从零开始手工实现卷积神经网络CNN以及img2col和col2img的实现方法
本文主要实现卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)中卷积操作的forward和backward函数。CNN主要包括卷积(Convolution),池化(pooling),全连接(Fully Connected)操作。相信点进来的同学对这些操作的细节已经很熟悉了,不熟悉的同学可以参考这一篇博文(本人看过讲CNN最简单易懂、最好的博文,没有之一):An Intuitive Explanation of Convolutional Neural Networks。
img2col
在讲img2col之前,我们先回顾一下卷积操作,假设我们有一个3*3的kernel如下:

那么用这个kernel对一幅二维图像做卷积的操作可以用如下动图表示:
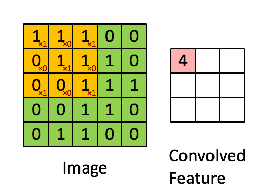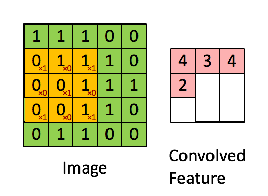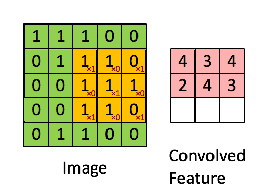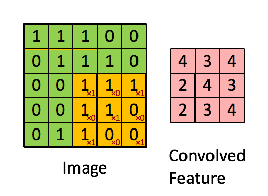
你可以使用numpy的切片操作来进行切片,按照上面动图的操作一步一步来,但是这种naive的方法非常慢,通常我们会用img2col操作把kernel变成行向量,把kernel对应的局部数据(receptive field)变成列向量,这样卷积操作就变成了矩阵乘法,速度成倍提升。img2col的操作细节,如下图可以概括:

具体代码如下,各种参数的含义可以参考上图:
def img2col(input, h_out, w_out, h_k, w_k, stride):
"""
Stacking ONLY Single Channel
:input: (batch, channel, height, weight)
:return: (batch, channel, h_k*w_k, h_out*w_out)
"""
b, c, h, w = input.shape
out = np.zeros((b, c, h_k*w_k, h_out*w_out))
convhIdx = 0
convwIdx = 0
for i in range(b):
for j in range(c):
# For each channel, scan from left-top
convwIdx = 0
convhIdx = 0
for k in range(h_out*w_out):
if convwIdx + w_k > w:
convwIdx = 0
convhIdx += stride
out[i, j, :, k] = input[i, j, convhIdx:convhIdx+h_k, convwIdx:convwIdx+w_k].flatten()
convwIdx += stride
return out
需要说明的是,卷积操作需要对所有channel的数据进行求和(大部分彩色图片都是3通道的,上图示例只显示了单通道的情况),但是池化操作需要分开计算各个channel的数据。考虑到复用问题,上面的img2col函数也是每个通道分开处理的,这样可以直接应用于池化操作。在卷积操作时需要对img2col输出的各个通道的数据进行合并。
卷积操作forward
代码如下:
def forward(self, input, weights, bias):
"""
# Arguments
input: numpy array with shape (batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width)
weights: numpy array with shape (out_channel, in_channel, kernel_h, kernel_w)
bias: numpy array with shape (out_channel)
# Returns
output: numpy array with shape (batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width)
"""
kernel_h = self.conv_params['kernel_h'] # height of kernel
kernel_w = self.conv_params['kernel_w'] # width of kernel
pad = self.conv_params['pad']
stride = self.conv_params['stride']
in_channel = self.conv_params['in_channel']
out_channel = self.conv_params['out_channel']
batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = input.shape
#####################################################################################
# computing output shape
out_h = int((in_height + pad - kernel_h)/stride) + 1
out_w = int((in_width + pad - kernel_w)/stride) + 1
# padding
pad_input = np.pad(input, ((0,0),(0,0),(int(pad/2), pad-int(pad/2)),(int(pad/2), pad-int(pad/2))), 'constant', constant_values=0)
in_height += pad
in_width += pad
# Img2Col
col_input = img2col(pad_input, out_h, out_w, kernel_h, kernel_w, stride)
# merge channel
col_input = col_input.reshape(col_input.shape[0], -1, col_input.shape[3])
# reshape kernel
weights_flatten = weights.reshape(weights.shape[0], -1)
# compute convolution
output = weights_flatten @ col_input + bias.reshape(-1, 1)
# reshape convolution result
output = output.reshape(output.shape[0], output.shape[1], out_h, out_w)
#####################################################################################
return output
col2img
在讲卷积操作的backward之前,需要先说一下col2img这个函数。卷积backward的时候需要把计算得到的梯度进行img2col的逆操作,也就是col2img。col2img实现如下:
def col2img(input_col, pad_h, pad_w, kernel_h, kernel_w, channel, pad, stride):
"""
Unstack columns to image
:input_col: (batch, channel*kernel_h*kernel_w, out_h*out_w)
:return: (batch, channel, pad_h - pad, pad_w - pad)
"""
batch = input_col.shape[0]
pad_out = np.zeros((batch, channel, pad_h, pad_w))
# unchannel input, get shape (batch, channel, kernel_h*kernel_w, out_h*out_w)
unchannel_input = input_col.reshape(input_col.shape[0], channel, -1, input_col.shape[2])
col_idx = 0
for i in range(batch):
for j in range(channel):
widx = 0
hidx = 0
# for each column in one channel
for col_idx in range(unchannel_input.shape[-1]):
# print(i, j, hidx, widx)
pad_out[i, j, hidx:hidx + kernel_h, widx:widx + kernel_w] += unchannel_input[i, j, :, col_idx].reshape(
kernel_h, -1)
widx += stride
if widx + kernel_w > pad_w:
widx = 0
hidx += stride
if pad<1:
result = pad_out
else:
result = pad_out[:, :, int(pad / 2):-(pad - int(pad / 2)), int(pad / 2):-(pad - int(pad / 2))]
return result
卷积操作backward
实现细节如下图:
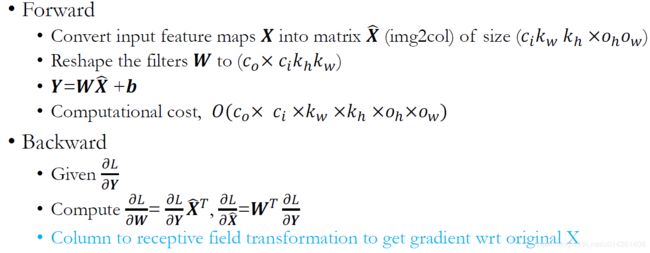
c i c_i ci表示图片channel的数目,即输入通道; c o c_o co表示kernel的数目,即输出通道。
本文backward的实现参考这篇博文:Convnet: Implementing Convolution Layer with Numpy。
def backward(self, out_grad, input, weights, bias):
"""
# Arguments
out_grad: gradient to the forward output of conv layer, with shape (batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width)
input: numpy array with shape (batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width)
weights: numpy array with shape (out_channel, in_channel, kernel_h, kernel_w)
bias: numpy array with shape (out_channel)
# Returns
in_grad: gradient to the forward input of conv layer, with same shape as input
w_grad: gradient to weights, with same shape as weights
b_bias: gradient to bias, with same shape as bias
"""
kernel_h = self.conv_params['kernel_h'] # height of kernel
kernel_w = self.conv_params['kernel_w'] # width of kernel
pad = self.conv_params['pad']
stride = self.conv_params['stride']
in_channel = self.conv_params['in_channel']
out_channel = self.conv_params['out_channel']
batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = input.shape
#################################################################################
batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width = out_grad.shape
"""
compute b_grad
"""
b_grad = np.sum(out_grad, axis=(0, 2, 3))
b_grad = b_grad.reshape(out_channel)
# pad zero to input
pad_input = np.pad(input, ((0,0),(0,0),(int(pad/2), pad-int(pad/2)),(int(pad/2), pad-int(pad/2))), 'constant', constant_values=0)
# Img2Col
col_input = img2col(pad_input, out_height, out_width, kernel_h, kernel_w, stride)
# merge channel
col_input = col_input.reshape(col_input.shape[0], -1, col_input.shape[3])
# transpose and reshape col_input to 2D matrix
X_hat = col_input.transpose(1, 2, 0).reshape(in_channel*kernel_h*kernel_w, -1)
# transpose and reshape out_grad
out_grad_reshape = out_grad.transpose(1, 2, 3, 0).reshape(out_channel, -1)
"""
compute w_grad
"""
w_grad = out_grad_reshape @ X_hat.T
w_grad = w_grad.reshape(weights.shape)
"""
compute in_grad
"""
# reshape kernel
W = weights.reshape(out_channel, -1)
in_grad_column = W.T @ out_grad_reshape
# Split batch dimension and transpose batch to first dimension
in_grad_column = in_grad_column.reshape(in_grad_column.shape[0], -1, batch).transpose(2, 0, 1)
in_grad = col2img(in_grad_column, in_height+pad, in_width+pad, kernel_h, kernel_w, in_channel, pad, stride)
#################################################################################
return in_grad, w_grad, b_grad
池化操作pooling
池化操作相对简单,对每个通道的数据分开计算即可:
class pool(operator):
def __init__(self, pool_params):
"""
# Arguments
pool_params: dictionary, containing these parameters:
'pool_type': The type of pooling, 'max' or 'avg'
'pool_h': The height of pooling kernel.
'pool_w': The width of pooling kernel.
'stride': The number of pixels between adjacent receptive fields in the horizontal and vertical directions.
'pad': The total number of 0s to be added along the height (or width) dimension; half of the 0s are added on the top (or left) and half at the bottom (or right). we will only test even numbers.
"""
super(pool, self).__init__()
self.pool_params = pool_params
def forward(self, input):
"""
# Arguments
input: numpy array with shape (batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width)
# Returns
output: numpy array with shape (batch, in_channel, out_height, out_width)
"""
pool_type = self.pool_params['pool_type']
pool_height = self.pool_params['pool_height']
pool_width = self.pool_params['pool_width']
stride = self.pool_params['stride']
pad = self.pool_params['pad']
batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = input.shape
#####################################################################################
# computing output shape
out_h = int((in_height + pad - pool_height) / stride) + 1
out_w = int((in_width + pad - pool_width) / stride) + 1
# padding
pad_input = np.pad(input,
((0, 0), (0, 0), (int(pad / 2), pad - int(pad / 2)), (int(pad / 2), pad - int(pad / 2))),
'constant', constant_values=0)
in_height += pad
in_width += pad
# Img2Col
col_input = img2col(pad_input, out_h, out_w, pool_height, pool_width, stride)
if pool_type == 'max':
output = col_input.max(axis=2).reshape(batch, in_channel, out_h, out_w)
elif pool_type == 'avg':
output = np.average(col_input, axis=2).reshape(batch, in_channel, out_h, out_w)
else:
output = None
#####################################################################################
return output
def backward(self, out_grad, input):
"""
# Arguments
out_grad: gradient to the forward output of conv layer, with shape (batch, in_channel, out_height, out_width)
input: numpy array with shape (batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width)
# Returns
in_grad: gradient to the forward input of pool layer, with same shape as input
"""
pool_type = self.pool_params['pool_type']
pool_height = self.pool_params['pool_height']
pool_width = self.pool_params['pool_width']
stride = self.pool_params['stride']
pad = self.pool_params['pad']
batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = input.shape
out_height = 1 + (in_height - pool_height + pad) // stride
out_width = 1 + (in_width - pool_width + pad) // stride
pad_scheme = (pad//2, pad - pad//2)
input_pad = np.pad(input, pad_width=((0,0), (0,0), pad_scheme, pad_scheme),
mode='constant', constant_values=0)
recep_fields_h = [stride*i for i in range(out_height)]
recep_fields_w = [stride*i for i in range(out_width)]
input_pool = nnFimg2col(input_pad, recep_fields_h,
recep_fields_w, pool_height, pool_width)
input_pool = input_pool.reshape(
batch, in_channel, -1, out_height, out_width)
if pool_type == 'max':
input_pool_grad = (input_pool == np.max(input_pool, axis=2, keepdims=True)) * \
out_grad[:, :, np.newaxis, :, :]
elif pool_type == 'avg':
scale = 1 / (pool_height*pool_width)
input_pool_grad = scale * \
np.repeat(out_grad[:, :, np.newaxis, :, :],
pool_height*pool_width, axis=2)
input_pool_grad = input_pool_grad.reshape(
batch, in_channel, -1, out_height*out_width)
input_pad_grad = np.zeros(input_pad.shape)
idx = 0
for i in recep_fields_h:
for j in recep_fields_w:
input_pad_grad[:, :, i:i+pool_height, j:j+pool_width] += \
input_pool_grad[:, :, :, idx].reshape(
batch, in_channel, pool_height, pool_width)
idx += 1
in_grad = input_pad_grad[:, :, pad:pad+in_height, pad:pad+in_width]
return in_grad