Python学习笔记--字符串及其常见操作
字符串及其常见操作
- 对字符串的了解
- 定义
- 转义
- 下标操作
- 字符串的操作
- 总结
- 上述知识点来源
对字符串的了解
(第一次认真使用这个编辑器进行总结我的学习,希望可以做好)字符串在python中是一个内置数据结构。
定义
如下分别对变量s进行定义:
- s = ‘hello world’
- s = “hello world”
- s = ‘’‘hello world’’’
- s = “”“hello world”""
前两种完全一样,后两种完全一样
hon中单引号和双引号的区别](https://blog.csdn.net/woainishifu/article/details/76105667)
三引号可以定义多行字符串
>>> s = '''python
... 加油学
... '''
>>> s
'python\n加油学\n'
#此处在终端输入
但是单引号并不能定义多行字符串
>>> s = 'sd
File "", line 1
s = 'sd
^
SyntaxError: EOL while scanning string literal
转义
所有的ASCII码都可以用“\”加数字(一般是8进制数字)来表示。\n \t等都是转义字符,因为后面的字符,都不是它本来的ASCII字符的意思了。
\n
>>> s = 'python\nxuying\nzuimei'
>>> print(s)
python
xuying
zuimei
如果我们需要输出的字符串中也存在单引号或者双引号,该怎么解决呢
s = 'I\'m smart'
print(s)
s = "I'm beautiful"
print(s)
s = '''"I'm superstart" 哈哈 '''
print(s)
下面是输出的结果
s = 'I\'m smart'
print(s)
s = "I'm beautiful"
print(s)
s = '''"I'm superstart" 哈哈 '''
print(s)
当然,也有一种更加直接的方法来转义:加上一个前缀关键词r,代表着后面这个字符串是raw string,也就是纯粹的字符串,不会有其它的额意思。
s = r'i\'m xixi\nyou\'re sb\t'
print(s)
s = 'i\'m xixi\nyou\'re sb\t'
print(s)
下面是输出的结果
i\'m xixi\nyou\'re sb\t
#此处是结果分割线
i'm xixi
you're sb
转义字符表
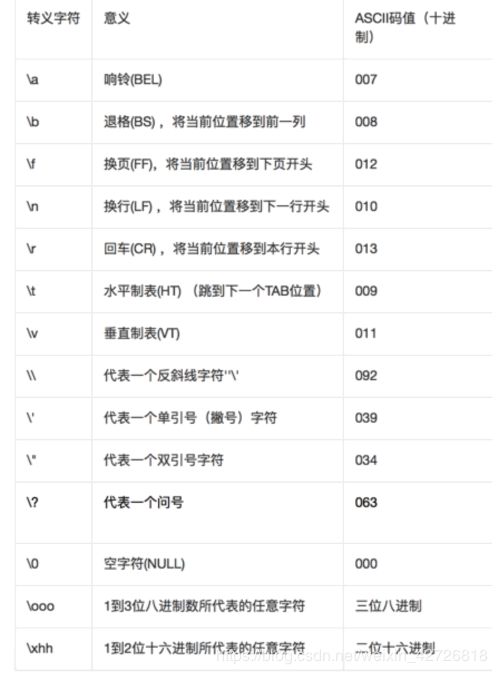
补充:u前缀代表unicode字符串;b前缀代表bytes
下标操作
python的字符串就像列表一样。可以使用下标来访问:
>>> s = 'hello\nworld'
>>> s[3]
'l'
>>> s[5]
'\n'
但是,我们并不能对其值进行修改,无法对其赋值,所以字符串是不可变的。
>>> s[5] = ' '
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
- 在python中:
- 目前只有list是可变的,其他都是不可变的。
- 字符串是迭代器,是可迭代对象
s = '123ni好'
for i in s:
print(i)
>>>
1
2
3
n
i
好
还可以使用list()这个方法快速的将字符串转化为列表,就等于将字符串的每一个元素拆开来,再通过append的方式放入list里面:
>>> list(s)
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\n', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd']
#解释起来就是如下
lst = []
for i in s:
lst.append(i)
lst #在终端输入lst查看
字符串中也可以使用s.count('你')来进行计算,同理s.index(''好)也可以使用。
字符串的操作
- join
join是字符串方法,参数是可迭代对象,接受者是分隔符
>>> l = ['人人','爱我','因为','没有理由']
>>> ''.join(l)
'人人爱我因为没有理由'
# join前面的这个字符串就是分隔符
# 用这个分隔符将列表里的每一个元素都拼起来
>>> ','.join(l)
'人人,爱我,因为,没有理由'
join这个方法是个原地不修改,有返回值的方法
2. 分割
>>> s
'人人 爱我 因为 没有理由'
>>> s.split()
['人人', '爱我', '因为', '没有理由']
>>> s.rsplit()
['人人', '爱我', '因为', '没有理由']
>>> s.splitlines()
['人人 爱我 因为 没有理由']
- str.split
>>> help(s.split)
Help on built-in function split:
split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) method of builtins.str instance
Return a list of the words in the string, using sep as the delimiter string.
sep
The delimiter according which to split the string.
None (the default value) means split according to any whitespace,
and discard empty strings from the result.
maxsplit
Maximum number of splits to do.
-1 (the default value) means no limit.
这里有两个函数签名:sep、maxsplit。
默认使用空格分割。遇到多个空格,默认当作一个空格处理
参数maxsplit表示从左往右分割多少次,默认为-1,no limit表示分割所有分隔符。
分割符可以是任意字符串
>>> s
'人人 爱我 因为 没有理由'
>>> s.split('因')
['人人 爱我 ', '为 没有理由']
- str.rsplit
>>> help(s.rsplit)
Help on built-in function rsplit:
rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) method of builtins.str instance
Return a list of the words in the string, using sep as the delimiter string.
sep
The delimiter according which to split the string.
None (the default value) means split according to any whitespace,
and discard empty strings from the result.
maxsplit
Maximum number of splits to do.
-1 (the default value) means no limit.
Splits are done starting at the end of the string and working to the front.
由上述可发现,rsplit其实是split的翻版,split是从左往右分割,rsplit是从右往左分割。
>>> s.split(maxsplit=2)
['人人', '爱我', '因为 没有理由']
>>> s.rsplit(maxsplit=2)
['人人 爱我', '因为', '没有理由']
>>> s
'人人 爱我 因为 没有理由'
当不使用maxsplit时,两者没有差别,但是split效率高于rsplit。
接下来分别用代码解释两者:
'''
s:传入的字符串
sep:分隔符
maxsplit:分割次数
'''
def _split(s,sep,maxsplit):
# ret 是用来保存最后的结果的
ret = []
# tmp是用来保存 循环字符串,直到遇到分隔符时的所有字符
tmp = []
i = 0
for c in s:
if c != sep:
tmp.append(c)
else:
i += 1
ret.append(''.join(tmp))
tmp.clear()
if i >= maxsplit and maxsplit > 0:
return ret
return ret
def _rsplit(s,sep,maxsplit):
ret = []
tmp = []
i = 0
# rsplit 不一样的地方在于,需要反转一次字符串
for c in reversed(s):
if c != sep:
tmp.append(c)
else:
i += 1
ret.append(''.join(tmp))
tmp.clear()
if i >= maxsplit and maxsplit > 0:#因为maxsplit=-1表示不限制分割次数
return reversed(ret)
return reversed(ret)
- str.splitlines
>>> help(s.splitlines)
Help on built-in function splitlines:
splitlines(keepends=False) method of builtins.str instance
Return a list of the lines in the string, breaking at line boundaries.
Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends is given and
true.
splitlines()这个方法相对简单使用,可以快速分割行。
>>> s = '''python
... 风花三月
... '''
#按行分割,返回结果不带换行符
>>> s.splitlines()
['python', '风花三月']
#按行分割,返回结果且带换行符
>>> s.splitlines(True)
['python\n', '风花三月\n']
- str.partition
>>> help(s.partition)
Help on built-in function partition:
partition(sep, /) method of builtins.str instance
Partition the string into three parts using the given separator.
This will search for the separator in the string. If the separator is found,
returns a 3-tuple containing the part before the separator, the separator
itself, and the part after it.
If the separator is not found, returns a 3-tuple containing the original string
and two empty strings.
partition()方法:
a. 总是返回一个三元组
b.按照传入的分隔符分割一次
c.返回结果是head、sep、tail(分割出来的头,分隔符,剩余部分)
>>> s.partition(' ')
('python\n风花三月\n', '', '')
>>> s.partition('\n')
('python', '\n', '风花三月\n')
>>> s
'python\n风花三月\n'
raprtition是partition的从右往左版本
通常在对配置文件做操作的时候,我们会利用partition
>>> cfg = 'mysql.connect = mysql://agdasgdawihdsu/test'
>>> cfg.partition('=')
('mysql.connect','=','mysql://agdasgdawihdsu/test')
写一个方法来理解,如下:
def _partition(s,sep):
if s == '':
return '','',''
tmp = s.split(sep,maxsplit=1)
if len(tmp) == 2:
return tmp[0],sep,tmp[1]
if len(tmp) == 1:
return tmp[0],sep,''
if len(tmp) == 0:
return '',sep,''
- 大小写转换
- str.upper & str.lower
>>> s
'tESt'
>>> s.upper()
'TEST'
>>> s.lower()
'test'
>>> s
'tESt'
两个方法都是原地不修改,有返回值
- str.casefold
转化成忽略大小写的字符串。原地不修改,有返回值。
不同平台表现形式不同
>>> s
'tESt'
>>> s.casefold()
'test'
- str.swapcase
大小写互换。原地不修改,有返回值。
>>> s = 'TesT'
>>> s.swapcase()
'tESt'
- 排版
- str.title
每个单词的首字母大写。原地不修改,有返回值。
>>> s.title()
'Test'
>>> s
'TesT'
- str.capitalize
一句话的首字母大写。原地不修改,有返回值。 - str.center
在100个字符中居中。原地不修改,有返回值
>>> s.center(100)
' TesT '
>>> s
'TesT'
- str.zfill
用0补足,和sql中的zerofill一样。原地不修改,有返回值。
>>> s.zfill(10) #补满10位
'000000tEsT'
- 修改
- str.replace
replace返回一个新的字符串,使用new替换old。原地不修改,有返回值。且有多少个替换多少个,可选的count参数代表替换多少次。
只能从前往后替换。
>>> l.replace(' ',':',1)
'人人:爱我\n因为 没有理由'
>>> l
'人人 爱我\n因为 没有理由'
- str.strip
移除字符串前后的空格
>>> l = ' 人人 爱我\n因为 没有理由 '
>>> l.strip()
'人人 爱我\n因为 没有理由'
事实上strip移除的是空白字符:
l = '\n\t\r 人人 爱我\n因为 没有理由 '
>>> l.strip()
'人人 爱我\n因为 没有理由'
还可以指定移除的字符
>>> l
'### i love ##'
>>> l.strip('#')
' i love '
- str.lstrip
只移除左边的 - str.rstrip
只移除右边的 - str.ljust
用来填充字符,原串在左边,若字符串长度大于给定的长度,那么不会有任何变化,还可以指定填充字符:
>>> l.ljust(20)
'### i love ## '
>>> l.ljust(20,'$')
'### i love ##$$$$$$$'
- str.rjust
原串在右边。
>>> l.rjust(20,'*')
'*******### i love ##'
- 查找
- str.find
**S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
**
从左往右查找,找到第一个匹配子串后,返回子串首字母的索引。
当子串不存在时返回-1;start参数指定从哪里开始查找,stop参数指定到哪结束;start和stop是左开右闭的,不包含end参数,end=-1代表最后。
>>> l.find('e')
9
>>> l.find('w')
-1
>>> l.find('#',3)
11
>>> l.find('#',2,3)
2
>>> l.find('#',5,-1)
11
>>> l
'### i love ##'
- str.rfind
从左往右find。但是start和stop还是从左往右。流程上是:先根据start和stop截取字符串后,再进行查找,只是查找的顺序发生了变化。 - str.index
index查找,子串不存在时,抛出ValueError;find查找,子串不存在时,返回-1。此外与find一致。 - str.rindex
index的从右往左版本。 - str.count
计算参数在s中的个数,当count计算的值不存在时返回0。同样也有start和end参数。
>>> l
'### i love ##'
>>> l.count('#')
5
- str.startswith
判断字符串是否已某个前缀开始,返回结果为bool值。start和end参数与之前相同。
>>> l
'### i love ##'
>>> l.startswith('##')
True
- str.endswith
判断字符串是否已某个后缀结束,返回结果为bool值。start和end参数与之前相同。 - is*
is*的意思为,字符串的方法里有一串以is开头的方法,代表的意思时‘是否是xxx’
isalnum判断是否只含有字母
>>> l
'### i love ##'
>>> l.isalnum()
False
isdecimal判断是否是数字str.isdecimal()
isidentifier判断是否是字母或者下划线开头,且仅包含字母数字和下划线。str.isidentifier()
总结
学习的路途总是很漫长的,打好基础吧,明明都过了几遍还是会有很多不记得的东西。