当前环境中,直接手写 css 的越来越少,主要是通过各种预编译器来做,主要原因会通过如下几点进行描述。
先看一下 css 的一些基础点,这里只说关键的,完整的可以自己查看 css2.1规范 。
css 基础知识点
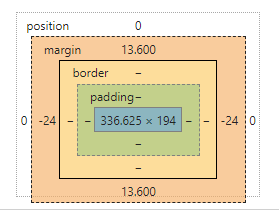
css 盒模型
页面都是通过盒模型来拼凑的,首先需要知道都有哪些块模型(也就是 display 的值):
- inline: 行内元素
- inline-block: 行内块元素
- block: 块元素
- none: 不显示元素,不占位置
- table 及其相关: 主要用于设置以表格的形式展示内容
- flex 及其相关: 弹性布局
- grid 及其相关: 网格布局
一般最常用的 div 就 display: block 的通用块。
css 变量
定义语法 --* ,使用语法 var(--*)
* 表示变量名称,可以是 数字字母下划线短横线 [0-9a-zA-Z_-] 进行组合。
无论变量定义还是使用都只能在声明块 {} 内:
/* 全局变量 */
:root {
--theme: #f00;
}
/* 局部变量 */
.side {
--color: #0f0;
}
.content {
color: var(--theme);
}
.footer {
color: var(--color);
}
javascript 可以获取和设置 css 中的变量:
// 获取 css 变量值
getComputedStyle(document.documentElement).getPropertyValue('--color')
// 设置 css 变量值
document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--color', '#' + Math.random().toString(16).slice(2,8))例子:
css变量
headerheaderheader
bodybodybody
Less
参考链接:Less文档
Less 变量
@width: 10px;
@height: @width + 10px;
#header {
width: @width;
height: @height;
}编译后:
#header {
width: 10px;
height: 20px;
}Less 变量还可以用与以下几种情况:
选择器
@my-selector: banner; .@{my-selector} { font-weight: bold; line-height: 40px; margin: 0 auto; }编译后:
.banner { font-weight: bold; line-height: 40px; margin: 0 auto; }URLs
@images: "../img"; body { color: #444; background: url("@{images}/white-sand.png"); }Import Statements
@themes: "../../src/themes"; @import "@{themes}/tidal-wave.less";Properties
@property: color; .widget { @{property}: #0ee; background-@{property}: #999; }编译后:
.widget { color: #0ee; background-color: #999; }Variable Variables
@primary: green; @secondary: blue; .section { @color: primary; .element { color: @@color; } }编译后:
.section .element { color: green; }
Less 混合
Less 混合 简单使用
.bordered {
border-top: dotted 1px black;
border-bottom: solid 2px black;
}
#menu a {
color: #111;
.bordered();
}
.post a {
color: red;
.bordered();
}编译后:
#menu a {
color: #111;
border-top: dotted 1px black;
border-bottom: solid 2px black;
}
.post a {
color: red;
border-top: dotted 1px black;
border-bottom: solid 2px black;
}Less 混合 带参数混合
.border-radius(@radius) {
-webkit-border-radius: @radius;
-moz-border-radius: @radius;
border-radius: @radius;
}
.button {
.border-radius(6px);
}Less 混合 参数默认值混合
.border-radius(@radius: 5px) {
-webkit-border-radius: @radius;
-moz-border-radius: @radius;
border-radius: @radius;
}
.button {
.border-radius();
}
#header {
.border-radius(4px);
}Less 嵌套
#header {
color: black;
.navigation {
font-size: 12px;
}
.logo {
width: 300px;
}
}编译后:
#header {
color: black;
}
#header .navigation {
font-size: 12px;
}
#header .logo {
width: 300px;
}注意:请勿过多的嵌套层。
在嵌套内可以使用 & 来指向父选择器
a {
color: blue;
&:hover {
color: green;
}
}编译后:
a {
color: blue;
}
a:hover {
color: green;
}Less 导入
@import "library.less";Sass
参考链接:Sass文档
Sass 变量
$nav-color: #F90;
nav {
$width: 100px;
width: $width;
color: $nav-color;
}编译后:
nav {
width: 100px;
color: #F90;
}默认变量值 !default ,如果这个变量被声明赋值了,那就用它声明的值,否则就用这个默认值。
$fancybox-width: 400px !default;
.fancybox {
width: $fancybox-width;
}在上例中,如果成员在导入你的 sass 局部文件之前声明了一个 $fancybox-width 变量,那么你的局部文件中对 $fancybox-width 赋值 400px 的操作就无效。如果成员没有做这样的声明,则 $fancybox-width 将默认为 400px。
Element-ui 的 var.scss 文件中就使用的默认变量值。
Sass 变量值可以借助插值 #{} 可以应用到如下模式:
选择器
$name: foo; $attr: border; p.#{$name} { #{$attr}-color: blue; }编译后:
p.foo { border-color: blue; }属性值,不过通常直接使用变量更方便
p { $font-size: 12px; $line-height: 30px; font: #{$font-size}/#{$line-height}; }编译后:
p { font: 12px/30px; }
Sass 混合
Sass 混合 简单使用
混合器使用 @mixin 标识符定义。
@mixin rounded-corners {
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}通过 @include 使用混合器。
.notice {
background-color: green;
border: 2px solid #00aa00;
@include rounded-corners;
}
//sass最终生成:
.notice {
background-color: green;
border: 2px solid #00aa00;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}Sass 混合器中的CSS规则
@mixin no-bullets {
list-style: none;
li {
list-style-image: none;
list-style-type: none;
margin-left: 0px;
}
}
ul.plain {
color: #444;
@include no-bullets;
}编译后:
ul.plain {
color: #444;
list-style: none;
}
ul.plain li {
list-style-image: none;
list-style-type: none;
margin-left: 0px;
}Sass 混合器传参
@mixin link-colors($normal, $hover, $visited) {
color: $normal;
&:hover { color: $hover; }
&:visited { color: $visited; }
}
a {
@include link-colors(blue, red, green);
}编译后:
a { color: blue; }
a:hover { color: red; }
a:visited { color: green; }传参的时候还可以通过 key:value ,这种方式不必在意参数顺序:
a {
@include link-colors(
$normal: blue,
$visited: green,
$hover: red
);
}Sass 默认参数值
@mixin link-colors(
$normal,
$hover: $normal,
$visited: $normal
)
{
color: $normal;
&:hover { color: $hover; }
&:visited { color: $visited; }
}
a {
@include link-colors(blue); // 相当于 @include link-colors(blue, blue, blue)
}Sass 嵌套
#content {
article {
h1 { color: #333 }
p { margin-bottom: 1.4em }
}
aside { background-color: #EEE }
}编译后:
#content article h1 { color: #333 }
#content article p { margin-bottom: 1.4em }
#content aside { background-color: #EEE }注意:请勿过多的嵌套层。
父选择器的标识符 &
article a {
color: blue;
&:hover { color: red }
}编译后:
article a { color: blue }
article a:hover { color: red }Sass 导入
@import "library.scss";Sass 部分文件
定义:当通过 @import 把 sass 样式分散到多个文件时,你通常只想生成少数几个 css 文件。那些专门为 @import 命令而编写的 sass 文件,并不需要生成对应的独立 css 文件,这样的 sass 文件称为局部文件。
sass 局部文件的文件名以下划线开头。
使用可以参照 https://github.com/ElemeFE/element/blob/dev/packages/theme-chalk/src/mixins/_button.scss 。
Sass 嵌套导入
嵌套导入生成对应的 css 文件时,局部文件会被直接插入到 css 规则内导入它的地方。
例如有一个名为 _blue-theme.scss 的局部文件,内容如下:
aside {
background: blue;
color: white;
}.blue-theme {@import "blue-theme"}生成的结果跟你直接在 .blue-theme 选择器内写 _blue-theme.scss 文件的内容完全一样。
.blue-theme {
aside {
background: blue;
color: #fff;
}
}Sass 原生CSS的导入
通常在 sass 中使用 @import 时,sass 会尝试找到对应的 sass 文件并导入进来,但在下列三种情况下会生成原生的 CSS@import,尽管这会造成浏览器解析 css 时的额外下载:
- 被导入文件的名字以
.css结尾; - 被导入文件的名字是一个URL地址(比如
http://www.sass.hk/css/css.css),由此可用谷歌字体API提供的相应服务; - 被导入文件的名字是
CSS的url()值。
这就是说,你不能用 sass 的 @import 直接导入一个原始的 css 文件,因为 sass 会认为你想用 css 原生的 @import。但是,因为 sass 的语法完全兼容 css,所以你可以把原始的 css 文件改名为 .scss 后缀,即可直接导入了。
Sass 静默注释
语法:
// 注释内容直到行末静默注释的内容不会出现在生成的 css 文件中。
Sass 选择器继承
//通过选择器继承继承样式
.error {
border: 1px red;
background-color: #fdd;
}
.seriousError {
@extend .error;
border-width: 3px;
}.seriousError 将会继承样式表中任何位置处为 .error 定义的所有样式。以 class="seriousError" 修饰的 html 元素最终的展示效果就好像是 class="seriousError error"。
.seriousError 不仅会继承 .error 自身的所有样式,任何跟 .error 有关的组合选择器样式也会被 .seriousError 以组合选择器的形式继承,如下代码:
//.seriousError从.error继承样式
.error a{ //应用到.seriousError a
color: red;
font-weight: 100;
}
h1.error { //应用到hl.seriousError
font-size: 1.2rem;
}关于 @extend 有两个要点:
- 跟混合器相比,继承生成的
css代码相对更少。因为继承仅仅是重复选择器,而不会重复属性,所以使用继承往往比混合器生成的css体积更小。如果你非常关心你站点的速度,请牢记这一点。 - 继承遵从
css层叠的规则。当两个不同的css规则应用到同一个html元素上时,并且这两个不同的css规则对同一属性的修饰存在不同的值,css层叠规则会决定应用哪个样式。相当直观:通常权重更高的选择器胜出,如果权重相同,定义在后边的规则胜出。
Sass 函数指令
$grid-width: 40px;
$gutter-width: 10px;
@function grid-width($n) {
@return $n * $grid-width + ($n - 1) * $gutter-width;
}
#sidebar { width: grid-width(5); }编译后:
#sidebar {
width: 240px;
}@function 用于定义函数。 @return 用于设置函数的返回值。
其他指令说明
@at-root
@at-root 指令导致一个或多个规则被限定输出在文档的根层级上,而不是被嵌套在其父选择器下。它可以被用于单一或内联选择器:
.parent {
...
@at-root .child { ... }
}编译后:
.parent { ... }
.child { ... }@if
@if 指令需要一个 SassScript 表达和嵌套在它下面要使用的样式,如果表达式返回值不为 false 或者 null ,那么后面花括号中的内容就会返回:
p {
@if 1 + 1 == 2 { border: 1px solid; }
@if 5 < 3 { border: 2px dotted; }
@if null { border: 3px double; }
}编译后:
p {
border: 1px solid;
}@if 语句后面可以跟多个 @else if 语句和一个 @else 语句。
$type: monster;
p {
@if $type == ocean {
color: blue;
} @else if $type == matador {
color: red;
} @else if $type == monster {
color: green;
} @else {
color: black;
}
}编译后:
p {
color: green;
}@for
@for 指令重复输出一组样式。对于每次重复,计数器变量用于调整输出结果。该指令有两种形式:@for $var from 和 @for $var from 。注意关键字 through 和 to 的区别。$var 可以是任何变量名,比如 $i ;
@for 语句将设置 $var 为指定的范围内每个连续的数值,并且每一次输出的嵌套样式中使用 $var 的值。对于 from ... through 的形式,范围包括 from ... to 的形式从
@for $i from 1 through 3 {
.item-#{$i} { width: 2em * $i; }
}
@for $i from 4 to 6 {
.item-#{$i} { width: 2em * $i; }
}编译后:
.item-1 {
width: 2em;
}
.item-2 {
width: 4em;
}
.item-3 {
width: 6em;
}
.item-4 {
width: 8em;
}
.item-5 {
width: 10em;
}快速实现栅栏布局:https://github.com/jdf2e/nutui/blob/master/src/packages/col/col.scss 。
@each
@each 指令通常格式是 @each $var in 。$var 可以是任何变量名,像 $length 或者 $name,和
@each 规则将 $var 设置为列表(list)或 map 中的每个项目,输出样式中包含使用 $var 的值。
@each $animal in puma, sea-slug, egret, salamander {
.#{$animal}-icon {
background-image: url('/images/#{$animal}.png');
}
}编译后:
.puma-icon {
background-image: url('/images/puma.png');
}
.sea-slug-icon {
background-image: url('/images/sea-slug.png');
}
.egret-icon {
background-image: url('/images/egret.png');
}
.salamander-icon {
background-image: url('/images/salamander.png');
}多重赋值:
list
@each $animal, $color, $cursor in (puma, black, default), (sea-slug, blue, pointer), (egret, white, move) { .#{$animal}-icon { background-image: url('/images/#{$animal}.png'); border: 2px solid $color; cursor: $cursor; } }编译后:
.puma-icon { background-image: url('/images/puma.png'); border: 2px solid black; cursor: default; } .sea-slug-icon { background-image: url('/images/sea-slug.png'); border: 2px solid blue; cursor: pointer; } .egret-icon { background-image: url('/images/egret.png'); border: 2px solid white; cursor: move; }maps
@each $header, $size in (h1: 2em, h2: 1.5em, h3: 1.2em) { #{$header} { font-size: $size; } }编译后:
h1 { font-size: 2em; } h2 { font-size: 1.5em; } h3 { font-size: 1.2em; }
@while
@while 指令重复输出嵌套样式,直到SassScript表达式返回结果为 false 。这可用于实现比 @for 语句更复杂的循环。
$i: 6;
@while $i > 0 {
.item-#{$i} {
width: 2em * $i;
}
$i: $i - 2;
}编译后:
.item-6 {
width: 12em;
}
.item-4 {
width: 8em;
}
.item-2 {
width: 4em;
}Sass 举例
// 清楚浮动
@mixin utils-clearfix {
$selector: &;
@at-root {
#{$selector}::before,
#{$selector}::after {
display: table;
content: "";
}
#{$selector}::after {
clear: both
}
}
}
// 垂直居中
@mixin utils-vertical-center {
$selector: &;
@at-root {
#{$selector}::after {
display: inline-block;
content: "";
height: 100%;
vertical-align: middle
}
}
}
// 超过...
@mixin utils-ellipsis {
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
white-space: nowrap;
}Stylus
参考链接:Stylus文档
stylus 可以写成下面的样子:
body
color whiteStylus 变量
Stylus 变量采用 key=value 来定义。
可以直接字符串定义:
font-size = 14px
body {
font: font-size Arial, sans-serif;
}建议添加标识符 $
$font-size = 14px
body {
font: $font-size Arial, sans-serif;
}Stylus 属性查找
#logo {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
width: 150px;
height: 80px;
margin-left: -(@width / 2);
margin-top: -(@height / 2);
}Stylus 插值
Stylus支持通过使用 {} 字符包围表达式来插入值,其会变成标识符的一部分。
vendor(prop, args)
-webkit-{prop} args
-moz-{prop} args
{prop} args
border-radius()
vendor('border-radius', arguments)
box-shadow()
vendor('box-shadow', arguments)
button
border-radius 1px 2px / 3px 4px编译后:
button {
-webkit-border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px;
-moz-border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px;
border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px;
}选择器插值
table
for row in 1 2 3 4 5
tr:nth-child({row})
height: 10px * row编译后:
table tr:nth-child(1) {
height: 10px;
}
table tr:nth-child(2) {
height: 20px;
}
table tr:nth-child(3) {
height: 30px;
}
table tr:nth-child(4) {
height: 40px;
}
table tr:nth-child(5) {
height: 50px;
}Stylus 混合
Stylus 混入
border-radius(n)
-webkit-border-radius n
-moz-border-radius n
border-radius n
form input[type=button]
border-radius(5px)编译后:
form input[type=button] {
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}上面的例子也可以书写为:
border-radius(n)
-webkit-border-radius n
-moz-border-radius n
border-radius n
form input[type=button]
border-radius 5px这个时候是把 border-radius 当做私有属性来对待。
还可以使用 arguments 局部变量,传递包含多值的表达式:
border-radius()
-webkit-border-radius arguments
-moz-border-radius arguments
border-radius arguments
form input[type=button]
border-radius 1px 2px / 3px 4px编译后:
form input[type=button] {
-webkit-border-radius: 1px 2px/3px 4px;
-moz-border-radius: 1px 2px/3px 4px;
border-radius: 1px 2px/3px 4px;
}Stylus 父级引用
父级引用字符 &
stripe(even = #fff, odd = #eee)
tr
background-color odd
&.even
&:nth-child(even)
background-color even
table
stripe()
td
padding 4px 10px
table#users
stripe #303030 #494848
td
color white编译后:
table tr {
background-color: #eee;
}
table tr.even,
table tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #fff;
}
table td {
padding: 4px 10px;
}
table#users tr {
background-color: #494848;
}
table#users tr.even,
table#users tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #303030;
}
table#users td {
color: #fff;
}Stylus 注释
Stylus支持三种注释,单行注释,多行注释,以及多行缓冲注释。
单行注释,双斜杠,CSS中不输出。
// 我是注释! body padding 5px多行注释
/*
*/
add(a, b)
a + b
```
多行缓冲注释
/*!
*/
add(a, b)
a + b
```
Stylus 导入
@import "library.styl";Stylus 继承
Stylus 的 @extend 指令受 SASS 实现的启发,基本一致,除了些轻微差异。