrorPath(filename) << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// 重定向
dup2(fd, 2);
// 程序替换
execvp(command[0], command);
perror("execvp");
LOG(ERROR, "Execvp failed!") << std::endl;
exit(0);
}
else
{
// father
waitpid(pid, NULL, 0);
}
// 3.验证是否产生可执行程序
// int stat(const char* filename, struct stat* buf); 通过filename获取文件信息,将信息保存在buf中,成功返回0,失败返回-1
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(ExePath(filename).c_str(), &st);
if(ret < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Compile error! Exe_filename is ") << ExePath(filename) << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
static int Run(std::string& filename)
{
// 1.创建子进程
// 父进程 --> 进程等待
// 子进程 --> 进程替换为编译出来的可执行程序
int pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Exec pragma failed! Create chile process failed!") << std::endl;
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
// child
// 对于子进程执行的限制
// 时间限制----alarm()
alarm(1);
// 内存大小限制
struct rlimit rl;
rl.rlim_cur = 1024 * 30000;
rl.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY; // 无限制
setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &rl);
// 获取标准输出,重定向到文件
int stdout_fd = open(StdoutPath(filename).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0664);
if(stdout_fd < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Open stdout file failed:") << StdoutPath(filename) << std::endl;
return -1;
}
dup2(stdout_fd, 1);
// 获取标准错误,重定向到文件
int stderr_fd = open(StderrPath(filename).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0664);
if(stdout_fd < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "Open stderr file failed:") << StderrPath(filename) << std::endl;
return -1;
}
dup2(stderr_fd, 2);
execl(ExePath(filename).c_str(), ExePath(filename).c_str(), NULL);
exit(1);
}
else
{
//father
int status = -1;
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
// 将是否收到信号的信息返回给调用者,如果调用者判断是0,则正常运行完毕,否则表明子进程时收到某个信号异常结束的
return status & 0x7f;
}
}
};
三、工具模块
- 时间工具类:获取时间戳
- 文件工具类:读文件,写文件
- 字符串工具类:拆分字符串
- URL工具类:对URL进行编码和解码操作
- 日志工具模块:对输出信息进行一定的组织和封装
如下:
时间工具类
class TimeTools
{
public:
// 获取系统时间戳
static int64_t TimeStamp()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return tv.tv_sec;
}
// 获取时间戳,并构造成常规认知的时间格式字符串
// 年-月-日 时:分:秒
static void TimeStampMS(std::string* TimeStamp)
{
time_t SysTime;
time(&SysTime);
struct tm* st = localtime(&SysTime);
char buf[32] = {'\0'};
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, "%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d", st->tm_year + 1900, st->tm_mon + 1, st->tm_mday, st->tm_hour, st->tm_min, st->tm_sec);
TimeStamp->assign(buf, strlen(buf));
}
};
文件工具类
class FileTools
{
public:
static int ReadDataFromFile(const std::string& filename, std::string* content)
{
std::ifstream file(filename.c_str());
if(!file.is_open())
{
LOG(ERROR, "Open file failed! Filename is ") << filename << std::endl;
return -1;
}
std::string line;
while(std::getline(file, line))
{
*content += line + "\n";
}
file.close();
return 0;
}
static int WriteDataToFile(const std::string& filename, const std::string& data)
{
std::ofstream file(filename.c_str());
if(!file.is_open())
{
LOG(ERROR, "Open file failed! Filename is ") << filename << std::endl;
return -1;
}
file.write(data.data(), data.size());
file.close();
return 0;
}
};
字符串工具类
class StringTools
{
public:
// 切分字符串
static void Split(const std::string& input, const std::string& split_char, std::vector<std::string>* output)
{
// boost::split(type, select_list, boost::is_any_of(","), boost::token_compress_on);
// type 用于存放切割之后的字符串,传址,不一定非得是vector,换成其他vector容器也是可以的
// select_list 传入的字符串(待切割的内容, string 类型),可以为空
// boost::is_any_of(",") 设定切割条件符号为,(逗号)
// boost::token_compress_on 将连续多个分隔符当做一个,默认为...off
boost::split(*output, input, boost::is_any_of(split_char), boost::token_compress_off);
}
};
URL编码操作类
class URLTools
{
public:
static void PraseBody(const std::string& body, std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string>* pram)
{
//name=xxx&stdin=xxx
std::vector<std::string> tokens;
StringTools::Split(body, "&", &tokens);
for(const auto& token : tokens)
{
// name=xxx
// stdin=xxxx
// ...
std::vector<std::string> vec;
StringTools::Split(token, "=", &vec);
if(2 != vec.size())
{
continue;
}
(*pram)[vec[0]] = URLDecode(vec[1]);
}
}
private:
static unsigned char ToHex(unsigned char c)
{
return c > 9 ? c + 55 : c + 48;
}
static unsigned char FromHex(unsigned char x)
{
unsigned char y;
if(x >= 'A' && x <= 'Z')
y = x - 'A' + 10;
else if(x >= 'a' && x <= 'z')
y = x - 'a' + 10;
else if(x >= '0' && x <= '9')
y = x - '0';
else
assert(0);
return y;
}
static std::string URLEncode(const std::string& str)
{
std::string strTemp = "";
size_t length = str.length();
for(size_t i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if(isalnum((unsigned char)str[i]) ||
(str[i] == '-') ||
(str[i] == '_') ||
(str[i] == '.') ||
(str[i] == '~'))
{
strTemp += str[i];
}
else if(str[i] == ' ')
{
strTemp += '+';
}
else
{
strTemp += '%';
strTemp += ToHex((unsigned char)str[i] >> 4);
strTemp += ToHex((unsigned char)str[i] % 16);
}
}
return strTemp;
}
static std::string URLDecode(const std::string& str)
{
std::string strTemp = "";
size_t length = str.length();
for(size_t i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if(str[i] == '+')
{
strTemp += ' ';
}
else if(str[i] == '%')
{
assert(i + 2 < length);
unsigned char high = FromHex((unsigned char)str[++i]);
unsigned char low = FromHex((unsigned char)str[++i]);
strTemp += high * 16 + low;
}
else
{
strTemp += str[i];
}
}
return strTemp;
}
};
日志工具
// 日志等级
const char* Level[] = { "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "FATAL", "DEBUG" };
enum LogLevel
{
INFO = 0,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL,
DEBUG
};
inline std::ostream& Log(LogLevel lev, const char* file, int line, const std::string& logmsg)
{
std::string level_info = Level[lev];
std::string TimeStamp;
TimeTools::TimeStampMS(&TimeStamp);
// [时间 日志等级 文件:行号] 具体的日志信息
std::cout << "[" << TimeStamp << " " << level_info << " " << file << ":" << line << "]" << " " << logmsg;
return std::cout;
}
#define LOG(lev, msg) Log(lev, __FILE__, __LINE__, msg)
至此,本项目的业务逻辑的基础功能就能够实现了,但是毕竟只是能实现 基本功能,并不能真的像leetcode一样美观舒适的使用,所以本项目仍存在很多不足之处,需要日后不断进行修改
待完善
- 界面美化,当务之急!!!
- 支持用户管理,包含注册,登录,做题记录统计等功能
- 支持管理员上传新的试题
- 服务器安全方面,防止用户通过提交一些恶意代码攻击编译服务器(比如:
system("rm -rf /* );) - 数据存储扩展:本项目中使用文件操作来存取数据,可以修改为用数据库来存取数据
- 前后端分离:本项目中使用MVC的方式,可以修改成 基于Vue 等方式 实现前端界面逻辑,后端提供 Restful API
- …